Nuclear Decay Equations
This lesson covers:
- How alpha and beta particles can be written as and
- The nuclear equations for alpha, beta, gamma, and neutron decay
When writing nuclear decay equations, we only care about the nuclei of atoms. So when we write something like: 24He We're describing a helium atom's nucleus: |
|
However, you can also think of the atomic number as the particle's charge. So the helium nucleus above has a positive charge of 2 (+2). |
For comparison, if you see something like this: 0−1β |
|
Which two the following represent an alpha particle?
|

The above nuclear equation shows thorium (Th) undergoing alpha decay.
Fill in the missing atomic mass (A)and atomic number (B):
A:
B:
|
Which of the following represent a beta particle?
|
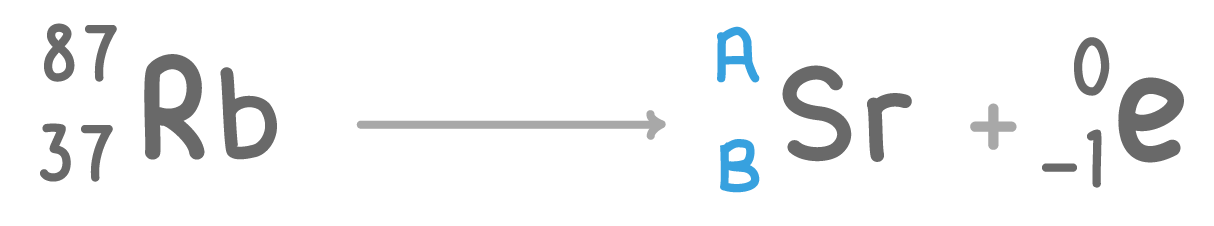
The above nuclear equation shows rubidium (Rb) undergoing beta decay.
Fill in the missing atomic mass A and atomic number B:
A:
B:
|
Which of the following represents gamma radiation?
|
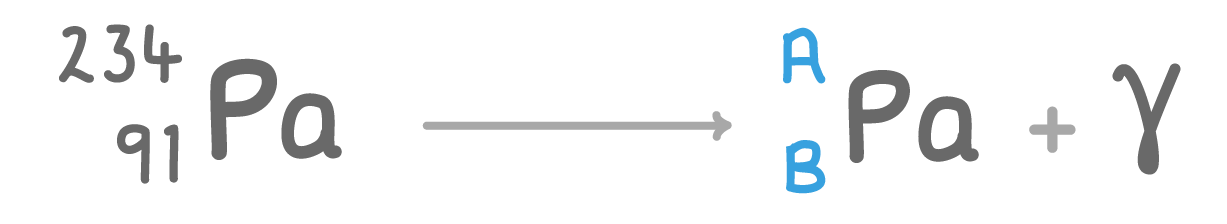
The above nuclear equation shows protactinium (Pa) undergoing gamma ray decay.
Fill in the missing atomic mass A and atomic number B:
A:
B:
|
Which of the following represents a neutron?
|
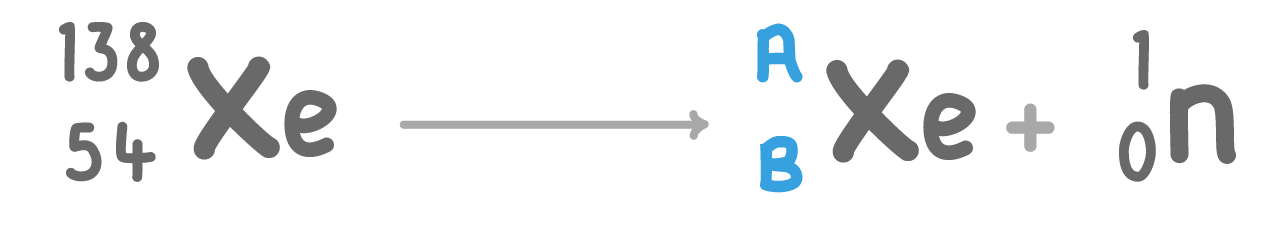
The above nuclear equation shows xenon (Xe) undergoing neutron decay.
Fill in the missing atomic mass number (A) and atomic number (B):
A:
B:
|
element / molecule / protons / neutrons
The nucleus of any can be represented in the following form:
This is the nucleus of the element carbon.
- The C is the elemental (or chemical) symbol
- The 12 is the 'mass number', which is the number of protons and neutrons combined
- The 6 is the 'atomic number', which is the number of . This can also be thought of as the particle's charge.
|