Particle Theory & States of Matter
This lesson covers:
- What particle (kinetic) theory is, and what its limitations are
- How it explains the 3 states of matter: solid, liquid, and gas
- How gaining and losing heat can cause matter to change state
'Forces of attraction' or 'bonds'? When discussing particle theory, some sources will talk in terms of 'forces of attraction' between the molecules, while others will call them 'bonds'. |
For example, as a solid is heated and melts into a liquid, you could say either: 'As the particles vibrate more, some of the forces of attraction between them weaken (or are overcome), causing the solid to melt into a liquid'. Or: |
'As the particles vibrate more, some of the bonds between them break, causing the solid to melt into a liquid' |
The key thing to understand here is that if you do use the term 'bonds' in this way, it's not referring to a specific type of bond (e.g. ionic or covalent). When used like this, 'bonds' just means the forces of attraction between particles. |
Which theory attempts to explain the three states of matter?
Nuclear theory
Condensation theory
Particle (kinetic) theory
|
The particle model (sometimes also called the kinetic model) has 3 main assumptions. These are that the particles are: |
Small Large
|
Elastic Inelastic
|
Spheres Cubes
|
|
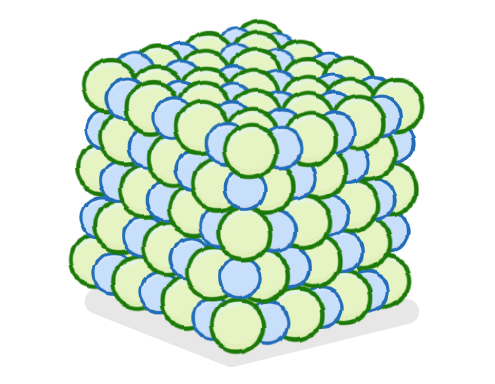
heated / cooled / vibrate / liquid / gas / melts / boils
In solids, strong attractive forces hold the particles in place, so that they can only in position.
As the substance is the particles gain energy and vibrate faster and faster. Eventually, the particles have so much energy that they can overcome the forces holding them together and the substance into a .
|
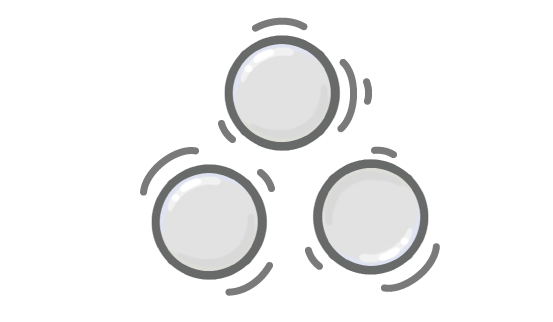
When a solid is heated, energy is transferred to the particles' ________ energy stores, which causes them to vibrate faster.
thermal
chemical
elastic
kinetic
|
freeze / boil / melt
As heat is applied to a liquid, the particles gain kinetic energy and move faster. With enough energy they can break the forces of attraction between the molecules. At this point the liquid would into a gas.
|
When a gas is heated, the particles gain energy and move faster.
If the gas is trapped within a container that cannot expand, it means that the of the gas is fixed, and so the inside the container increases.
|
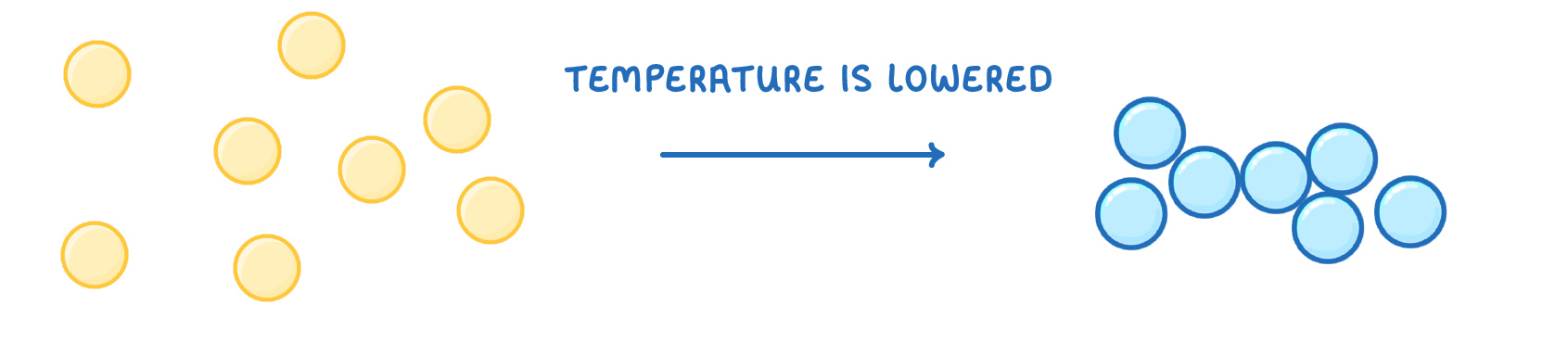
In gases, the particles have enough energy to overcome the attractive forces between them, and so spread out randomly.
If the temperature is lowered, they will no longer be able to overcome these attractive forces, and the particles move closer together, and turn into a liquid.
This process is called ________.
boiling
condensation
freezing
melting
|
The temperature at which a solid converts into a liquid is called the point.
The temperature at which a liquid converts into a gas is called the point.
|

Which state of matter matches each of the descriptions below?
Solid / Liquid / Gas
- Strong forces of attraction between particles:
- Weak forces of attraction between particles:
- Very weak forces of attraction between particles:
|
When a gas is heated, which of the following statements are true?
(Select all that apply)
If it's in an expandable container the volume will increase
If it's in an expandable container the pressure will increase
If it's in a fixed container the volume will increase
If it's in a fixed container the pressure will increase
|
In a closed system, changes in state won't change the mass at all.
Why is this the case?
The number of particles remains the same
The bonds between the particles remain the same
The velocity of the particles remain the same
|
Which state has the lowest density?
Liquids
Gases
Solids
|
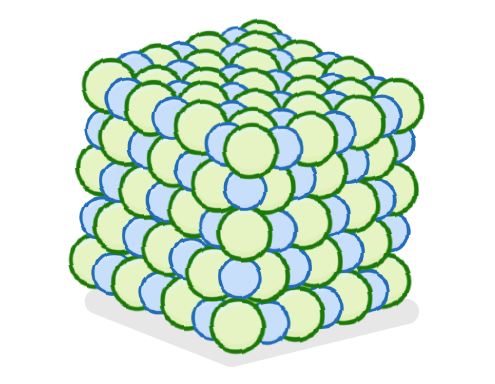
"Particles are arranged in a regular lattice structure and can only vibrate in place."
Which state of matter does this describe?
Liquid
Gas
Solid
|
"When heat is lost, the particles won't have enough energy to overcome forces of attraction. Thus, bonds start to form between the particles."
Which change of state does this describe?
Boiling
Condensing
Melting
|