Parallel Circuits
This lesson covers:
- What a parallel circuit is
- How parallel circuits affect potential difference, current, and resistance

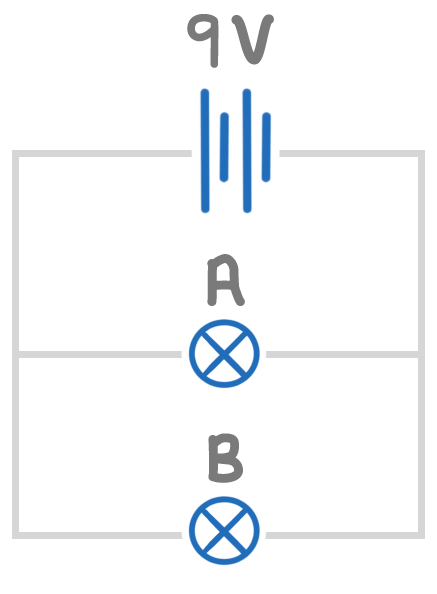
Which of these circuits is series, and which is parallel?
A is parallel and B is series
A is series and B is parallel
|
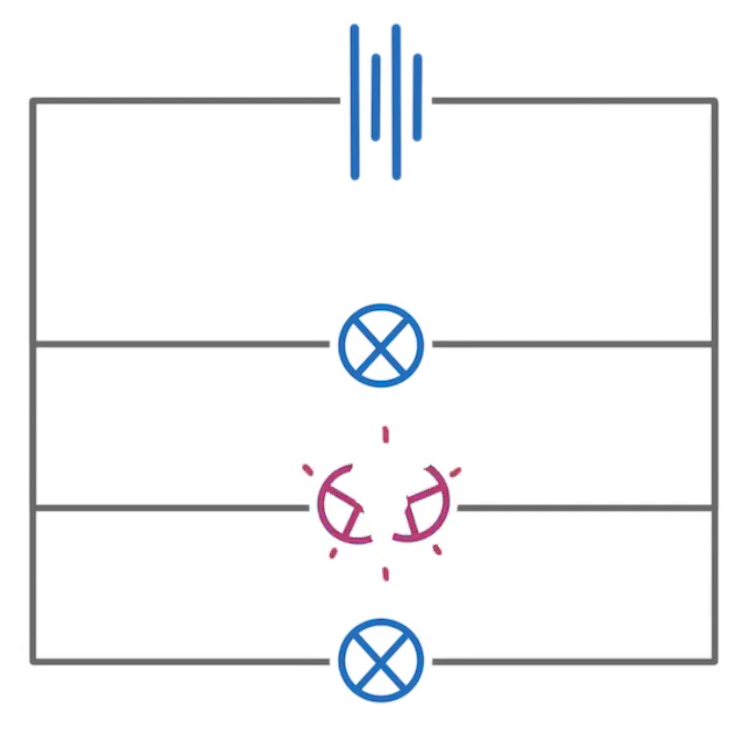
In the parallel circuit above, one of the filament lamps has blown and broken that part of the circuit.
In this scenario the other two lamps will:
Stay on
Turn off
|
All the components in a parallel circuit have the same potential difference.
The filament lamps A and B are in parallel.
The potential difference across filament lamp A is V.
The potential difference across filament lamp B is V.
|
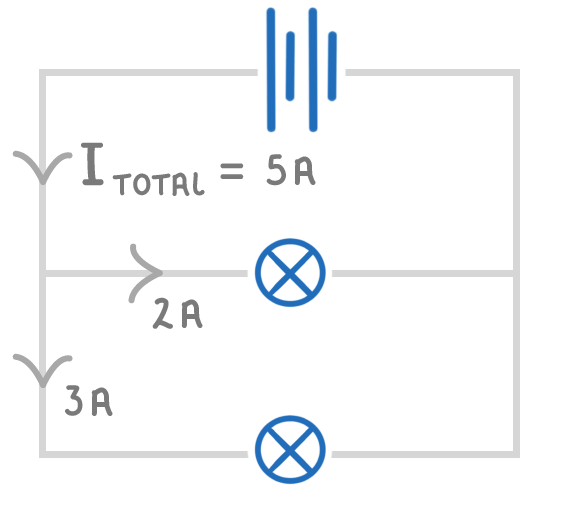
equal / shared / sum
The total current is between all of the parallel loops.
The of the current in each loop is equal to the total current.
|
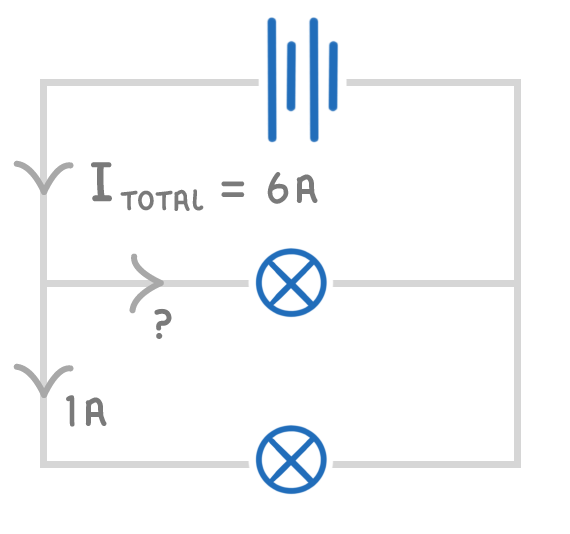
The above diagram shows a parallel circuit.
The total current is 6 A, and 1 A is flowing through the bottom filament lamp.
What is the current flowing through the top filament lamp?
A
|
Adding a resistor in parallel with an existing resistor will ________ the overall resistance.
decrease
increase
|