Potential Dividers
This lesson covers:
- What a potential divider is
- How variable resistors can be used to provide a variable potential difference
- How potentiometers can be used to provide a variable potential difference
Potential dividers In its most basic form, a potential divider is a circuit with two resistors in series with a power supply such as a cell. The diagram below shows a simple potential divider circuit. 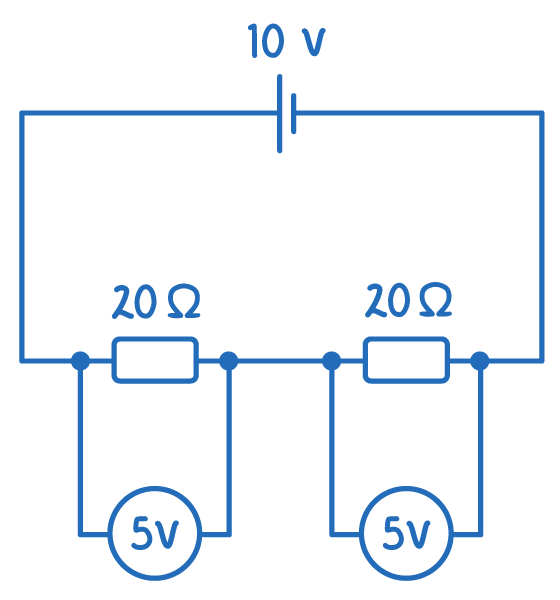 |
When the resistors are identical, the potential difference is split evenly across each resistor. If there are 2 identical resistors, the potential difference across each resistor will be half the supply voltage. If there are 3 identical resistors, the potential difference across each resistor will be a third of the supply voltage. |
Worked example: Potential divider calculation
The diagram below shows a potential divider circuit where the resistors are not identical.
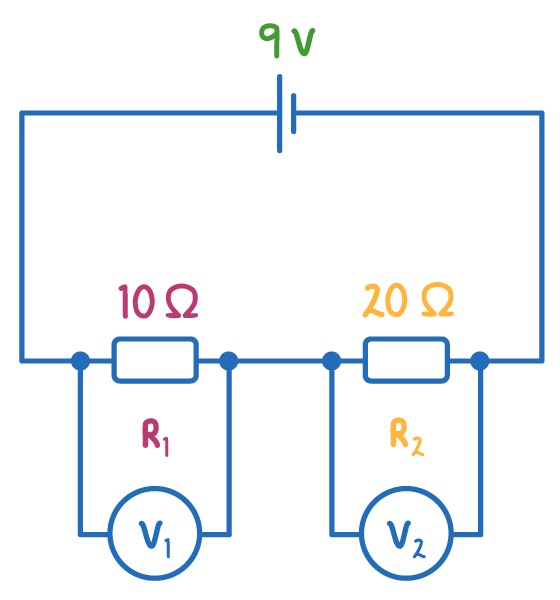
If the resistors are not identical, the potential difference across each will split based on the ratio of their resistances.
This is how to calculate the voltage across each resistor:
Variable resistors Variable resistors can be used in a potential divider to provide a variable potential difference. 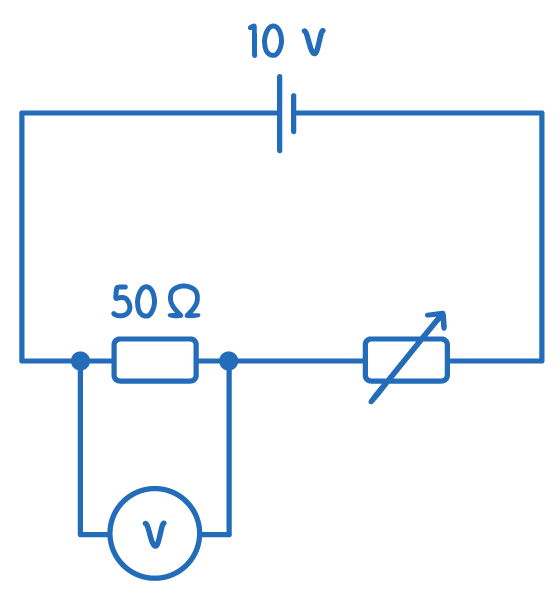 |
When the variable resistor is set to 0 Ω A variable resistor can vary it's resistance from 0 Ω to its maximum rated value. When the variable resistor is set to 0 Ω:
|
Increasing the resistance of the variable resistor As the resistance of the variable resistor increases:
|
Potentiometers
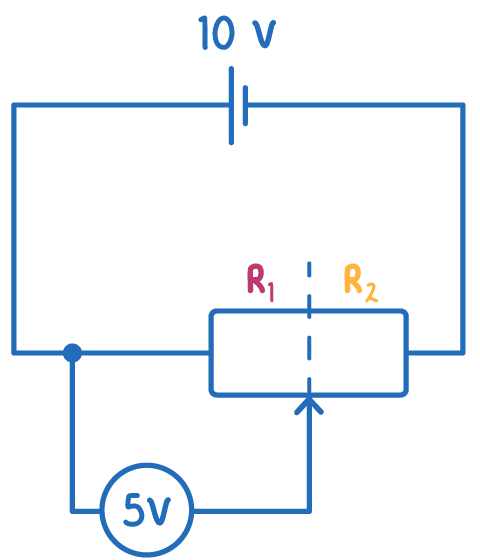
A potentiometer uses the same concept as a potential divider, with a single variable resistor taking the place of the two fixed resistors.
The variable resistor allows the ratio of resistances R1 and R2 to be adjusted by moving a slider.
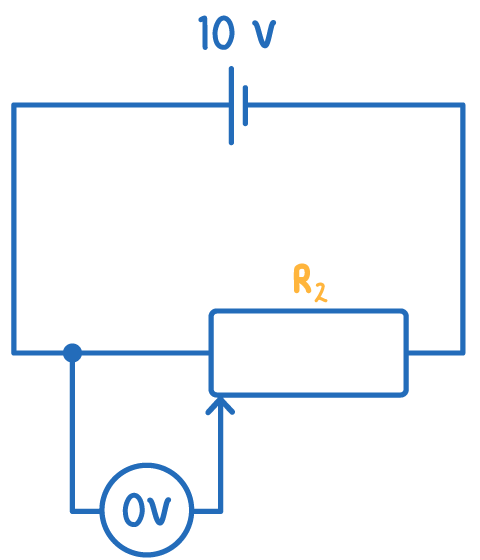
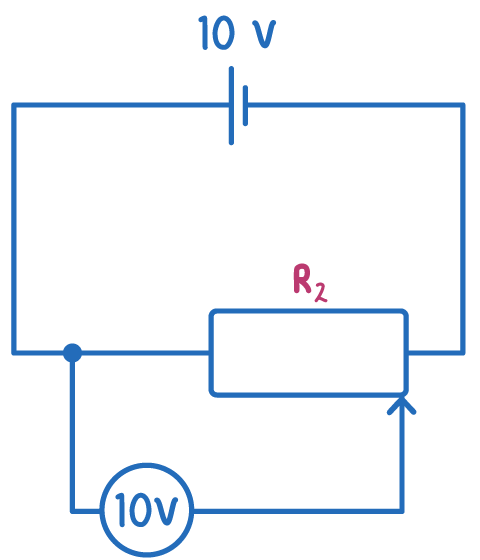
When the potentiometer wiper is all the way to the left, R1 is zero and R2 is maximum.
The voltmeter is in parallel with R1, so the voltmeter reading is zero.
Worked example: Potentiometer
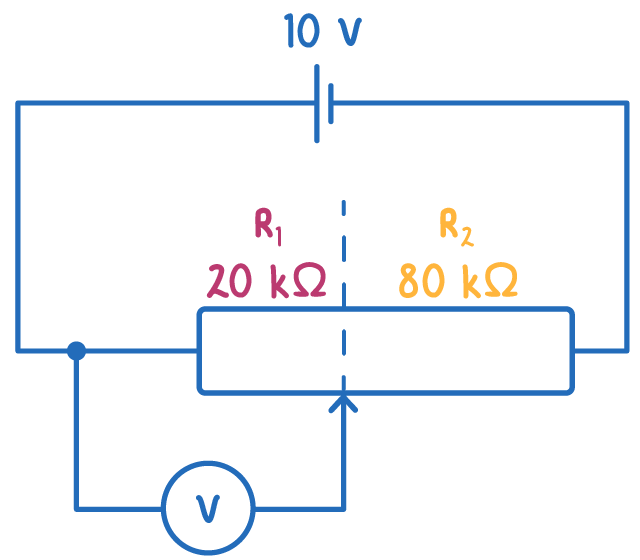
The diagram below shows a potentiometer being used to provide a variable output voltage.
The output voltage of the potential divider can be calculated using:
This is how to calculate the voltage shown on the voltmeter:
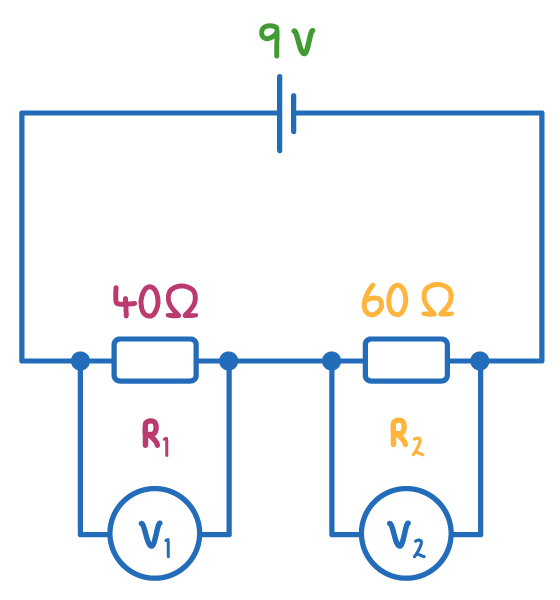
Which of the following shows the correct readings for the voltmeter readings?
V1 = 4.5 V and V2 = 4.5 V
V1 = 9 V and V2 = 0 V
V1 = 3.6 V and V2 = 5.4 V
V1 = 3 V and V2 = 6 V
|
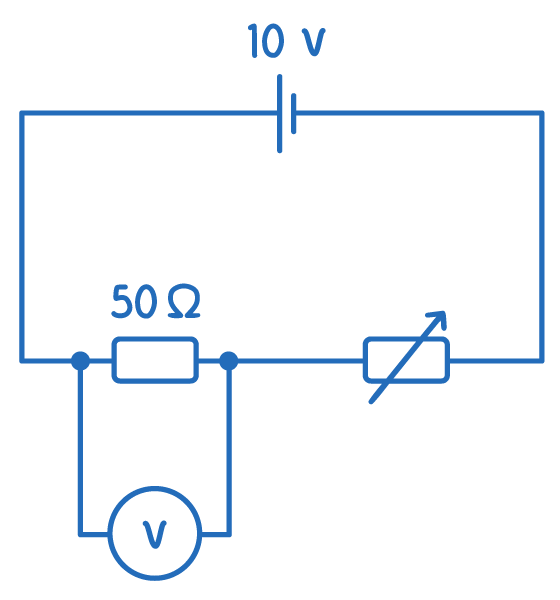
What happens to the voltmeter reading as the variable resistor increases in resistance?
voltmeter reading decreases
voltmeter reading increases
voltmeter reading stays the same
|
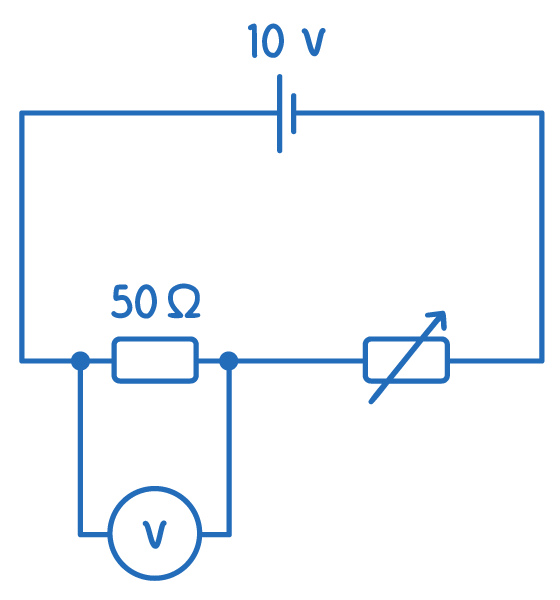
The resistance of the variable resistor is 75 Ω. Which of the following represents the voltmeter reading?
7 V
10 V
4 V
6 V
|
Which of the following best describes a potential divider?
A system that separates charges
A circuit that distributes current evenly
A device that divides electrical energy
A component that splits potential difference
|
Which of the following is a common application of potentiometers?
Controlling the speed of a motor
Adjusting screen brightness on a smartphone
Monitoring air pressure in a weather station
Measuring heart rate in a fitness tracker
|