Life cycle of stars
This lesson covers:
- The life cycle of stars
- Details of each stage, including: nebulas, protostars, main sequence stars, red giants, red super giants, white and black dwarfs, neutron stars, and black holes
What is a nebula?
A large cloud of dust and gas
A young star
A star at the end of its life
|

What pulls the gas and dust in a nebula together, to form a protostar?
The electrostatic attraction between particles
Space pressure
The attraction of gravity
|
As a protostar grows in size and attracts more particles from the surrounding nebula, what changes may take place within it?
(Select all that apply)
It becomes more dense
The temperature increases
The protostar dissipates back into a nebula
The star explodes
Nuclear fusion could initiate
|
Once nuclear fusion starts in a protostar, what does it become?
A black hole
A supernova
A main sequence star
A white dwarf
|
inward / outward / sideways
The energy released from nuclear fusion creates an pressure that balances against the pressure from gravity.
|
What stage of a star's life cycle is the sun currently in?
(Only the star at the centre of our solar system is called the 'sun'. All other stars are just stars)
Main sequence star
Nebula
Protostar
Red giant
|

After the main sequence, what could a star become?
A red giant
A green giant
A red super giant
A brown giant
|
It's important that you know which elements nuclear fusion forms at each stage of a stars life cycle.
A sequence star only fuses together hydrogen to make .
Then in red giants or red giants, nuclear fusion can form heavier elements up to iron on the periodic table.
Elements heavier than iron are formed by .
|
For a red giant, what happens next in the star's lifecycle?
It becomes a white dwarf and then a black dwarf
It becomes a black dwarf and then a white dwarf
It becomes a neutron star
It collapses into a black hole
|

For a red super giant, what happens next in the star's lifecycle?
It explodes as a supernova
It becomes a black dwarf
It becomes a white dwarf
|
sky / universe / giant / elements
A red super eventually explodes into a supernova. This can form even heavier than iron. These elements are ejected all across the universe.
|
What two alternative things might happen to a star after a supernova explosion?
Condense into a neutron star
Collapse into a black hole
Become a black dwarf
Become a white dwarf
|
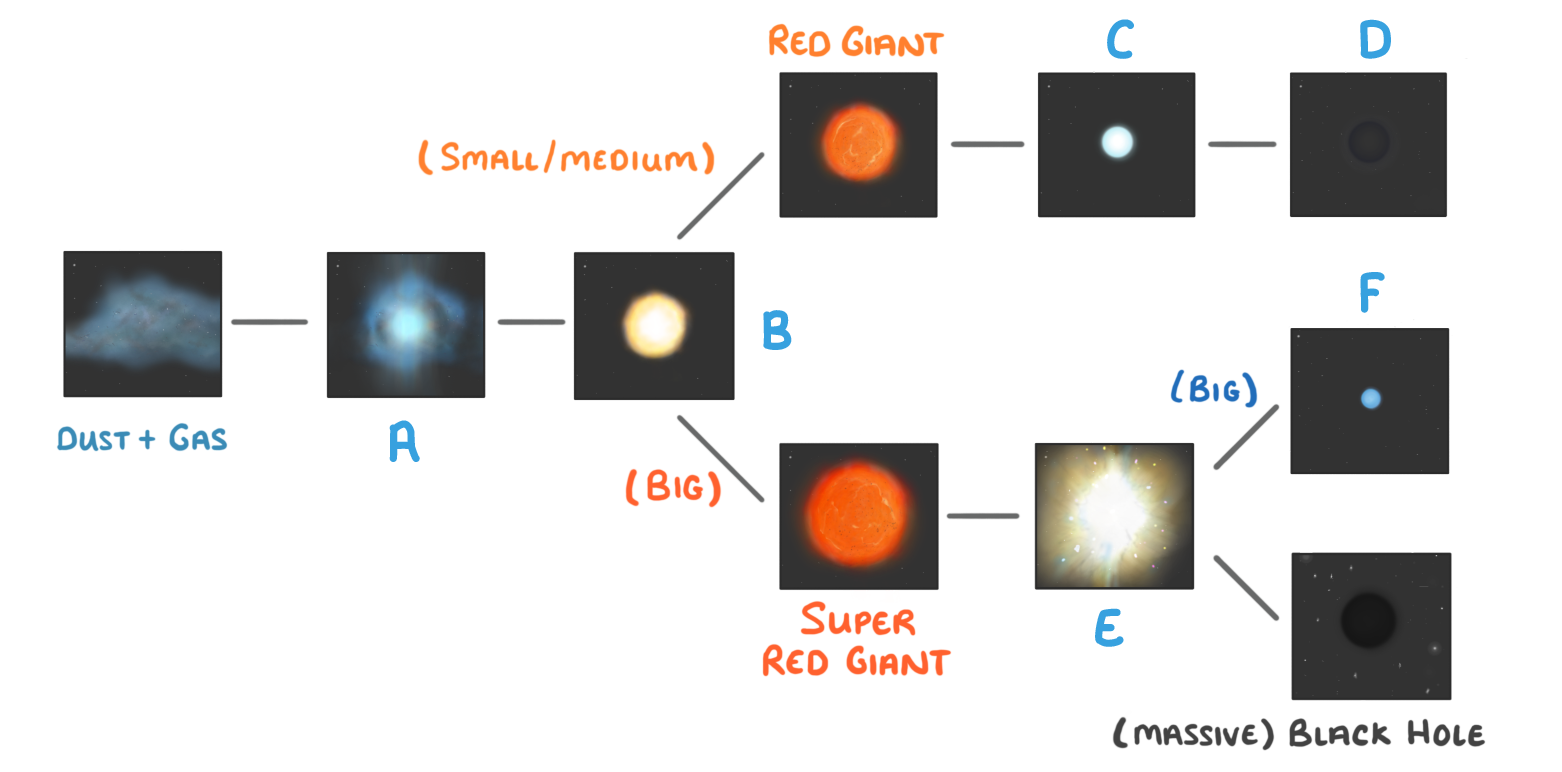
Match the letters A to F on the diagram above with the following labels:
Main sequence star:
Neutron star:
White dwarf:
Protostar:
Supernova:
Black dwarf:
|