Stopping Distances
This lesson covers:
- What factors affect the stopping distance of a moving vehicle
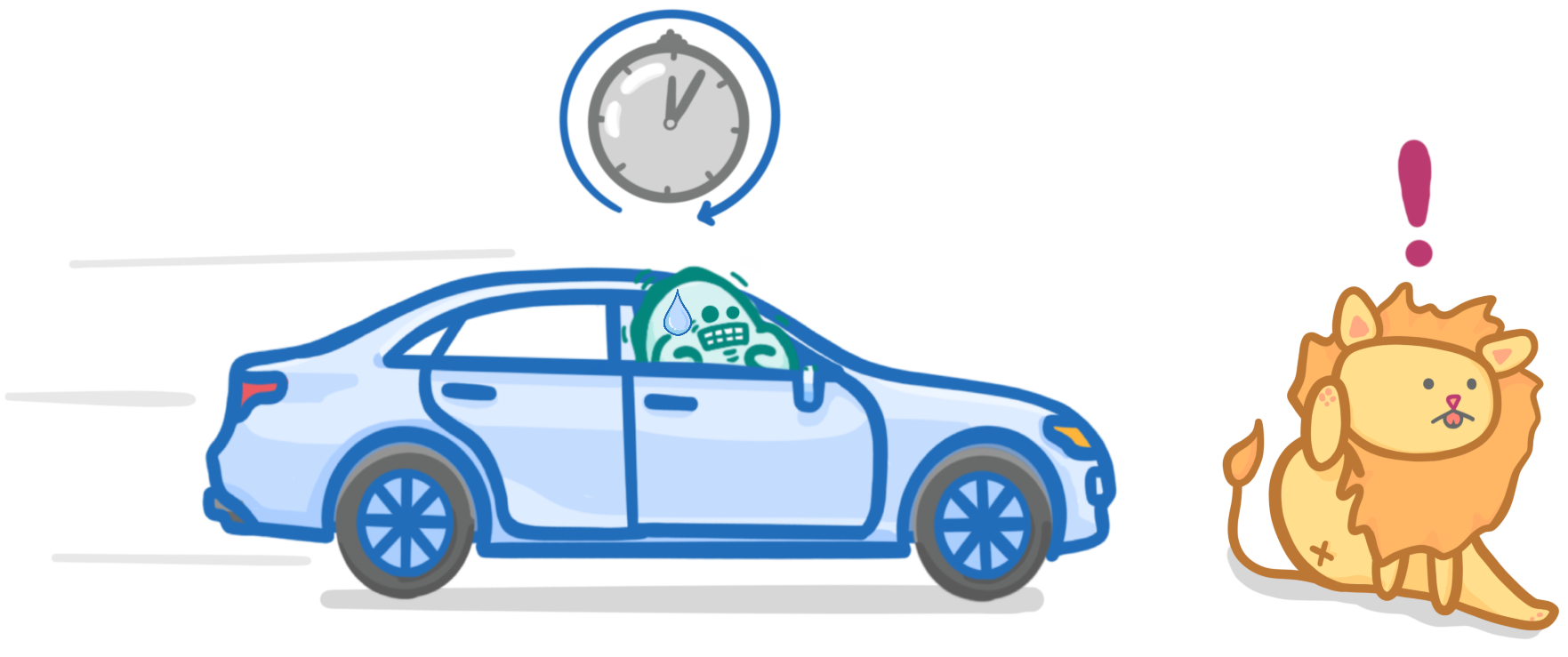
'Stopping distance' is the total distance a car travels from the moment when the driver first notices an obstruction, to when the car stops.
Stopping distance equals:
Thinking distance + braking distance
Vehicle distance + braking distance
Vehicle distance + thinking distance
|
Which of the following will slow a person's reaction time?
(Select all that apply)
Icy road surface
Being distracted
Consuming alcohol
Tiredness
|
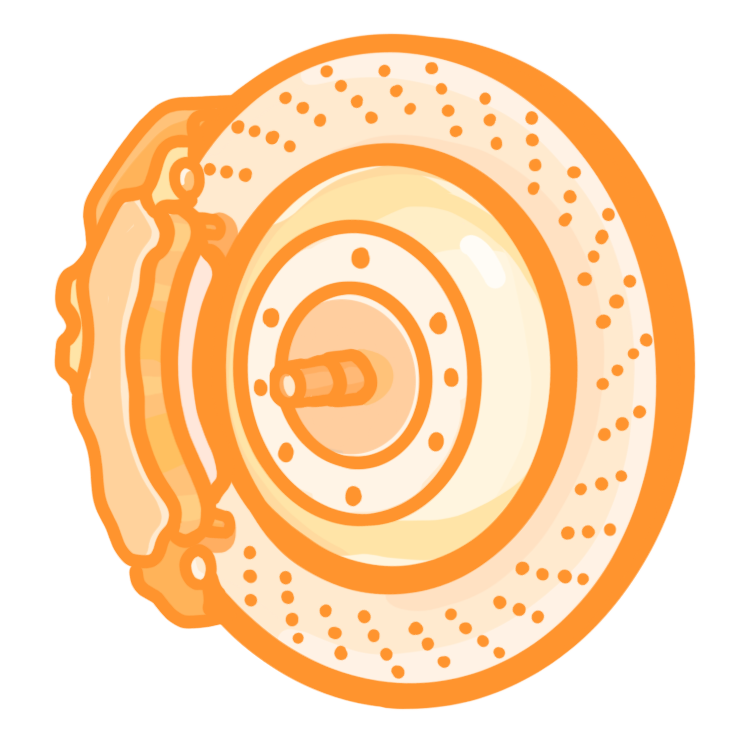
Which of the following will increase the braking distance?
(Select all that apply)
Worn brakes
Worn tyre tread
Being drunk
Ice on the road
|
A vehicle drives twice as fast.
What happens to the breaking distance?
The breaking distance increases by four times
The breaking distance doubles
The breaking distance stays the same
The breaking distance halves
|
Which factor affects both the thinking distance and the braking distance?
Road conditions
Reaction time
Speed of the vehicle
|