Electric Field Strength
This lesson covers:
- Defining electric field strength and its units
- Electric field strength around a point charge (radial field)
- The relationship between electric field strength and distance from a point charge
- Understanding uniform electric fields between parallel plates
- Calculating electric field strength using potential difference and plate separation
Defining electric field strength
Electric field strength, symbolised as E, is the force experienced by a unit positive charge in an electric field. It's the force that a charge of +1 Coulomb (C) would feel in this field.
E = QF
Where:
E = electric field strength (N C-1)
F = force (N)
Q = charge (C)
Key Points:
- E is a vector, indicating both magnitude and direction, and points the way a positive charge would move.
- Field strength can vary at different positions within the field.
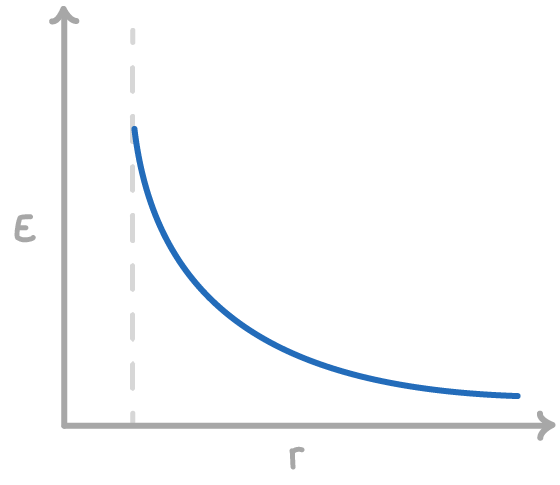
Radial electric fields and point charges
In radial electric fields, originating from point charges, the charge creating the field is labelled Q, and the test charge is labelled q.
The field lines emanate outward from positive point charges and inward towards negative point charges.
In a radial field, the formula for electric field strength is:
E = 4πϵ0r2Q
Where:
- E = electric field strength (N C-1)
- Q = point charge (C)
- ϵ0 = permittivity of free space (F m-1)
- r = distance from the point charge (m)
This demonstrates an inverse square relationship, meaning E decreases quickly as distance (r) increases.
Worked example - Calculate the electric field strength around a point charge
Calculate the electric field strength 50mm from a +3 nC charge.
Step 1: Formula
E = 4πϵ0r2Q
Step 2: Substitution and correct evaluation
E = 4π(8.85×10−12)×(50×10−3)23×10−9 = 10,790.2 N C−1
Uniform electric fields
In uniform electric fields, created between two electrically charged parallel plates, the field strength E is constant throughout.
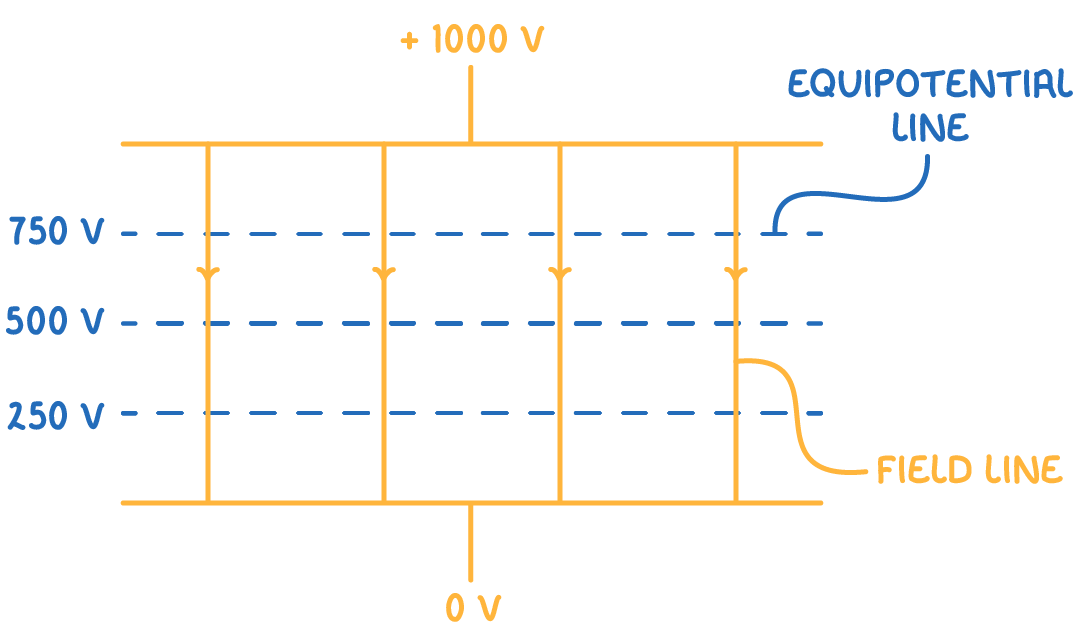
In a uniform field, the formula is:
E = dV
Where:
- E = electric field strength (V m-1)
- V = potential difference between the plates (V)
- d = separation between the plates (m)
Worked example - Calculating electric field strength between parallel plates
Two parallel plates have a potential difference of 600 V across a 2 mm gap. Determine the electric field strength between them.
Step 1: Formula
E=dV
Step 2: Convert mm to m
to convert mm to m, divide by 1,000
2 mm = 0.002 m
Step 3: Substitution and correct evaluation
E=0.002600=3×105 V m−1