Scalar & Vector Quantities
This lesson covers:
1The difference between scalar and vector quantities
Scalar quantities only have a magnitude and do not have a .
Vector quantities have both a and a direction.
|
When deciding whether a quantity is vector or scalar, just ask yourself:
"does it have a direction?"
If it does, it's a vector quantity
If it doesn't, it's a scalar quantity
Which of the following are examples of scalar quantities?
(Select all that apply)
Velocity
Temperature
Displacement
Force
Distance
Speed
|
Which of the following are examples of vector quantities?
(Select all that apply)
Weight
Velocity
Time
Distance
Displacement
Mass
|
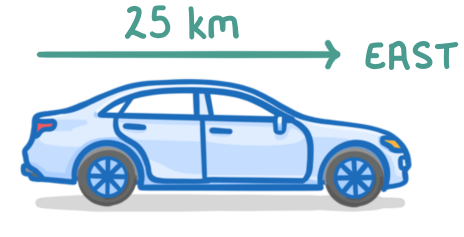
In the diagram above, what does the labelled arrow represent?
Displacement, which is a vector quantity
Distance, which is a scalar quantity
Distance, which is a vector quantity
Displacement, which is a scalar quantity
|
A 20 m displacement North is the same as:
-20 m displacement North
-20 m displacement East
-20 m displacement South
20 m displacement East
|
A women walks 500 m from her home to the shop. She then walks 200 m to the park and finally 400 m back to her home. What is the overall distance and displacement of her journey?
Distance = m
Displacement = m
|
 |
A man cycles 12 km south east. What does the 12 km represent? Magnitude Direction
|
What does the south-east represent? Magnitude Direction
|
|
Is power a vector or a scalar quantity? Explain your answer.
|
 |
Look at the vector arrow above. What does the way the arrow is pointing represent? Magnitude Direction
|
What does the length of the arrow represent? Magnitude Direction
|
|