Kinetic Energy
This lesson covers:
- What 'kinetic energy' is
- How to calculate kinetic energy
The kinetic energy of an object is the energy that it possesses due to its motion.
Which two measurements are required to calculate the kinetic energy of an object?
Velocity
Force
Distance
Mass
|
What is the formula for kinetic energy?
|
The units for kinetic energy are:
Newtons (N)
Joules (J)
Pascals (Pa)
Kilograms (kg)
|
The units for mass when calculating kinetic energy should be:
Litres (L)
Kilograms (kg)
Grams (g)
Pounds (lb)
|
The units for velocity are:
m/s2
km/hr
m/s
ms
|
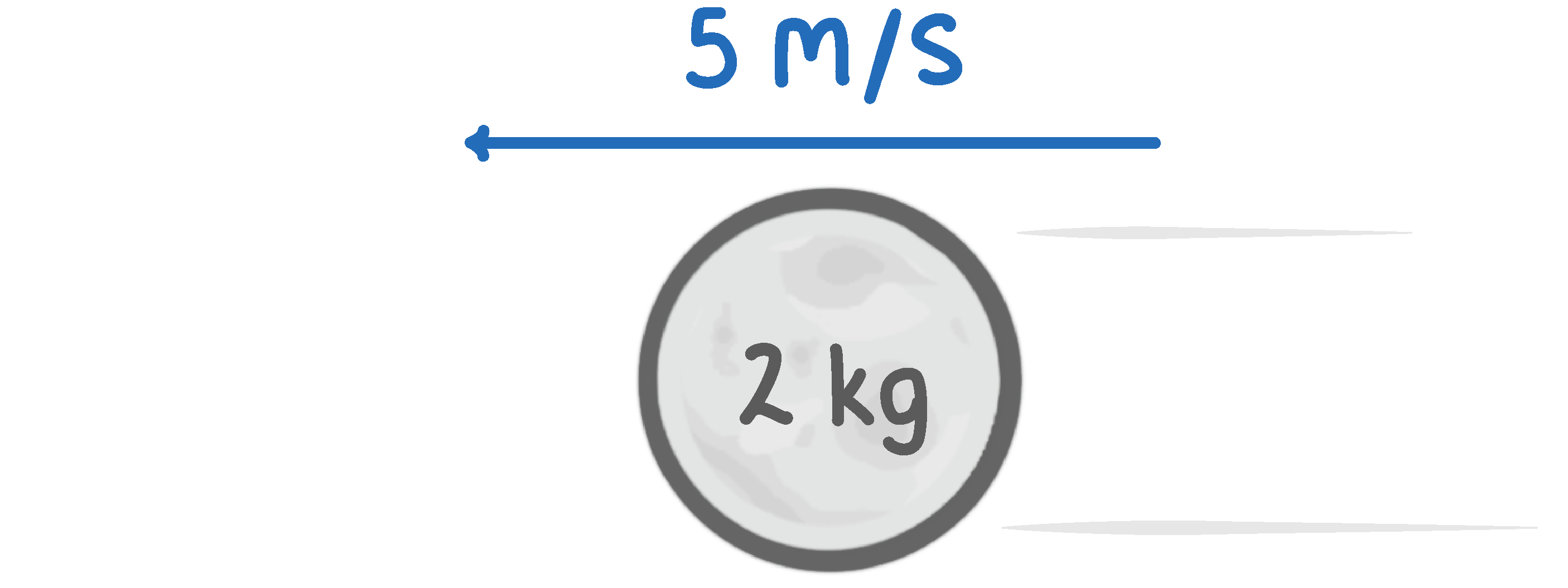
An object has a mass of 2 kg, and is travelling at a velocity of 5 m/s.
How much kinetic energy does the object have?
J
|
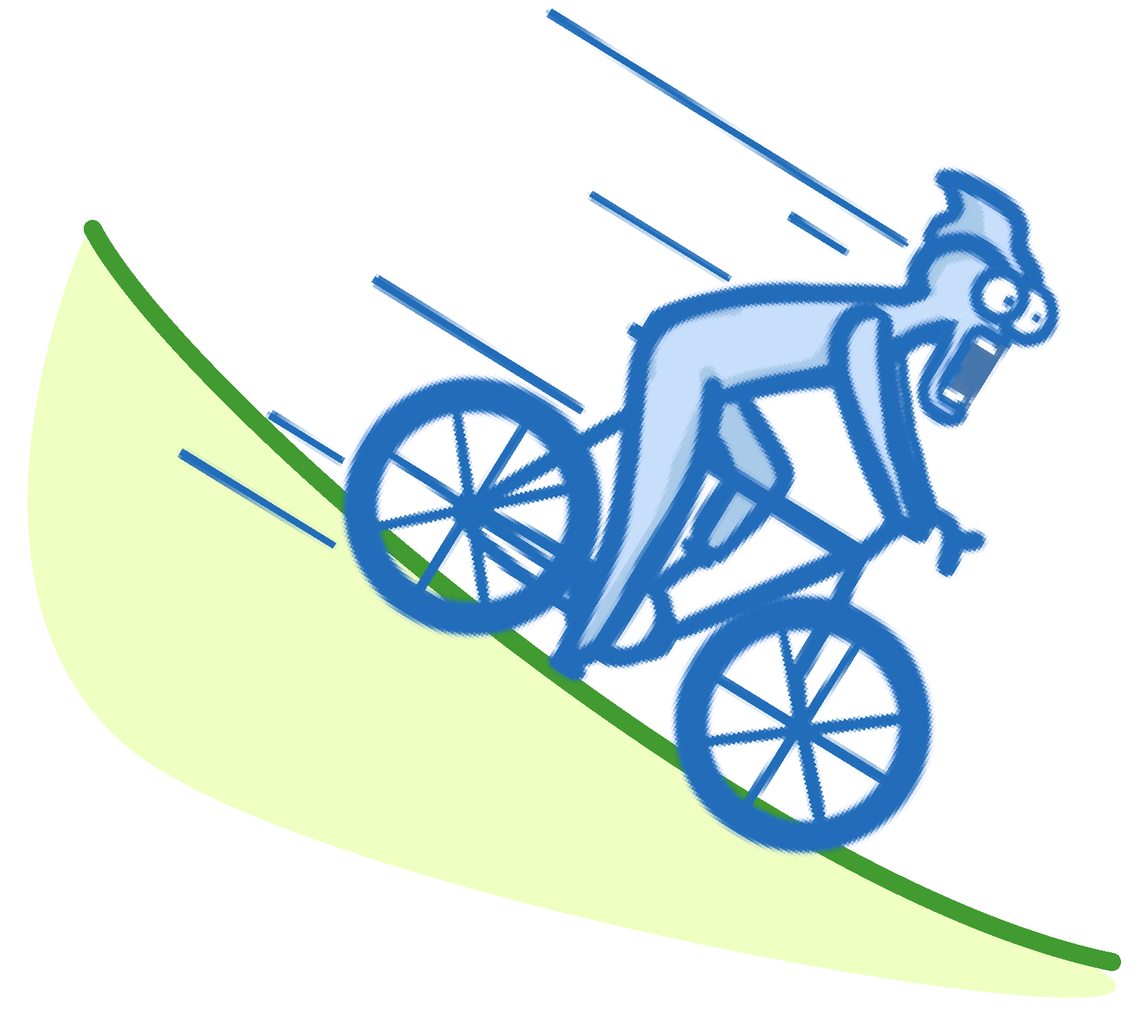

A cyclist is riding down a hill at a speed of 10 m/s.
The cyclist has 4 kJ of kinetic energy.
Calculate the cyclist's mass.
kg
|