How Lenses Work
This lesson covers:
- How lenses focus and disperse light via refraction
- How the power of a lens changes with curvature
- The difference between real and virtual images

Which of the below statements about the lenses above is correct?
A is a convex lens and B is concave lens
B is a convex lens and A is concave lens
|
Another name for a convex lens is a:
Converging lens
Diverging lens
|
The distance between the principle focus and the centre of the lens is called the 'f l'.
|
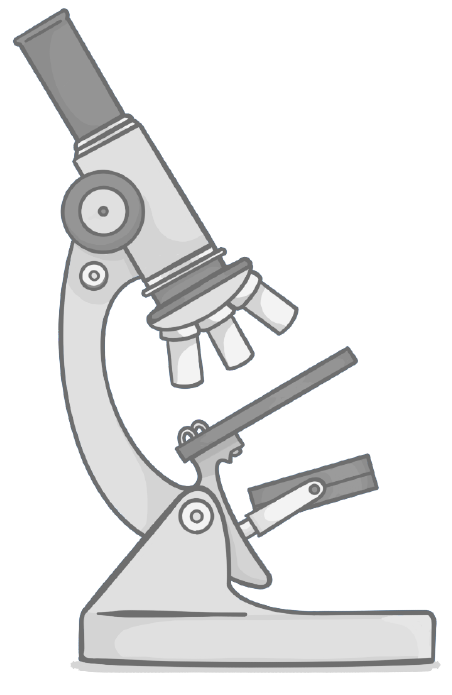
Higher power lenses are:
(Select all that apply)
More curved
Made of a material which refracts light less strongly
Less curved
Made of a material which refracts light more strongly
|
What type of image is being described by the statement below:
'Light rays come together to form an image.
The image can be captured on a screen.'
Real image
Virtual image
|
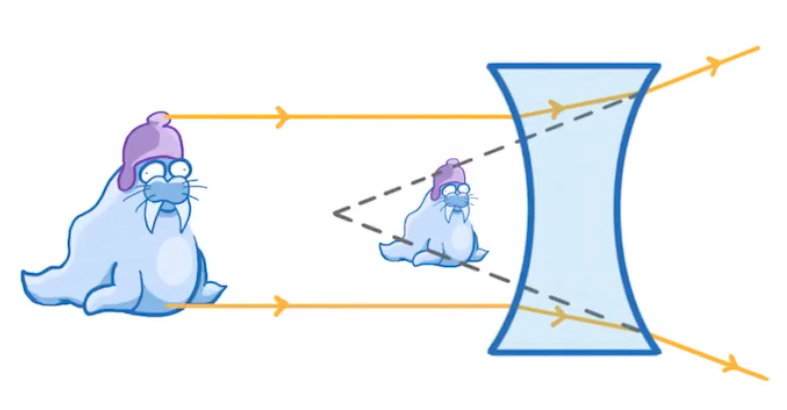
Compared to the object, please state whether the image is:
'real' or 'virtual':
'upright' or 'inverted':
'bigger' or 'smaller':
|
What type of image is being described by the statement below:
'Light rays don't come together where the image appears to be.
The image cannot be captured on a screen'
Virtual image
Real image
|