Potential Dividers
This lesson covers:
- What a potential divider circuit is and its purpose
- Calculating the output voltage of a potential divider
- Choosing resistance values to obtain a desired output voltage
- Using a potential divider for voltage calibration
- Issues with connecting a low resistance load
Introduction to the potential divider
A potential divider is a simple circuit containing resistors in series, across which the source voltage is divided. It allows only a fraction of the total voltage to be used a the output voltage.
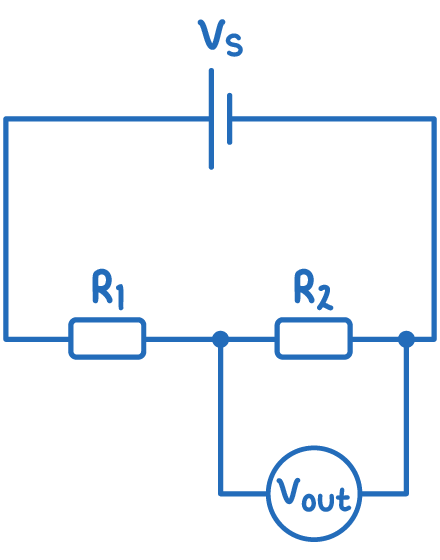
Calculating the output voltage
The output voltage (Vout) depends on the resistor values and input voltage (Vs) according to this equation:
Vout=R1+R2R2 Vs
Where:
- Vout = output voltage (V)
- R1 = resistance of resistor 1 (Ω)
- R2 = resistance of resistor 2 (Ω)
- Vs = source voltage (V)
So the output voltage is always a fraction of the input voltage, determined by the resistor ratio.
Worked example - Calculating output potential
Calculate Vout for a potential divider with R1 = 560 Ω, R2 = 3.9 kΩ, and Vs = 12 V.
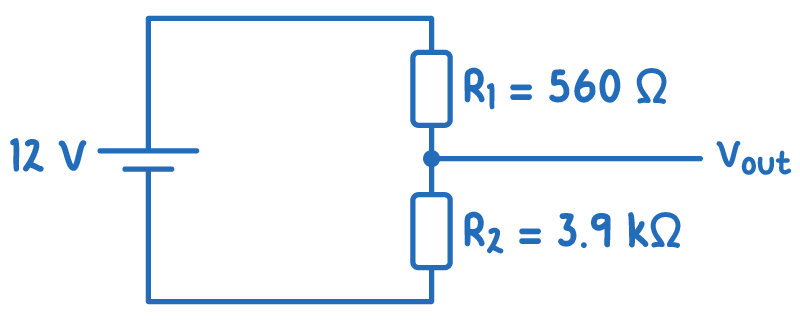
Step 1: Formula
Vout=R1+R2R2Vs
Step 2: convert kΩ to Ω
to convert from kΩ to Ω, multiply by 1,000
3.9 kΩ = 3,900 Ω
Step 3: Substitution and correct evaluation
Vout = 560 + 3,9003,900× 12 = 10.49 V