Density
This lesson covers:
- Defining density as mass per unit volume
- Understanding that density is dependent on material, not the size or shape of the object
- Using density to determine if objects will float or sink in a fluid
- How to calculate density using mass and volume
Defining Density
Objects made from the same material have the same density.
Density is a measure of how densely packed the particles within it are.
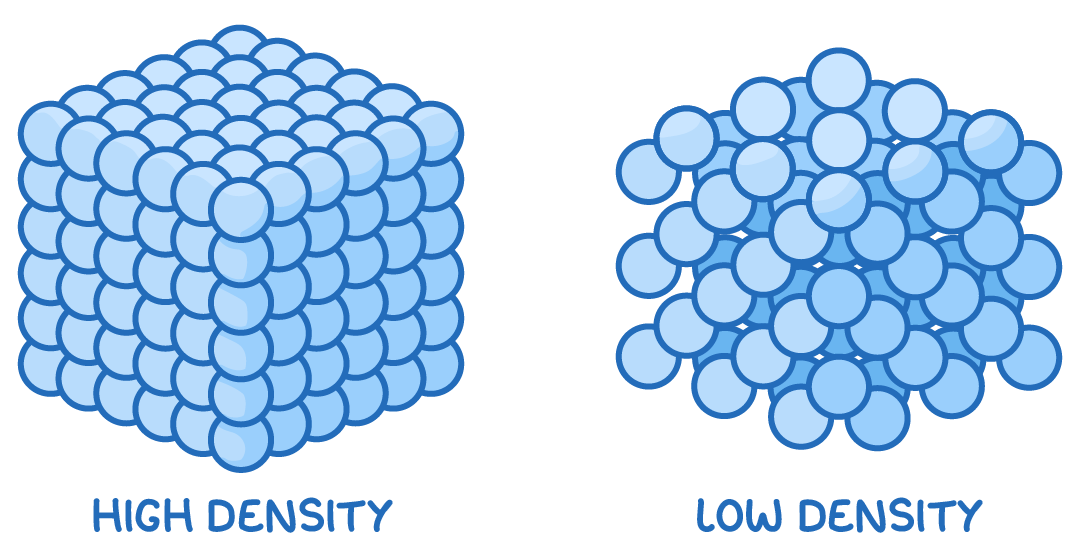
Density indicates how closely packed or concentrated a material is.
Density (ρ) is the ratio of the mass (m) of a substance to its volume (V).
It is expressed using the formula:
ρ=Vm
Where:
- ρ = density (kg m-3)
- m = mass (kg)
- V = volume (m3)
Float or sink?
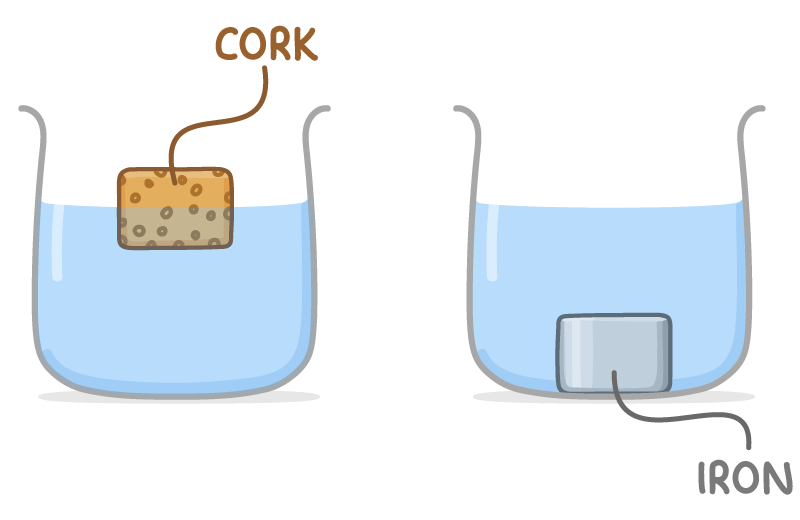
An object's ability to float or sink in a fluid is based on its average density relative to the fluid's density.
- Objects with a density lower than that of the fluid will float.
- Objects with a higher density will sink.
Example:
Iron, with a density of 7.9 g cm-3, sinks in water, which has a density of 1 g cm-3.
Worked example - Calculating the density of an iron cube
Calculate the density of a metal cube with dimensions 2 cm x 2 cm x 2 cm and a mass of 25 g. Deduce if the cube is made from iron. The density of iron is 7,900 kg m-3.
Step 1: Calculate volume of cube
V = length x width. height
V = 0.02 x 0.02 x 0.02 = 8 x 10-6 m3
Step 2: Convert g to kg
to convert from g to kg, divide by 1,000
25 g = 25 x 10-3 kg
Step 3: Density formula
ρ=Vm
Step 4: Substitution and correct evaluation
ρ=8×10−625×10−3= 3,125 kg m−3
Comparison:
The calculated density is significantly lower than the known density of iron. This discrepancy suggests either an error in the mass measurement or that the material might not be pure iron.