Refraction
This lesson covers:
- Why light is refracted as it passes from one medium to another
- How to draw ray diagrams for refraction
- What happens when white light is refracted through a prism
direction / intensity / colour / speed / amplitude
Refraction refers to the change in of a wave, as it passes from one medium to another, and is caused by its change in .
|
Light travels more ________ in a more dense material.
quickly
slowly
|
Light travelling from a less dense material, into a more dense material, will bend ________ the normal.
towards
away from
|
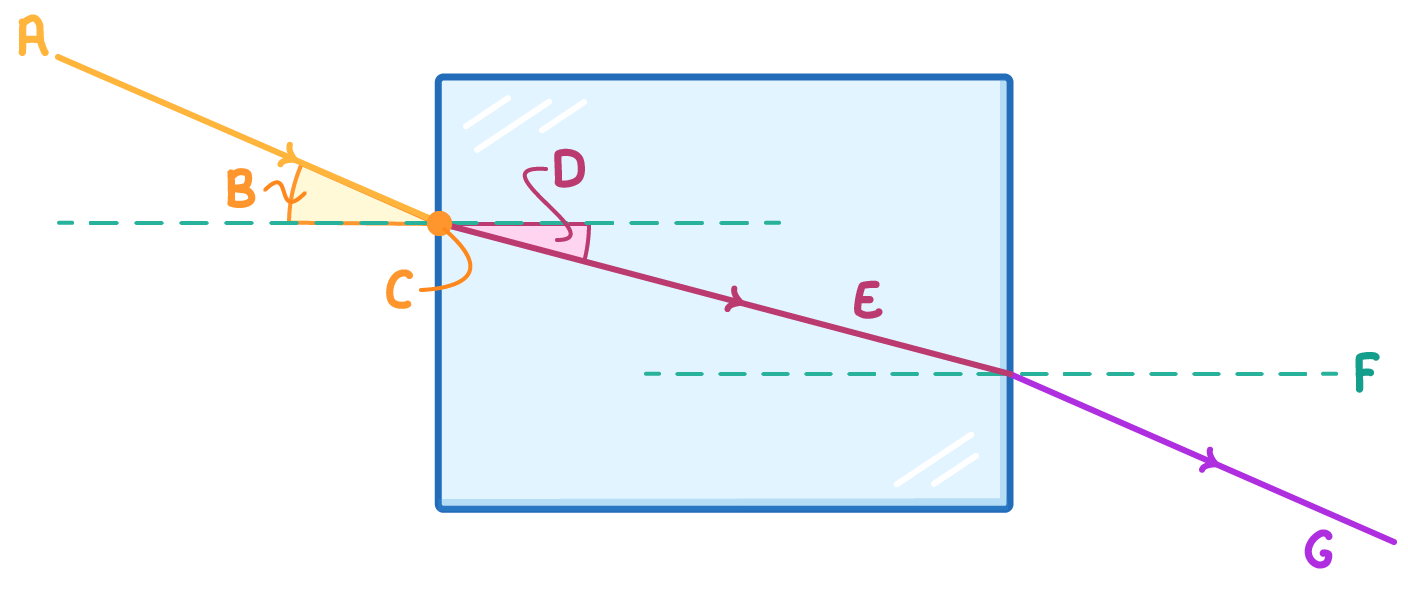
Match the letters A to G on the above diagram with the following labels:
Point of incidence:
Refracted ray:
Incident ray:
Angle of incidence:
Emergent ray:
Angle of refraction:
Normal:
|
When a wave travels into a more dense medium, the wave speed decreases.
The frequency of the wave:
Stays the same
Increases
Decreases
|
When a wave travels into a more dense medium, the wave speed decreases.
The wavelength of the wave:
Stays the same
Increases
Decreases
|
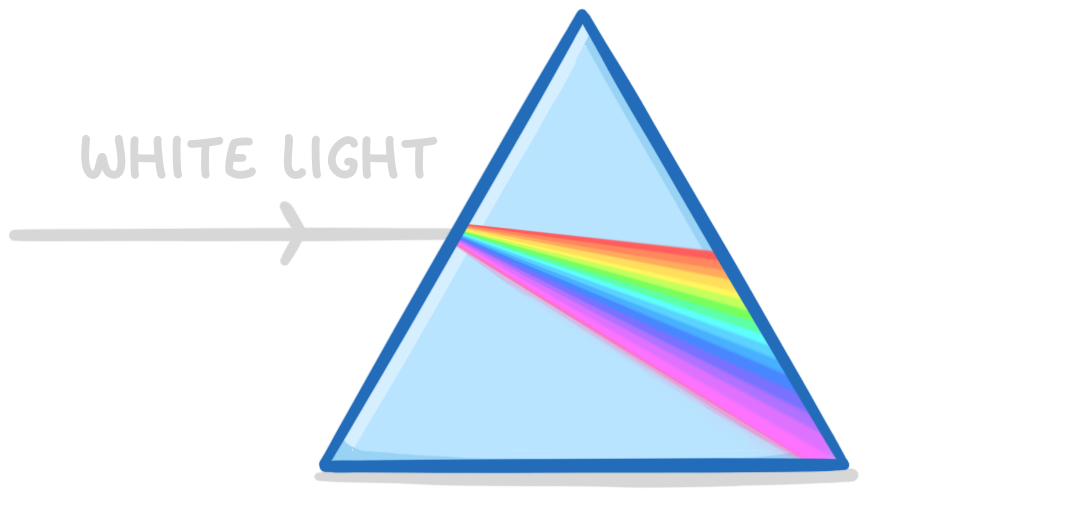
In the above image, white light waves are travelling from a less dense medium (air), into a more dense medium (glass).
What has happened to the different wavelengths of light contained within the white light?
They have all refracted at the same angle
They have all refracted at different angles
|