PET Scanning
This lesson covers:
- The use of positron-emitting radiotracers in PET scans
- Electron-positron annihilation and gamma ray emission
- PET scanner detection and image reconstruction
- Relating radiotracer distribution to metabolic activity
- Applications of PET scanning for medical diagnosis
Positron-emitting radiotracers
In a PET scan, the patient is injected with a radiotracer containing a positron-emitting radioisotope, such as:
- 13N
- 15O
- 18F
These have a short half-life. The radiotracer attaches to molecules used by the body like glucose. This allows it to concentrate in certain organs and tissues.
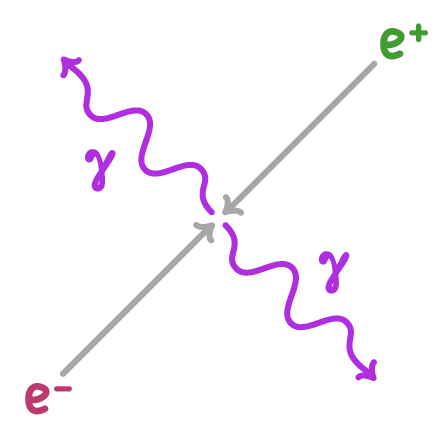
Positron-electron annihilation
The positrons emitted collide with electrons in the patient's tissues. This annihilation produces a pair of gamma rays propagating in opposite directions.
Annihilation process:
- Positron collides with electron
- Both are annihilated
- Two 511 keV gamma rays are emitted at 180° to each other
PET scanner detection and image reconstruction
The PET scanner contains gamma ray detectors in a ring around the patient. These detect the annihilation photons, and a computer uses this data to build a 3D map of radiotracer distribution.
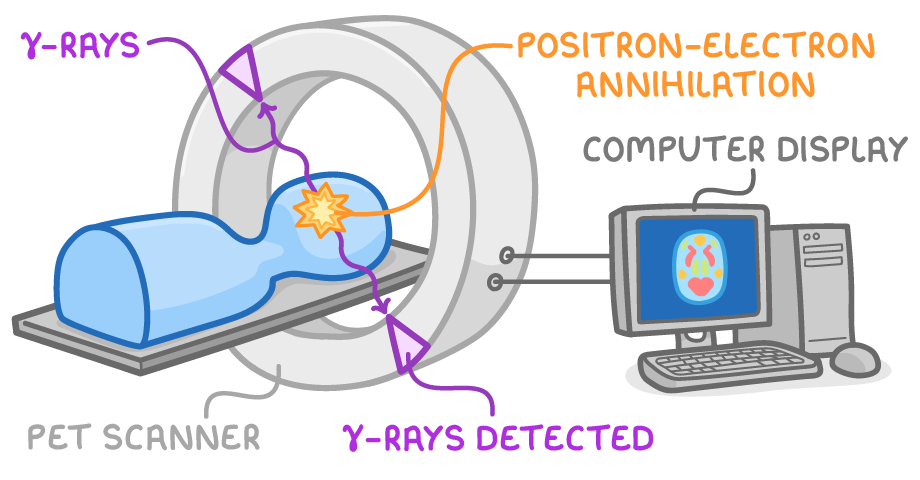
Image reconstruction steps:
- Record gamma ray detection events.
- Localise origin along line between paired detectors.
- Reconstruct image slice-by-slice.
Relating radiotracer distribution to metabolic activity
Areas of high radioactivity indicate increased metabolic activity. This results from greater radiotracer uptake:
- More radioactive molecules used
- Faster turnover
- Increased consumption
Cancer cells can display heightened metabolism.
Applications in medical diagnosis
By locating areas of abnormal metabolic activity, PET scans help diagnose:
- Cancer
- Heart disease
- Brain disorders
The short half-life minimises radiation exposure.