Classifying Stars
This lesson covers:
1The classification of stars by temperature and colour
2Absolute and apparent magnitude
3The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram
Star temperature and colour
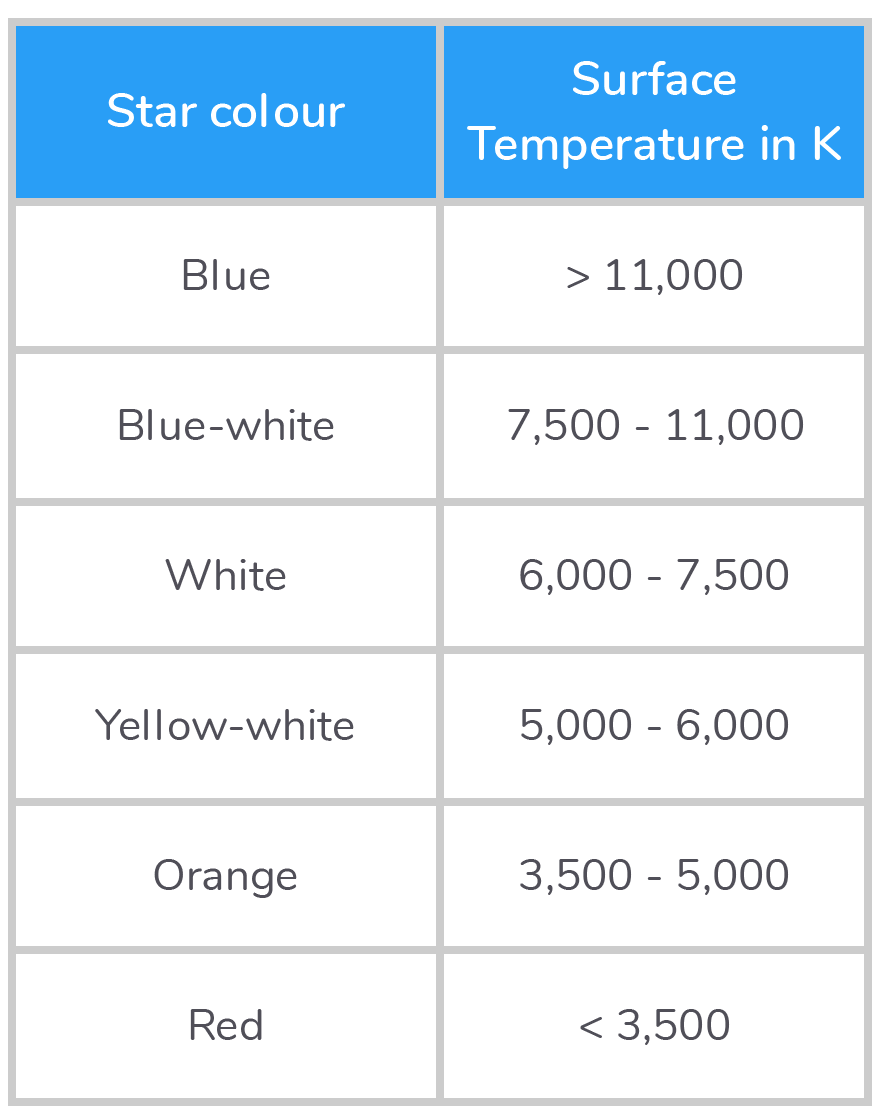
When gazing at the stars, not all stars look the same. Some appear brighter and/or a different colour. Astronomers examine the light emitted by stars and categorise them by colour and temperature.
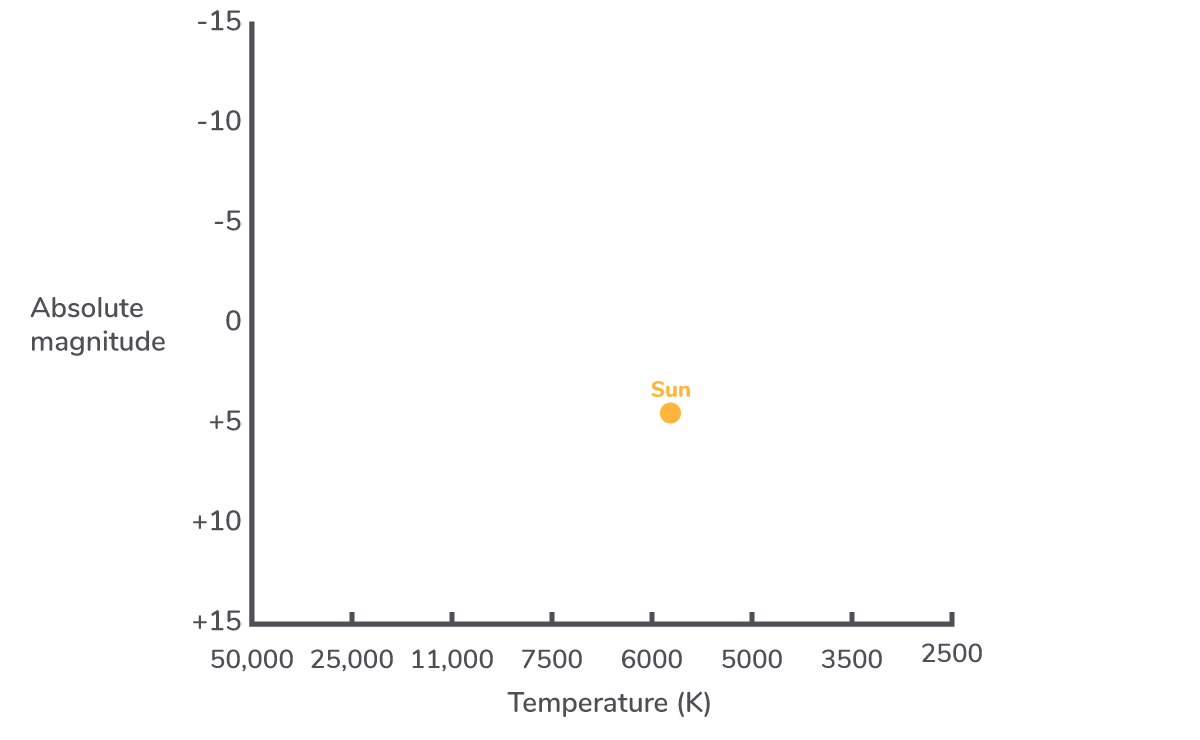
Hot stars appear blue or white in colour. Cooler stars appear red. Our sun has a temperature of 5,800 K and so appears yellow-white to us on Earth.
The amount of energy emitted by a star per second is known as its luminosity. The brighter the star, the higher the luminosity.
Apparent magnitude
When observed from Earth, some stars appear brighter than others. This could either be because they emit more light, or because they are closer to us.
We measure this brightness using the apparent magnitude scale which is a measure of how bright a star appears from Earth.
Oddly, the lower the number, the brighter the star appears from Earth.
An apparent magnitude of -1 would appear significantly brighter than a star with an apparent magnitude of +2.
Absolute magnitude
Absolute magnitude on the other hand is a measure of the intrinsic brightness of a star (its luminosity), at a specific distance from Earth. Specifically, it is the apparent magnitude a star would have if it were observed from a standard distance of 10 parsecs (about 32.6 light-years).
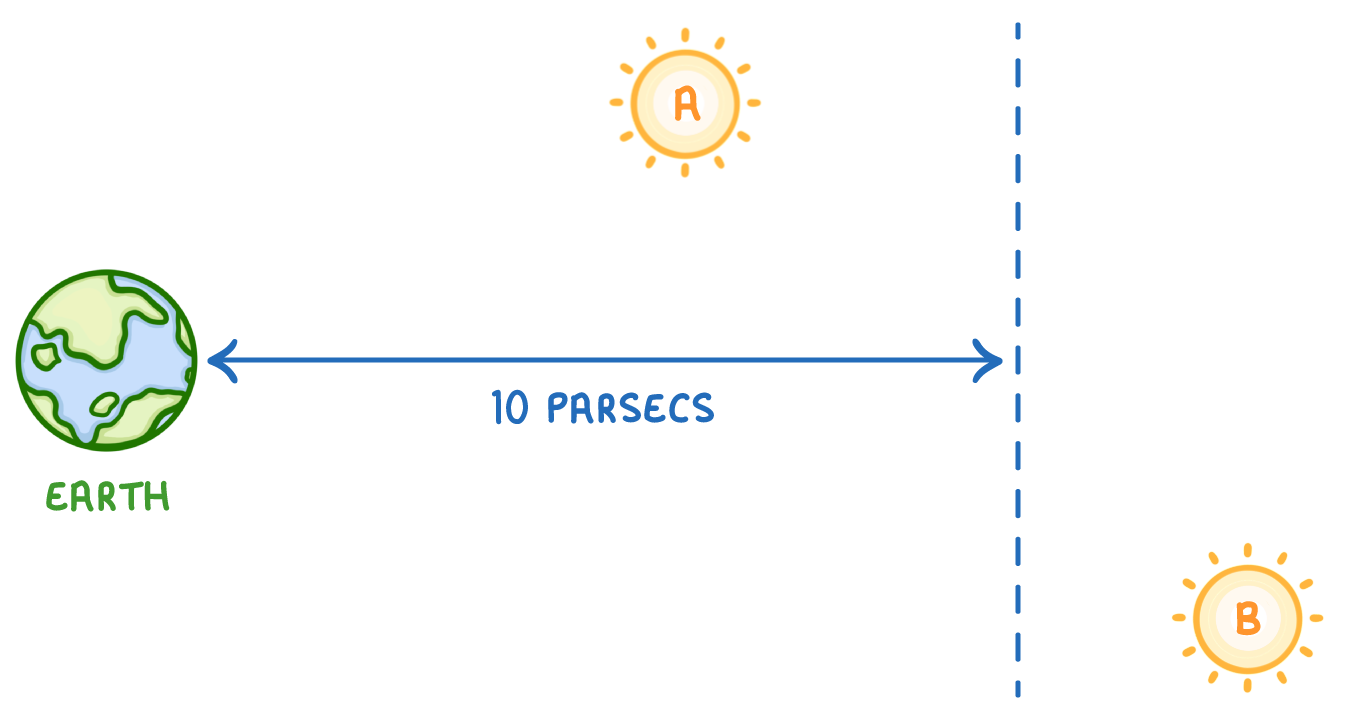
In the example above, star A and star B are identical, but Star A will appear brighter to an observer on Earth because it is closer. In other words, star A will have a lower apparent magnitude (remember that apparent magnitude has the weird scale where lower values mean brighter).
However, because both stars are identical, if they were the same distance from earth (e.g. 10 parsecs), then they would be equally bright. Both stars therefore have the same absolute magnitude.
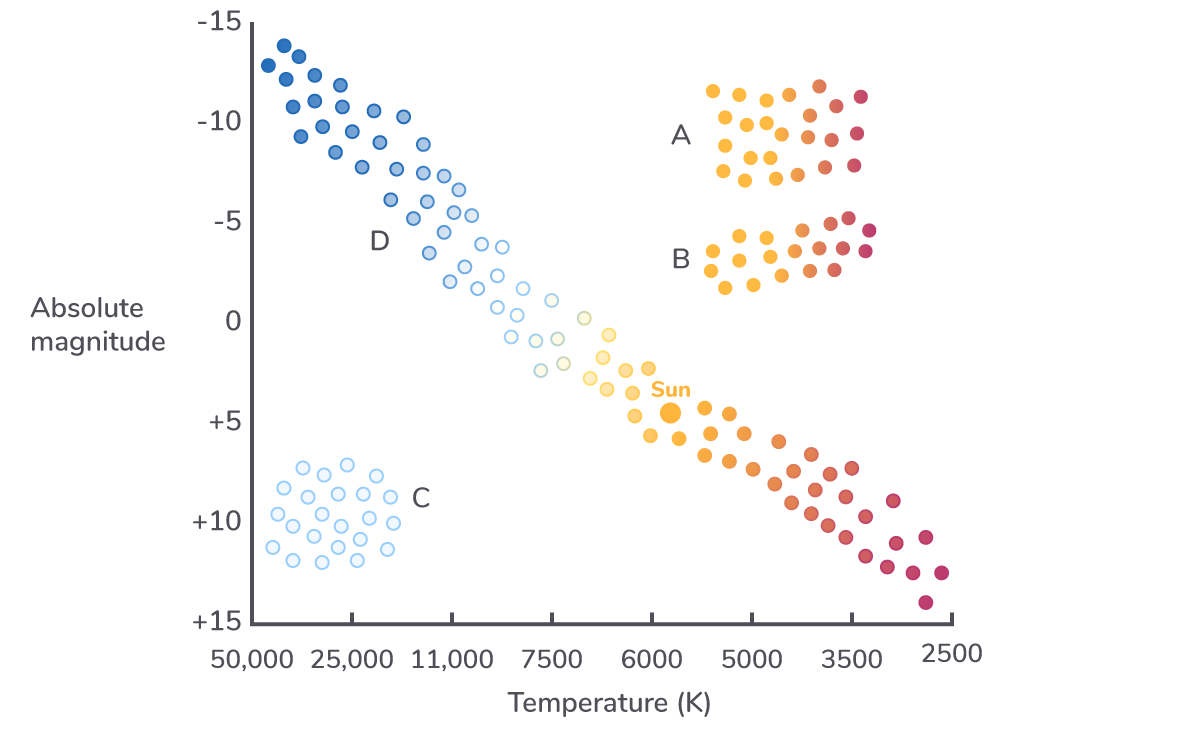
The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram
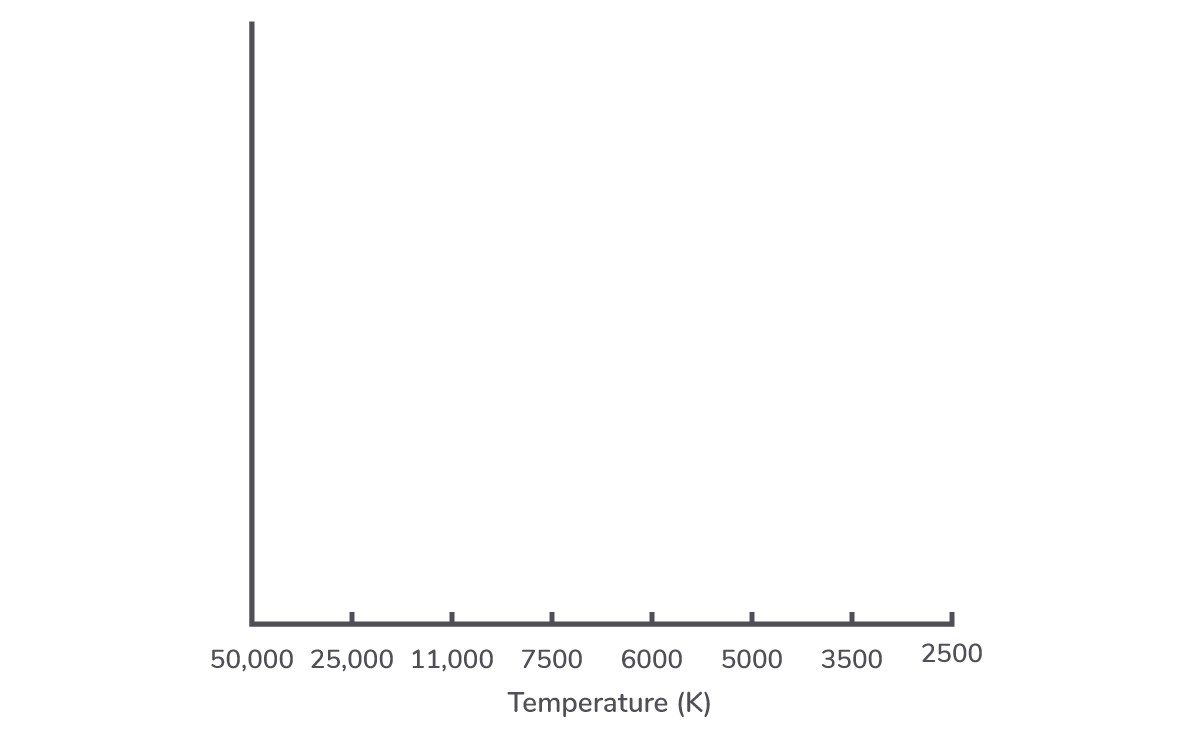
x-axis
The x axis of the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is temperature in Kelvin. (Note that the values decreases as you go along the x-axis).
Hot stars will therefore be on the left and cool stars will be on the right.
Which colour is associated with hot stars?
White
Yellow
Red
Blue
|
What does the apparent magnitude scale measure?
Star temperature
Star brightness from Earth
Star luminosity
Star distance from Earth
|
What is the main difference between absolute magnitude and apparent magnitude?
Absolute magnitude compares star distance from Earth, while apparent magnitude compares star distance from the sun
Absolute magnitude compares star brightness from Earth, while apparent magnitude compares star brightness at a standard distance
Absolute magnitude compares star brightness at a standard distance, while apparent magnitude compares star brightness from Earth
Absolute magnitude compares star temperature, while apparent magnitude compares star color
|
What does the x-axis of the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram represent?
Star luminosity
Star brightness from Earth
Star temperature
Star distance from Earth
|
Where are the hottest stars located on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram?
Right
Bottom
Top
Left
|