How Transformers Work
This lesson covers:
- How transformers are used to minimise power loss when transmitting electricity across the national grid
- How a transformer works
Which type of transformer increases the voltage, and decreases the current, minimising energy loss whilst the electricity is transmitted across the national grid?
Step-down transformer
Step-up transformer
|
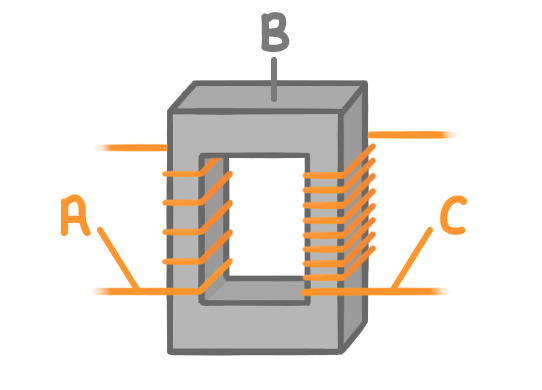
Match the letters A to C on the diagram above with the following parts of the step-up transformer:
Primary coil:
Secondary coil:
Iron core:
|
Which type of transformer decreases the voltage, and increases the current, making the electricity safe to use in our homes?
Step-down transformer
Step-up transformer
|
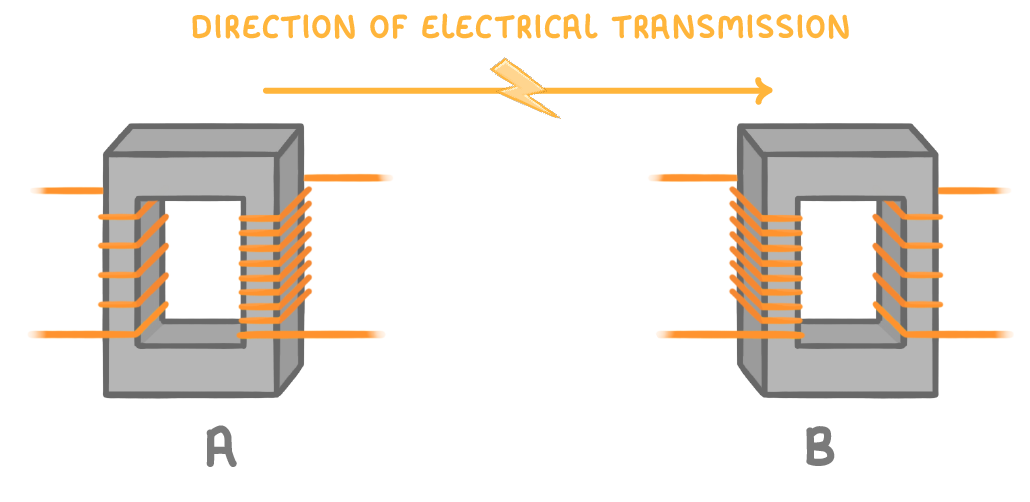
In this diagram the electricity is being transmitted from left to right.
Which transformer is the step-up transformer, and which is the step-down transformer?
A is the step-down transformer, and B is the step-up transformer
A is the step-up transformer, and B is the step-down transformer
|
For transformers to work, the current in the primary coil must be current.
|
How transformers work
strength / electric / iron core / magnetic field / direct / alternating current
- When supplied with an alternating current, the primary coil will generate an alternating .
- This then induces an alternating magnetic field in the .
- This in turn induces an alternating voltage in the secondary coil, which if the circuit is complete will lead to an .
|
The ratio of turns in the primary and secondary coil will affect:
(Select all that apply)
The resistance in the secondary coil
The voltage in the secondary coil
The current in the secondary coil
|