Series Circuits
This lesson covers:
- What a 'series' circuit is
- How series circuits affect potential difference, current, and resistance
Parallel / Series
circuits only have a single loop.
circuits have more than one loop.
|
In a series circuit, the potential difference of the battery is:
Shared across all of the components
The same everywhere in the circuit
|
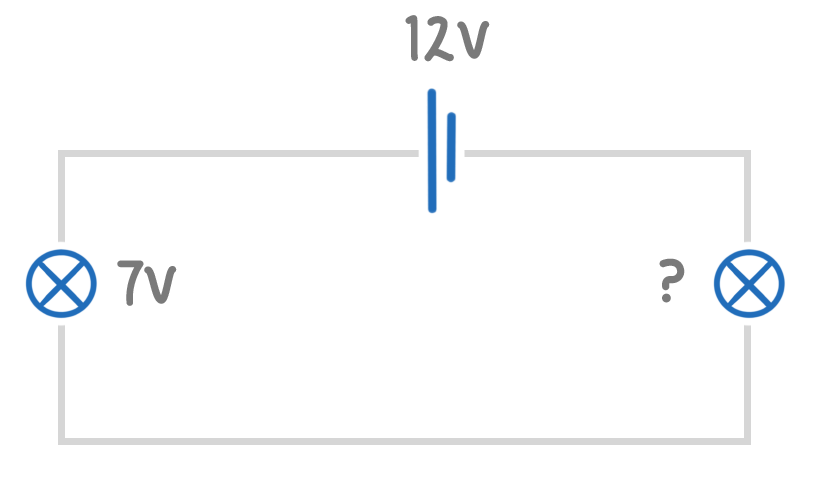
The above series circuit shows a 12 V battery supply.
The left filament lamp has a voltage of 7 V measured across it.
What is the voltage across the right filament lamp?
V
|
In a series circuit, the current is:
Shared across all of the components
The same everywhere in the circuit
|

The above series circuit has a battery, two filament lamps, and three ammeters.
The left ammeter shows 3 A.
What current would the other two ammeters show?
A
|
In a series circuit, the total resistance is ________ the sum of the individual resistances of each component.
less than
equal to
more than
|
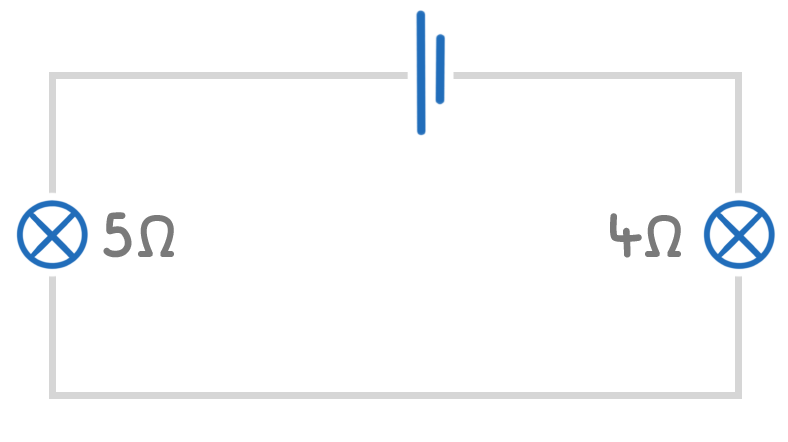
The above series circuit has a battery and two filament lamps.
The left filament lamp has a resistance of 5 Ω and the right filament lamp has a resistance of 4 Ω.
What is the total resistance of the circuit?
Ω
|
Ohm's law, which describes the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance is:
|
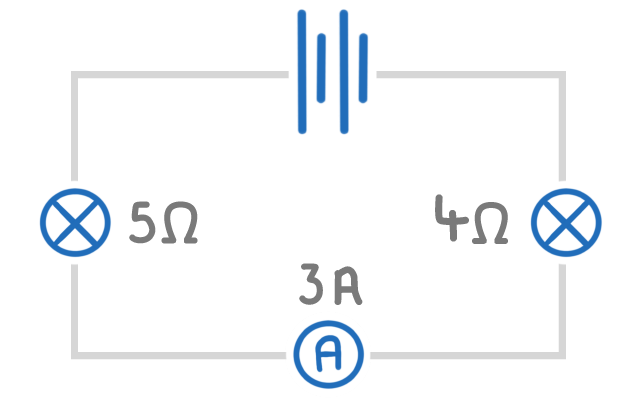
The above series circuit has a battery, two filament lamps, and an ammeter.
The left filament lamp has a resistance of 5 Ω, the right filament lamp has a resistance of 4 Ω, and the ammeter shows 3 A.
What is the potential difference across the left filament lamp?
V
|
In a series circuit, components with a greater resistance will always have a ________ share of the voltage.
equal
greater
lesser
|