Alternators, Dynamos & Oscilloscopes
This lesson covers:
- The two types of generators: alternators and dynamos
- How alternators generate alternating current (a.c.)
- How dynamos generate direct current (d.c.)
- What a.c. and d.c. look like on an oscilloscope
Alternators and dynamos 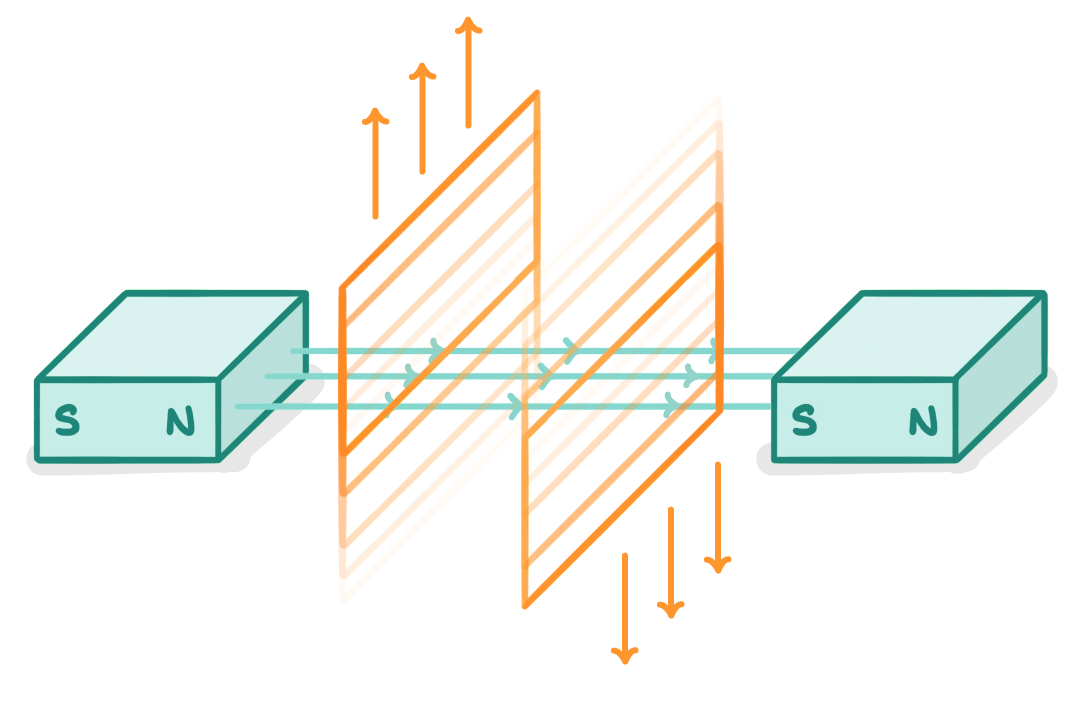 If you remember from a previous lesson, electromagnetic induction (the 'generator effect') is the idea that we generate an electric current by moving a wire relative to a magnetic field. |
 Alternators and dynamos are generators We use the generator effect in devices called 'generators'. These devices generate electricity from rotational motion (e.g. rotating a coil of wire). 'Alternators' and 'dynamos' are different types of generator. |
 A key difference 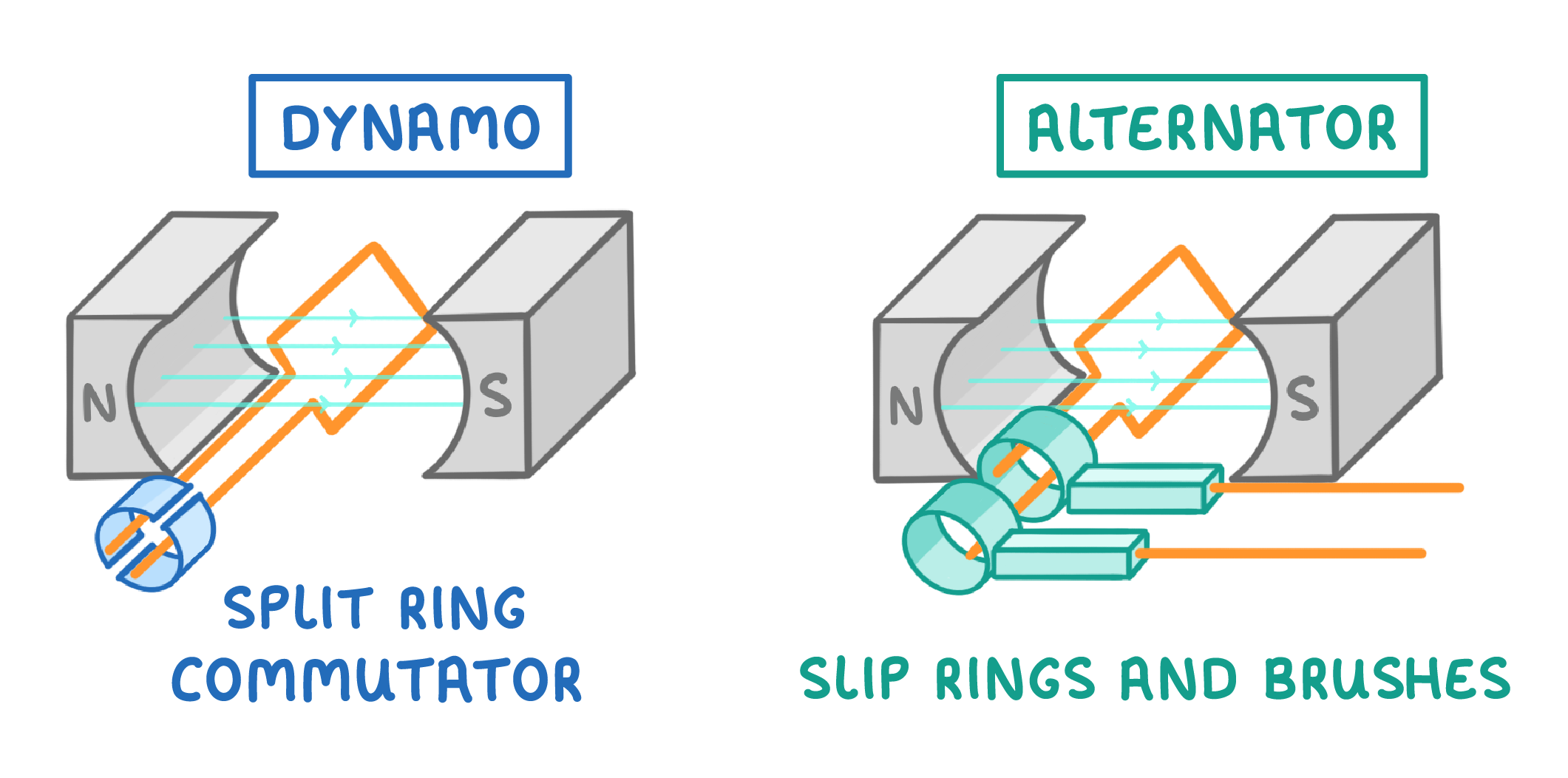 Alternators and dynamos look very similar - the key difference is that dynamos have a split ring commutator, whilst alternators have slip rings and brushes. |
1Due to the split ring commutator, dynamos produce direct current. |
2Due to the slip rings and brushes, alternators produce alternating current. |
How alternators work |
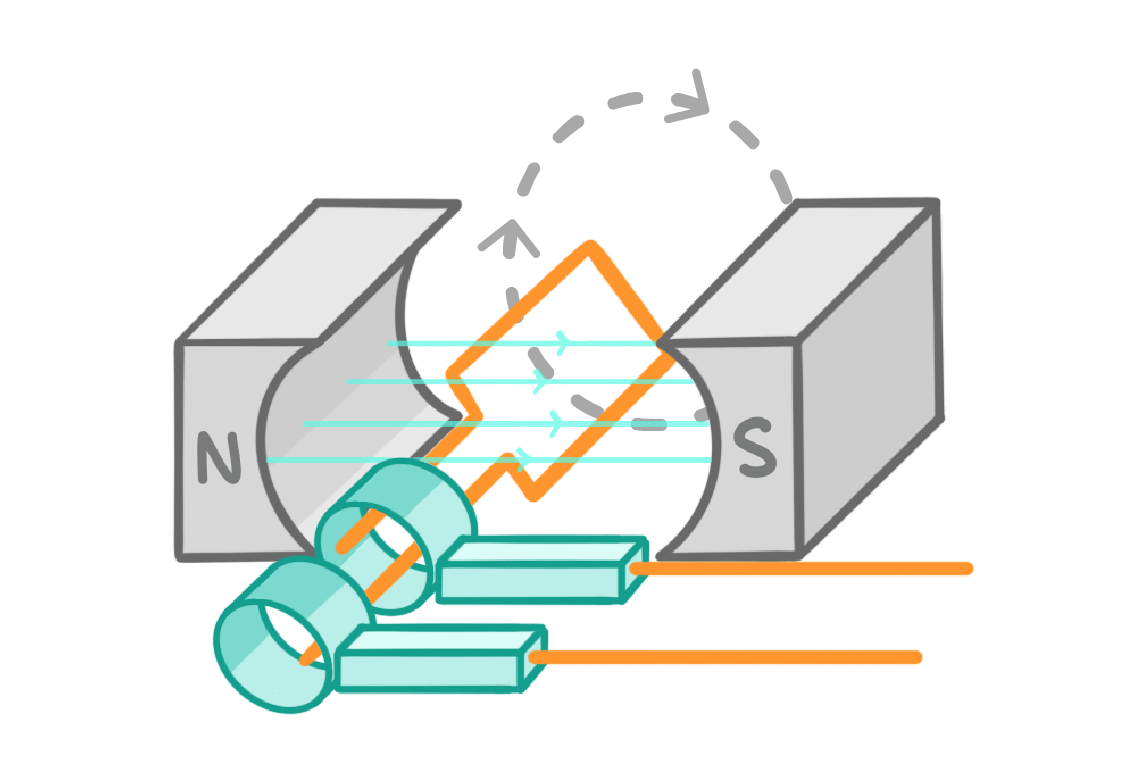 1The coil of wire rotates relative to the magnets, this induces a magnetic field in the coil, which then induces a voltage and current in the coil. |
 2The slip rings and brushes mean that the contacts don't swap every half turn (like they do in a motor or dynamo). |
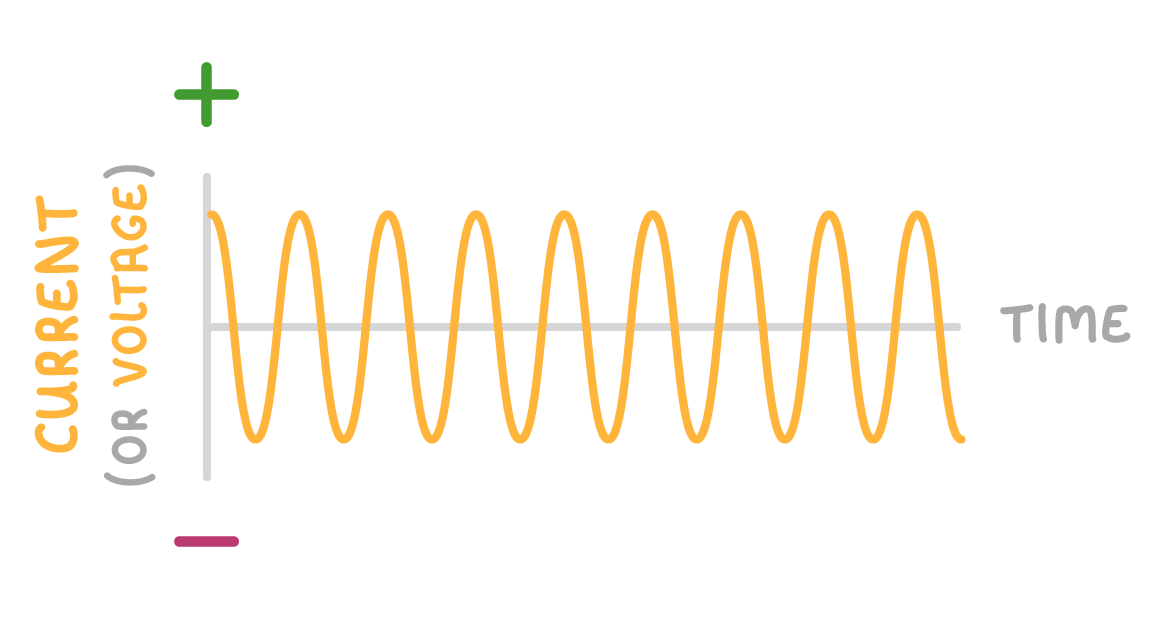 3This means that they produce an alternating potential difference and an alternating current (a.c.). A visualisation of the current, like the image above, is produced by an oscilloscope. |
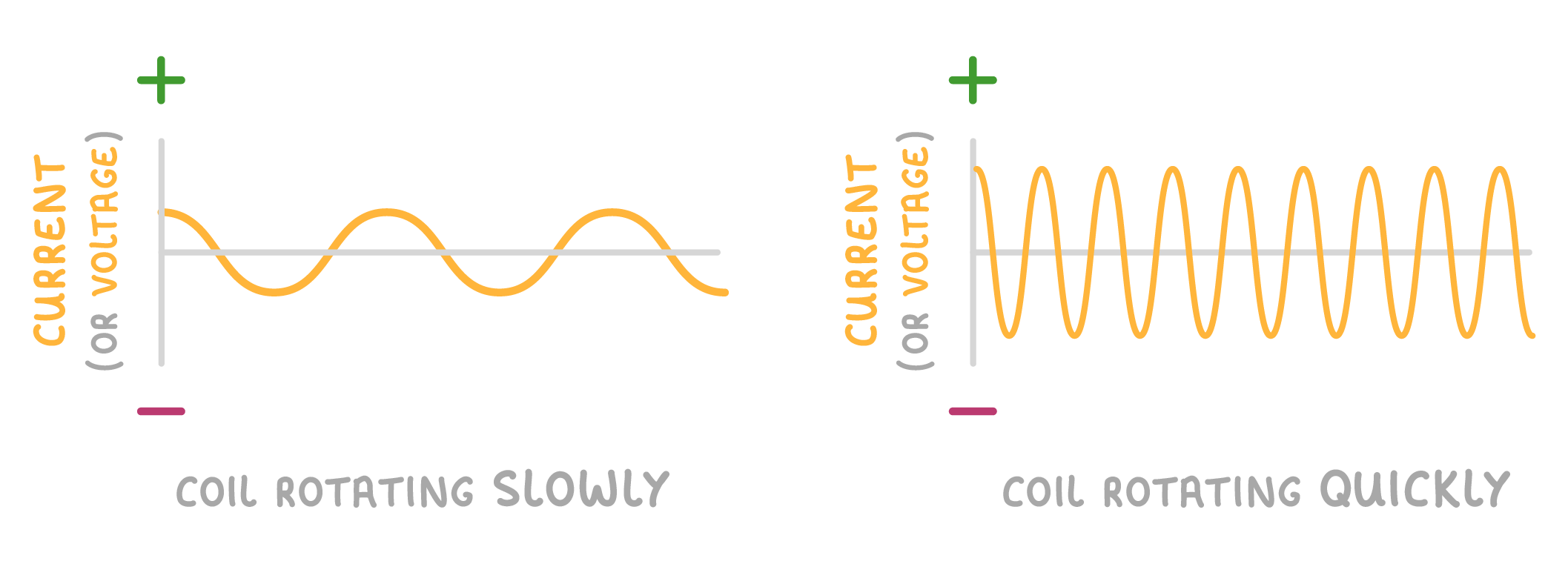 4As the coil rotates faster, the peaks of the oscillations get larger, and more frequent. |
How dynamos work |
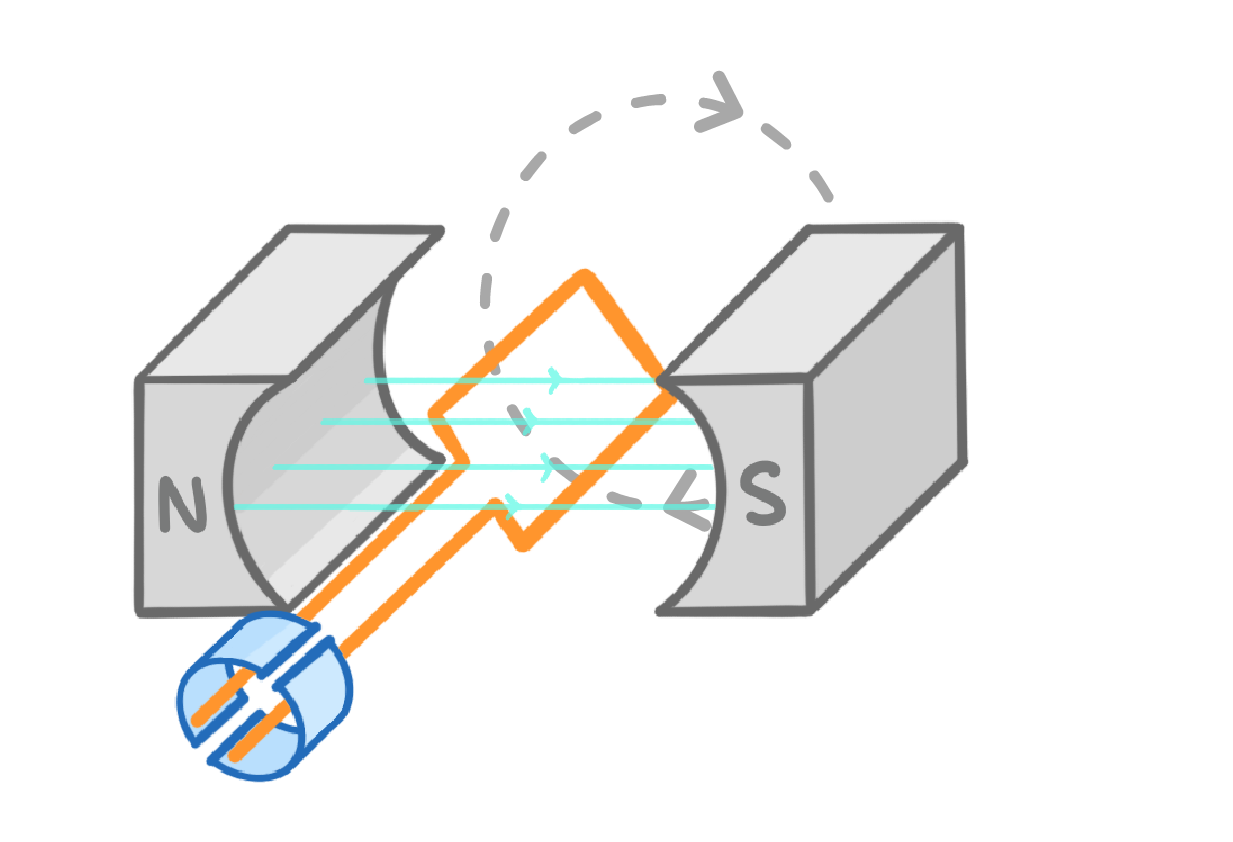 1As the coil of wire spins relative to the magnet, a magnetic field, and hence a voltage and current, is induced in the coil. |
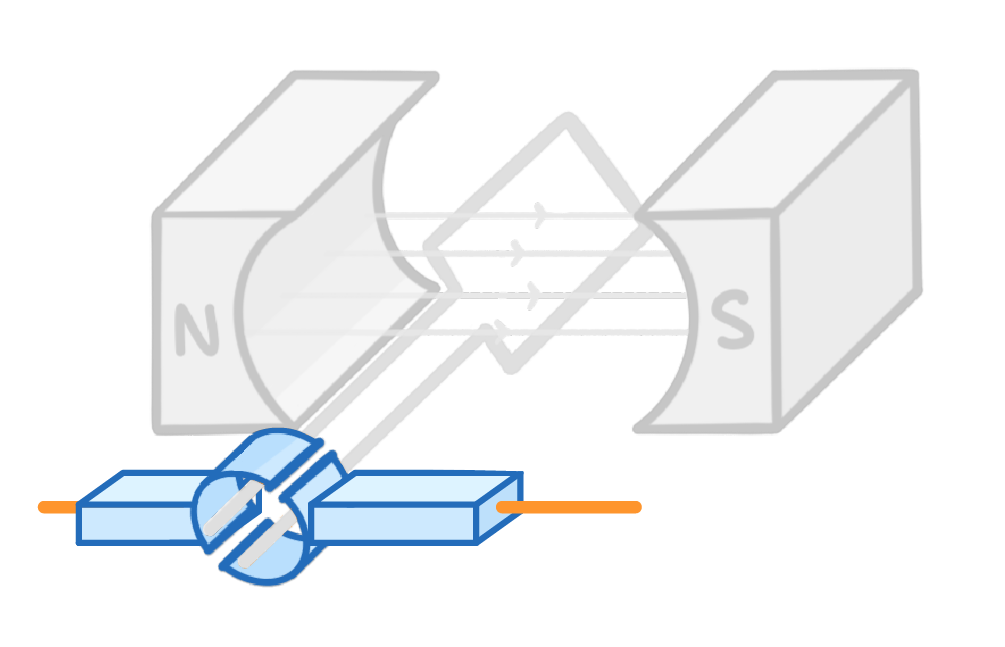 2The split ring commutator means that the contacts swap every half turn. |
 3This means that they produce a direct potential difference and hence a direct current (d.c.). It's called direct current because the current is always flowing in the same direction (which is why it's always positive on the oscilloscope graph above). |
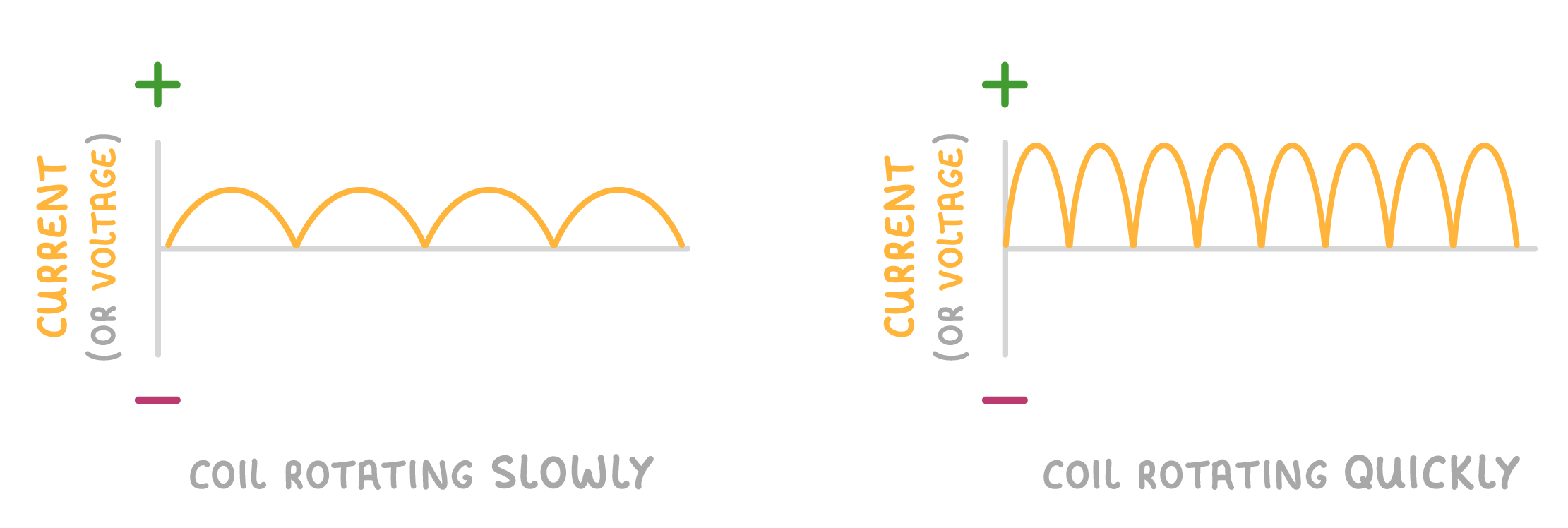 4As the coil rotates faster, the peaks of the oscillations get larger and more frequent. |
What does a.c. stand for?
|
What type of current is generated by a dynamo?
Alternating current
Direct current
|
What is the difference between the design of an alternator and the design of a dynamo?
|
Explain how an electromagnetic induction (generator effect) is used in dynamos.
|
What happens to the oscillations on an oscilloscope when you increase the speed at which a coil rotates in an alternator?
The amplitude increases, but the frequency stays the same.
The amplitude and the frequency both increase.
The amplitude and the frequency both stay the same.
The frequency increases, but the amplitude stays the same.
|