Speed, distance & Time
This lesson covers:
- Defining speed, displacement, velocity, and acceleration
- Understanding uniform acceleration as constant acceleration
- Using the four key equations for motion under uniform acceleration
- Calculating unknown values like final velocity, displacement, and time taken
- Solving problems using the equations of motion
Key Definitions
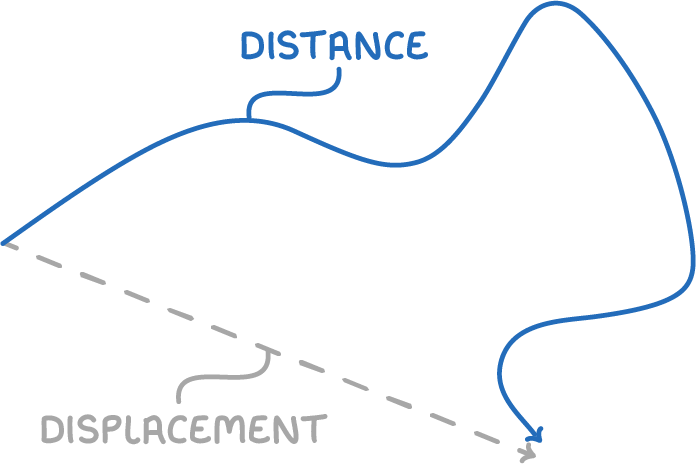
- Speed - The rate at which an object covers distance, without considering its direction.
- Displacement - The overall change in position of an object in a specific direction.
- Velocity - Speed with direction, or how quickly displacement changes over time.
- Acceleration - How quickly velocity changes over time, indicating a speed increase or decrease in a particular direction.
Velocity and acceleration are vector quantities, meaning they include both magnitude (how much) and direction (which way). The average speed of an object during a trip is the total distance travelled divided by the total time it took. The instantaneous speed is the speed of an object at any specific moment.
Introducing suvat
In suvat problems, each letter represents a quantity:
- s - displacement (m)
- u - initial velocity ( m s-1)
- v - final velocity ( m s-1)
- a - acceleration ( m s-2)
- t - time (s)
suvat equations
Motion can be represented through a variety of motion equations:
v = u + at
s = ut + 21a t2
v2 = u2 + 2 a s
These equations can be used to find an unknown value when other variables are known.
Solving problems using the suvar formulae
To effectively solve problems:
- Write down all given values - displacement, initial velocity, acceleration, and time taken.
- Determine the unknown value you need to find.
- Choose the formula that allows you to solve for the unknown with the information provided.
- Substitute the known values into the equation and solve for the unknown.
Worked example: Calculating velocity and time for a falling object
A tile falls from a roof's edge, 2.5 meters above the ground. Given gravity's acceleration is 9.81 m s^-2}, calculate (a) its velocity upon impact and (b) the time it takes to fall.
(a) Calculating final velocity:
Step 1: Identify suvat variables:
s = 2.5 m
u = 0 m s-1
v = ?
a = 9.81 m s-2
t = ?
Step 2: Formula for final velocity
v2 = u2 + 2 a s
Step 3: Substitution and correct evaluation
v2 = 0 + 2 x 9.81 x 2.5 = 49.05
v = √49.05=7.00 m s−1
(b) the time it takes to fall
Step 1: Identify known suvat variables
s = 2.5 m
u = 0 m s-1
v = 7.00 m s-1
a = 9.81 m s-2
t = ?
Step 2: Formula
t = av − u
Step 3: Substitution and correct evaluation
t = 9.817.00−0 = 0.71 s