Sound Waves & Hearing
This lesson covers:
- How sound waves travel through materials
- How human hearing works
Sound waves are:
Longitudinal waves
Transverse waves
|
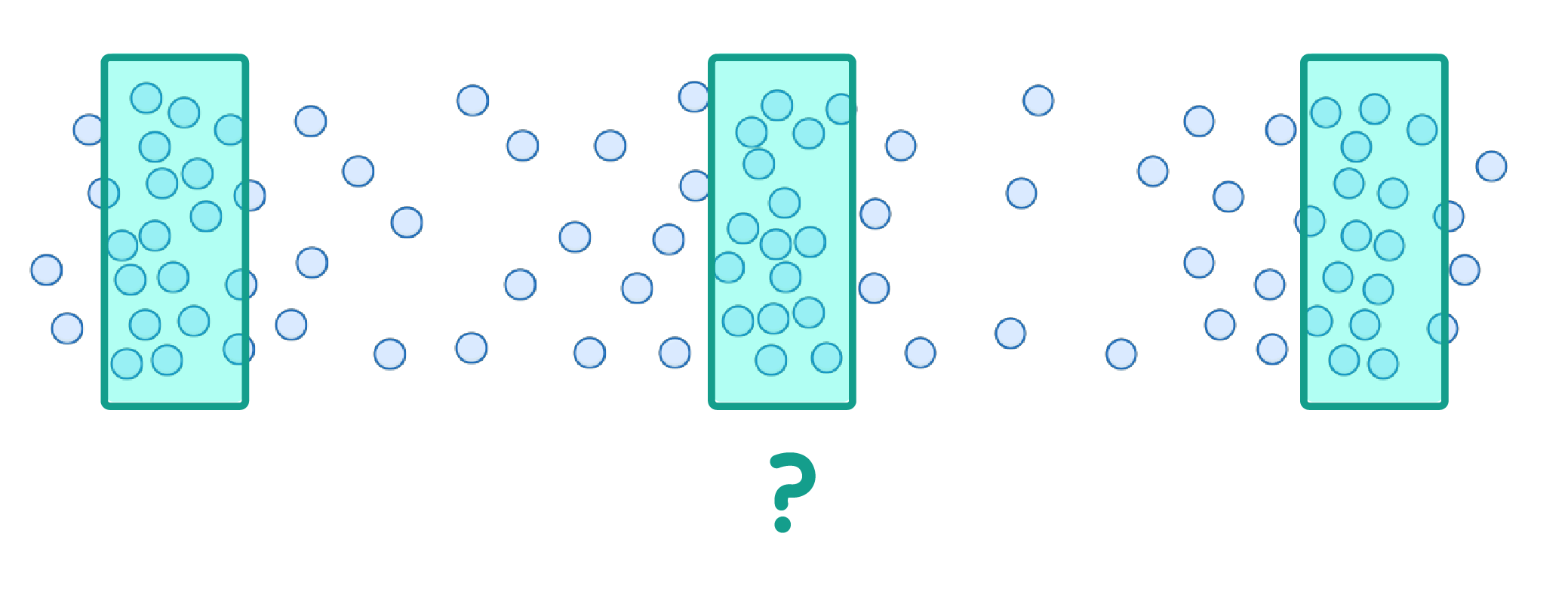
In a longitudinal wave, the regions where the vibrating particles are closest together are called:
Compressions
Rarefactions
|
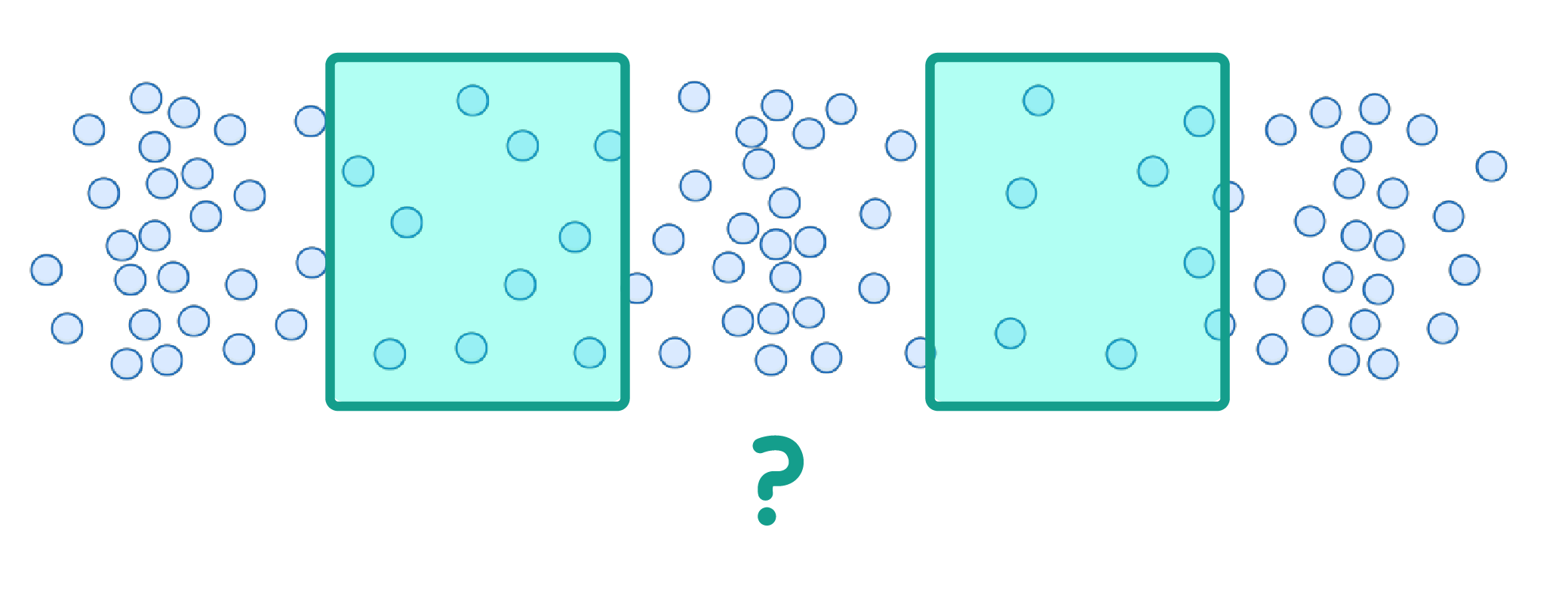
In a longitudinal wave, the regions where the vibrating particles are the furthest apart are called:
Compressions
Rarefactions
|
True or false? In a solid, sound waves travel by particles vibrating and colliding with their neighbours.
True
False
|
What happens when sound waves travel from a less dense medium, to a more dense medium?
Their speed increases
Their speed decreases
|
gases / liquids / solids
Sound travels at different speeds in different materials. Rank the speed of sound in the three states of matter in order of fastest to slowest:
Fastest:
Middle:
Slowest:
|
Sound waves can be:
(Select all that apply)
Translated
Reflected
Refracted
Absorbed
|
The frequency of a sound wave determines the pitch of the noise we hear. We hear higher frequency sounds as having a ________ pitch.
lower
higher
|
The role of the ear drum is to:
Transmit the vibrations of the sound wave to the ossicles
Transmit the electrical signals from the cochlea to the brain
Amplify the vibrations
Convert the vibrations into electrical signals
|
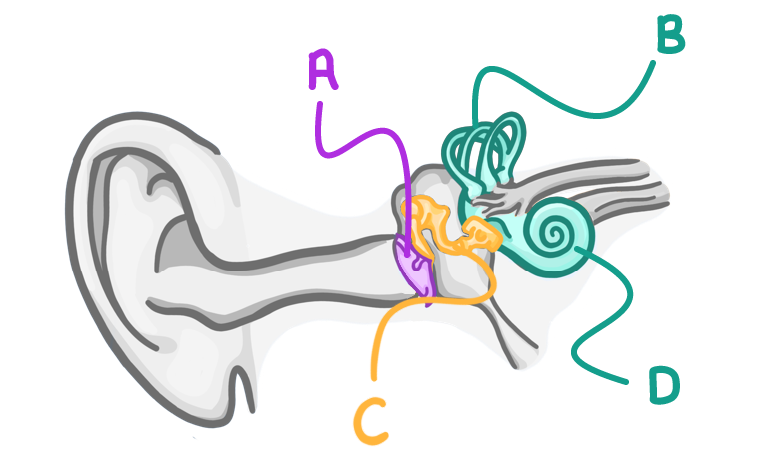
Match the letters A to D on the diagram above with the following labels:
Cochlea:
Ossicles:
Ear drum:
Semicircular canals:
|
Can sound waves travel through a vacuum?
Yes
No
|
The role of the auditory nerve is to:
Transmit the vibrations of the sound wave to the ossicles
Transmit the electrical signals from the cochlea to the brain
Convert the vibrations into electrical signals
Amplify the vibrations
|
The range of human hearing is approximately Hz to 20,000 Hz
|

As people get older, their hearing range can:
Decrease
Increase
|
The role of the cochlea is to:
Transmit the electrical signals from the cochlea to the brain
Convert the vibrations into electrical signals
Amplify the vibrations
Transmit the vibrations of the sound wave to the ossicles
|