Longitudinal & Transverse Waves
This lesson covers:
- The basics of waves
- The wave frequency equation:
- The wave speed equation:
- The difference between 'transverse' and 'longitudinal' waves
Waves transfer energy from one place to another without transferring matter.
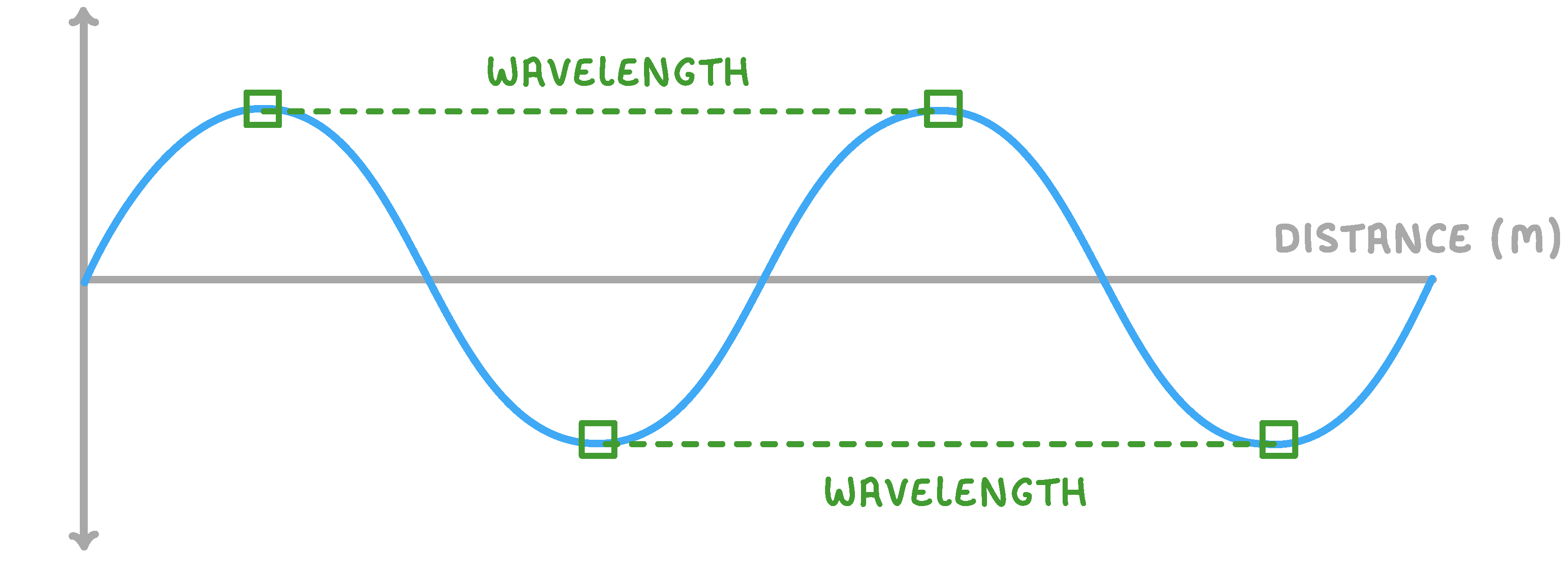
The wavelength of a wave is the d of one entire oscillation of that wave.
|
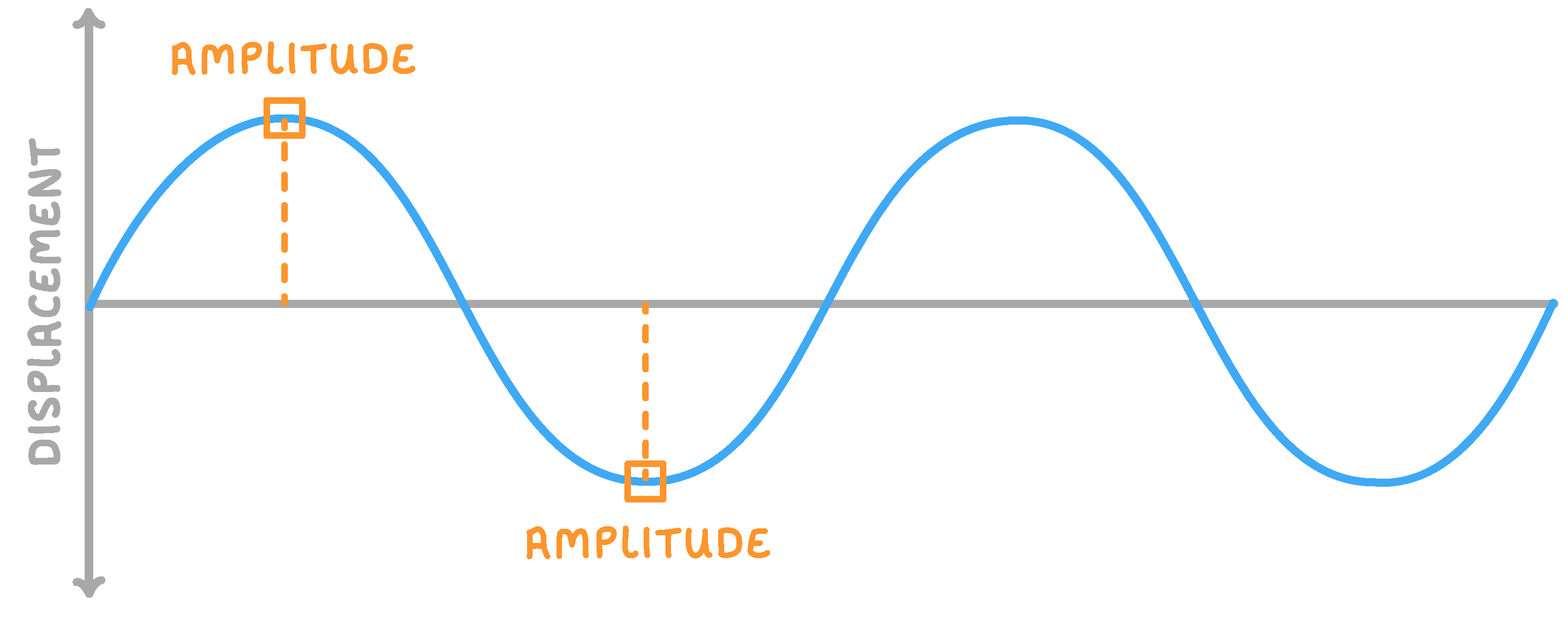
The amplitude of a wave is the maximum d from the equilibrium position (the x-axis).
|
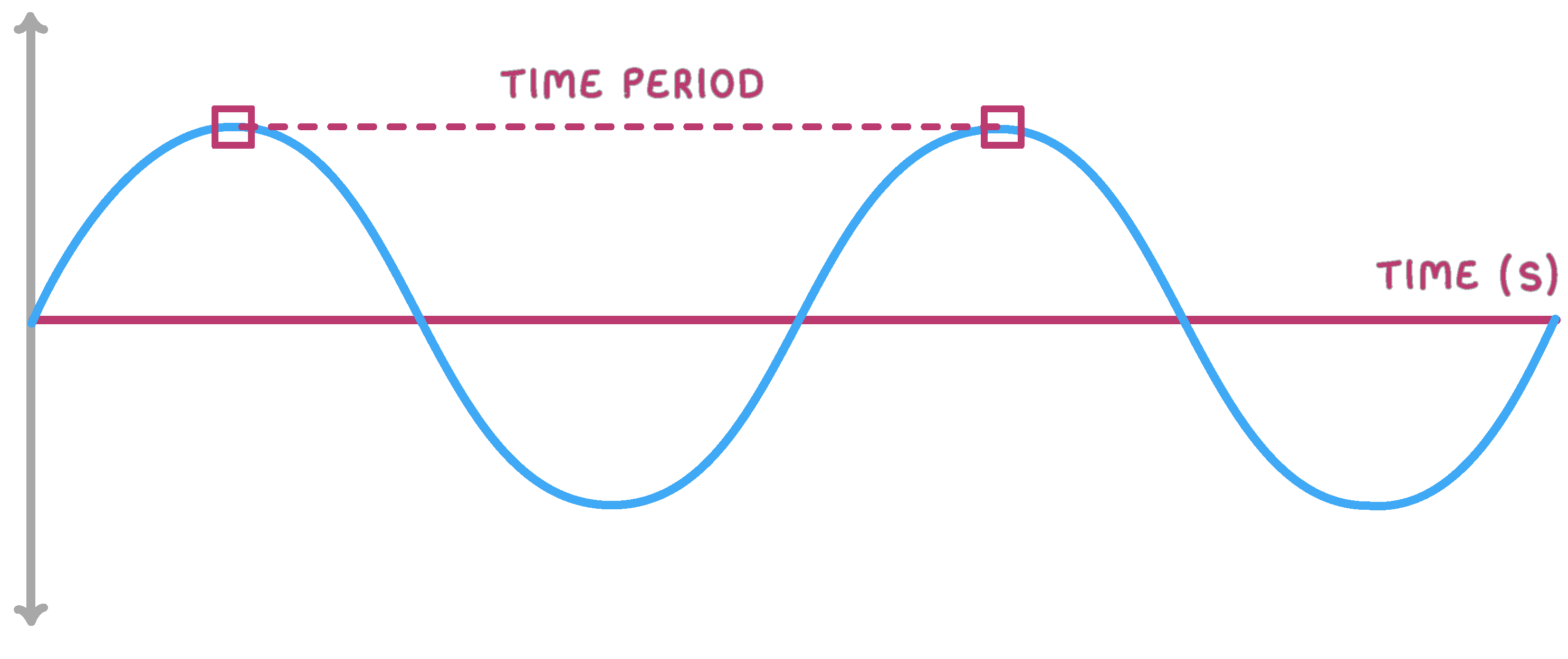
The is the time it takes for one entire oscillation of a wave.
|
The formula for frequency is:
|
The unit for frequency is:
Hz
Hs
m/s
|
A wave has a time period (T) of 0.2 s.
What is the wave's frequency?
Hz
|
The formula for wave speed is:
|
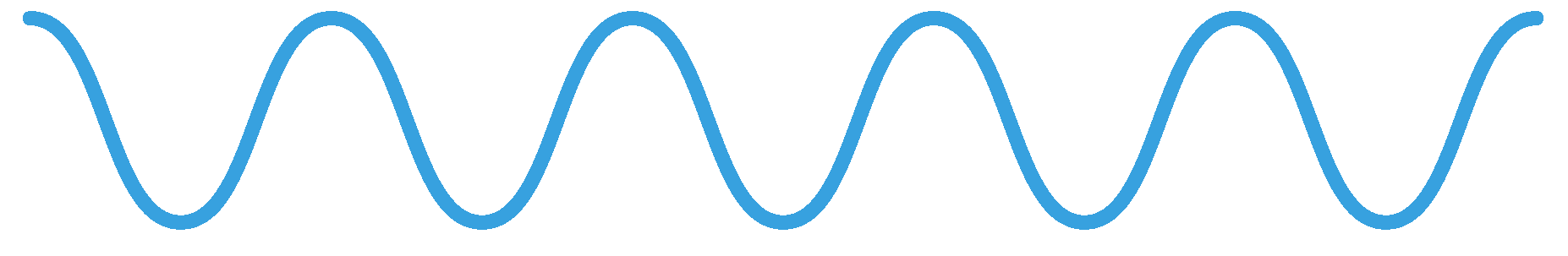
A wave has a wavelength of 3 m and frequency of 20 Hz.
What is the wave's speed?
m/s
|
A wave where the oscillations are perpendicular to the direction of energy transfer is a:
Longitudinal wave
Transverse wave
|
A wave where the oscillations are parallel to the direction of energy transfer is a:
Transverse wave
Longitudinal wave
|