AC & DC Current
This lesson covers:
- The difference between 'alternating current' (AC) and 'direct current' (DC)
- How AC and DC differ when shown on current/time and voltage/time graphs
Which type of current periodically reverses its direction?
Direct current
Alternating current
|
When charge always flows around a circuit in the same direction, we call it:
Alternating current
Direct current
|
True or false? Alternating current is caused by an alternating potential difference.
True
False
|
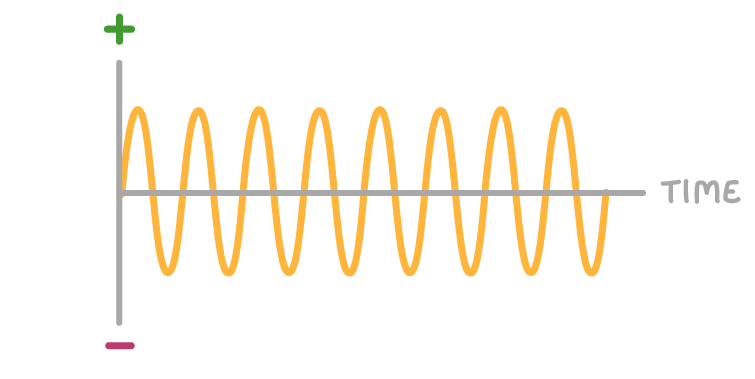
The above graph could be for:
(Select all that apply)
Direct current
Direct voltage
Alternating current
Alternating voltage
|
Direct current is supplied by:
(Select all that apply)
Batteries
Cells
The mains supply
|
All countries use alternating current as their mains supply.
In the UK, the mains supply has a frequency of Hz, and a voltage of V.
|
The role of an oscilloscope is to:
Power circuits
Display how voltage changes with time
Generate alternating current
|

Which type of current would be generated from the supply shown in the diagram above?
Direct current
Alternating current
|