Pressure
This lesson covers:
- How pressure is related to force and area
- Calculating pressure at a depth in a fluid
- Defining upthrust on submerged objects
- Understanding Archimedes' principle in relation to upthrust and displaced fluid
Understanding pressure as force per unit area
Pressure, denoted as P, is essentially the amount of force, F, applied evenly over a unit area, A:
P = AF
Where:
P = pressure (Pa)
F = force (N)
A = area(m2)
1 Pascal equals 1 Newton per square meter (1 N m-2).
Pressure changes with depth in fluids
In fluids at rest, pressure increases steadily with depth (h). This increase is due to the weight of the fluid above the point of measurement.
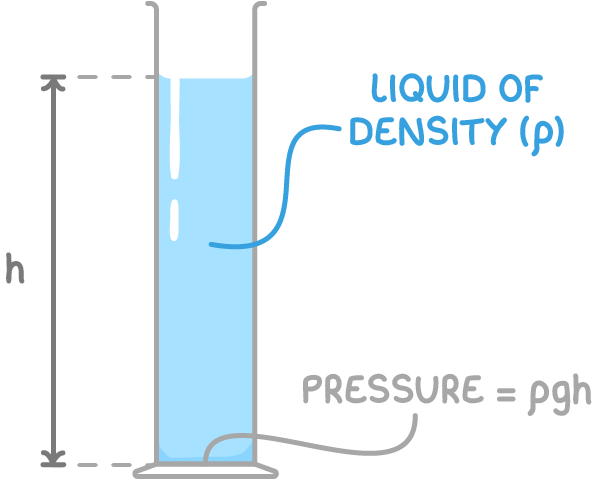
The formula to calculate pressure at a certain depth is:
P = h ρ g
Where:
P = pressure (Pa)
h = depth (m)
ρ = density (kg m-3)
g = gravitational field strength (m s-2)
Worked example - Calculating the pressure at a depth in a fluid
An engineer needs to determine the pressure at 15 meters depth in a lake for designing an underwater structure. Calculate the pressure at a depth of 15 m in water.
Step 1: Density Formula
P = h ρ g
Step 2: Substitution and correct evaluation
P = 15 ×1,000 ×9.81 = 147,150 Pa = 147.2 kPa
Defining Upthrust
When an object is fully or partially submerged in a fluid, it experiences an upward force known as upthrust (Fu).
This force results from the pressure difference between the top and bottom of the object, which is caused by the variation of pressure with depth in the fluid.
Linking Upthrust to Archimedes' Principle
Archimedes' principle asserts that the upthrust on a submerged object is equal to the weight of the fluid that the object displaces.
If the displaced fluid volume is V, the formula for upthrust is:
Fu = V ρ g
Where:
Fu = upthrust (N)
V = volume (m3)
ρ = density (kg m-3)
g = gravitational field strength (m s^-2)
Worked Example - Calculating upthrust on a submerged object
Calculate the upthrust acting on a cube submerged in water. The volume of the cube is 0.002 m3. The density of water is 1,000 kg m-3.
Step 1: Formula
Fu = V ρ g
Step 2: Substitution and correct evaluation
Fu = 0.002 ×1,000 × 9.81 = 19.62 N