Why Radiation is Harmful
This lesson covers:
- The meaning of the terms 'contamination' and 'irradiation'
- Why radiation is harmful to our DNA and cells
- The most and least harmful types of radiation
- Some of the safety precautions required when handling radioactive substances
Irradiation is the process by which objects are __________ radiation.
protected from
exposed to
|
Which of the following are ionising radiation?
(Select all that apply)
Gamma rays
Visible light
Alpha particles
Microwave radiation
|
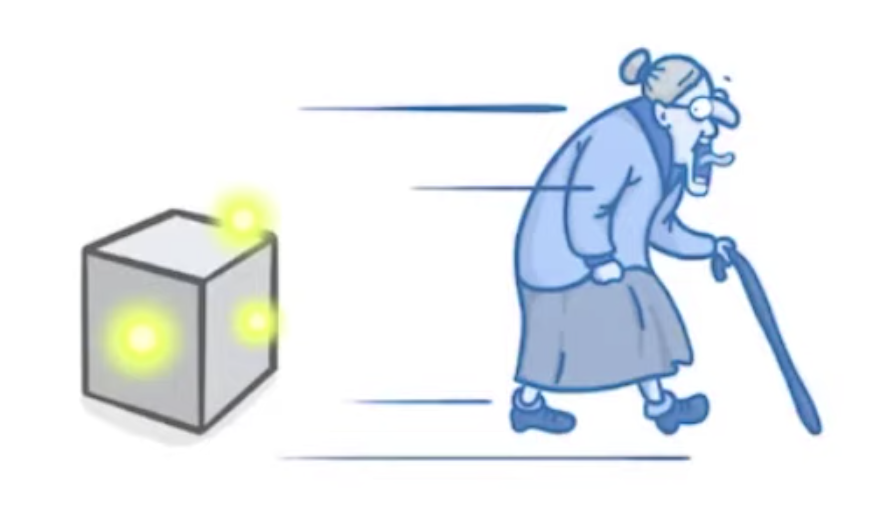
Irradiation / Contamination
is when radioactive particles get onto your body or other objects.
|
Infrared radiation
Beta particles
X-rays
|
Which factors determine how harmful the radiation is?
(Select all that apply)
The type of radiation
Where you're exposed to the radiation
The amount of radiation you receive
The amount of antioxidants in your body
|
What might happen if DNA is exposed to ionising radiation?
(Select all that apply)
The DNA could mutate
The DNA could become radioactive
The DNA could be destroyed
The cell could divide uncontrollably and become cancerous
|
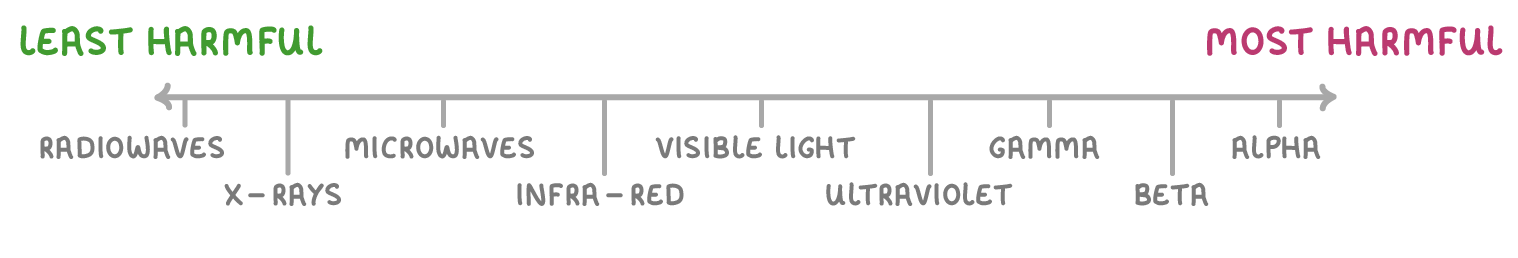
The above diagram shows radiation in order of harm, when the source of radiation is in close contact with your body.
Which radiation is out of place in the diagram?
X-ray radiation
Infra-red radiation
Ultraviolet radiation
Alpha radiation
|
Four radioactive substances are on the table across the room from you. Which is the least harmful and why?
Gamma radiation because it's not very ionising
Alpha radiation because it's not very ionising
Alpha radiation because it can't penetrate very far in air
Beta radiation because it's not very ionising
|
Which radioactive substance is the most harmful inside the body and why?
|

What are the factors that affect the amount of radiation you receive?
(Select all that apply)
Whether you're in good or poor health
How long you're exposed for
How far away from the source you are
How radioactive the substance is
|
What safety precautions can be taken when handling radioactive substances?
(Select all that apply)
Store the radioactive substance in a lead-lined box
Wear overalls
Freeze the radioactive substance first
Use tongs when picking up the radioactive substance
|
True or false? Once you've become irradiated, you become radioactive and can emit radiation to others.
True
False
|