Transformer Calculation
This lesson covers:
- How to use the transformer equations: p}{Vs}=\frac{np}{ns} and p\ Ip=Vs\ Is
increase / decrease
Step-up transformers the potential difference.
Step-down transformers the potential difference.
|
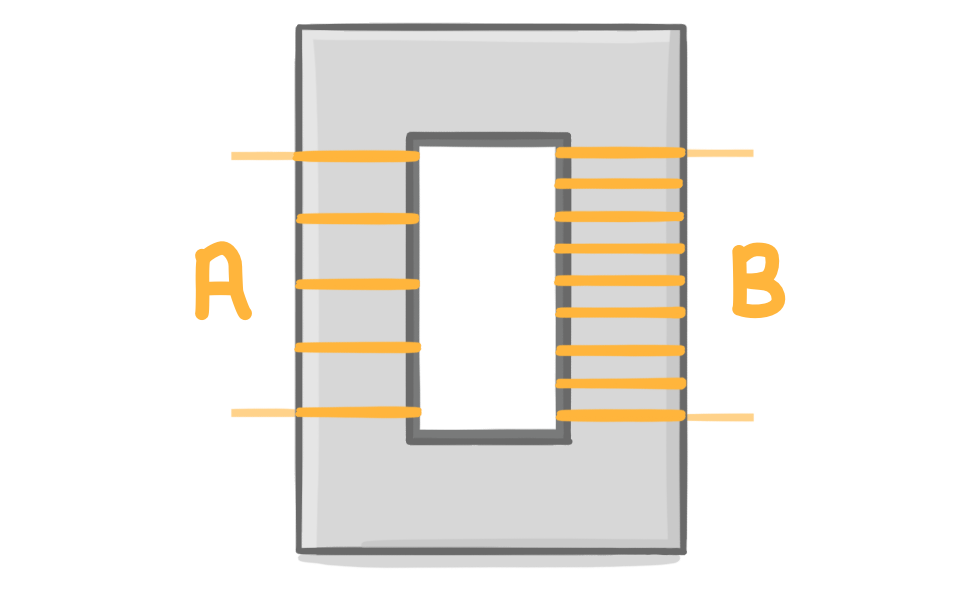
The number of turns on the primary coil A is:
The number of turns on the secondary coil B is:
|
In a transformer, the ratio of the voltage in the primary coil (Vp) and secondary coil (Vs) is equal to the ratio of the turns in the primary coil (np) and secondary coil (ns).
The formula for this is:
p}{Vs}=\frac{np}{ns}
p\ Vs=np\ ns
|
A step-up transformer has 20 turns in its primary coil and 60 turns in its secondary coil.
The primary coil has a potential difference of 50 V.
What is the potential difference in the secondary coil?
V
|
A step-down transformer has 120 turns in its primary coil and 10 turns in its secondary coil.
The secondary coil has a potential difference of 30 V.
What is the potential difference in the primary coil?
V
|
The power in the primary coil is equal to the power in the secondary coil.
Therefore, which formula is correct?
(Remember that P = IV)
p}{Ip}=\frac{Vs}{Is}
p\ Ip=Vs\ Is
|
A step-down transformer has 500 V in the primary coil and 100 V in the secondary coil.
The primary coil has a current of 0.4 A.
What is the current in the secondary coil?
A
|
A step-up transformer has 40 V in the primary coil and 600 V in the secondary coil.
The secondary coil has a current of 24 A.
What is the current in the primary coil?
A
|