Thermal Expansion
This lesson covers:
- Thermal expansion of solids, liquids, and gases
- The uses and drawbacks of thermal expansion
- Examples of thermal expansion in everyday life
Thermal expansion Thermal expansion is a process where objects expand as a result of being heated. 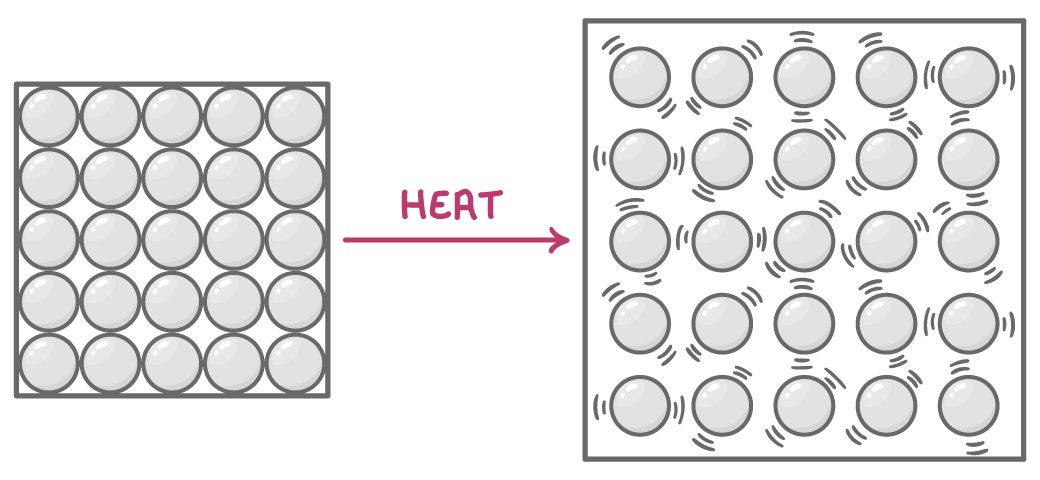 |
How thermal expansion works
|
How thermal expansion varies for solids, liquids, and gases How much a substance expands depends on the intermolecular forces between its molecules.
|
Applications of thermal expansion You need to be able to explain thermal expansion in applications such as riveting, expansion joints, and power lines. |
Riveting Rivets are pieces of metal which are used to tightly fix metal sheets together. An example of rivets is in the assembly of aircraft fuselages. 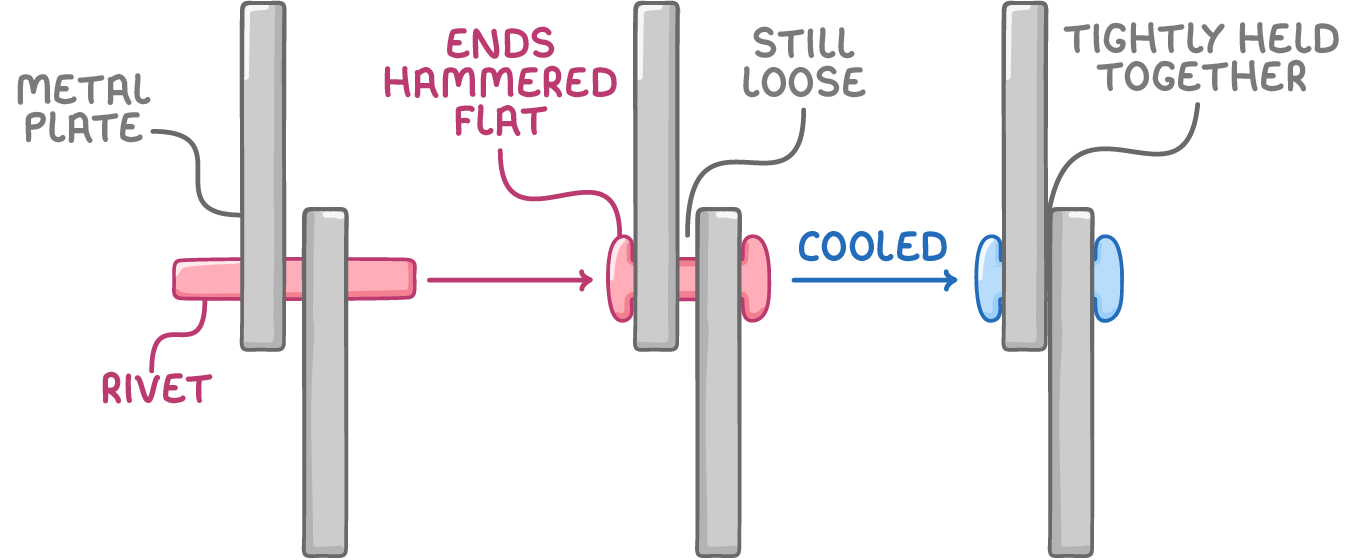
|
Expansion joints Expansion joints are used in civil engineering when the size of the construction materials may vary depending on their temperature. 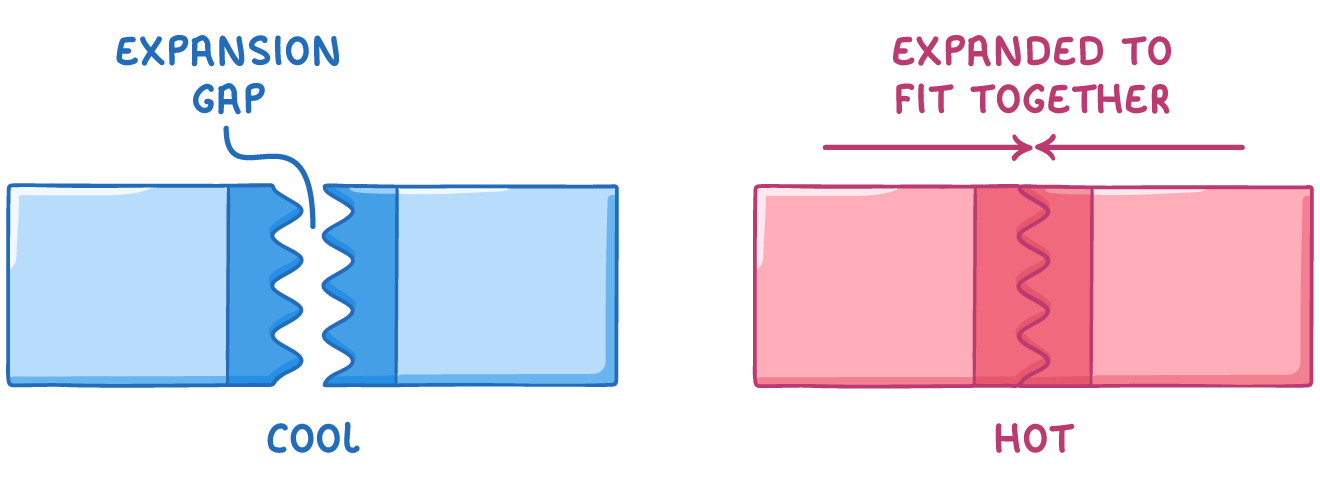
These expansion gaps are essential to avoid permanent damage to the structures. |
Power lines Power lines are essential for power distribution around the country. Overhead power lines are suspended from pylons. 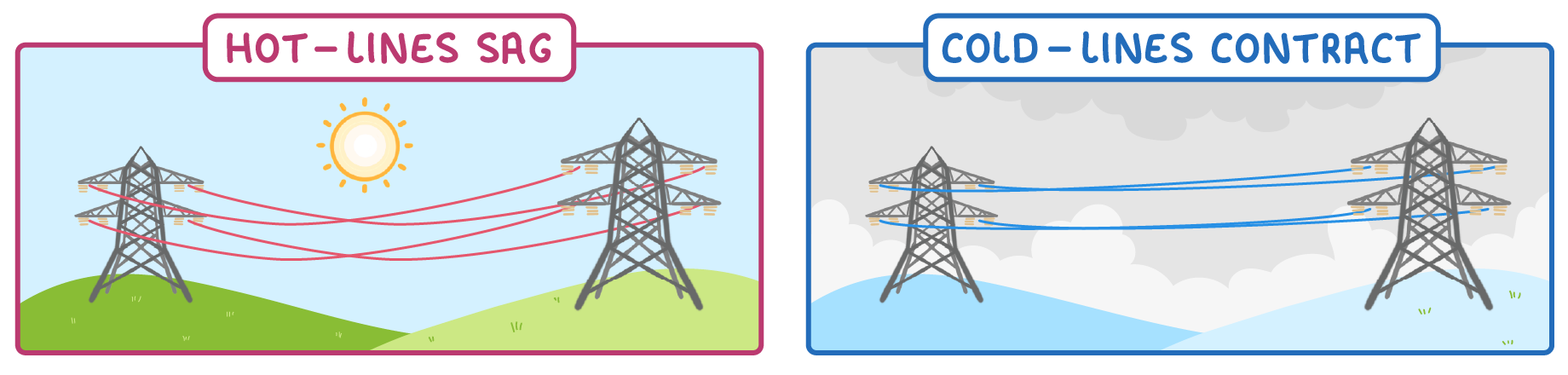
|
Which state of matter expands the most due to thermal expansion?
Solids
Gases
Liquids
|
What is the main purpose of expansion gaps in structures like bridges and buildings?
To allow for thermal expansion and contraction
To provide additional support
To improve aesthetic appearance
|
Why are power lines deliberately built to sag slightly?
To improve electrical conductivity
To reduce the weight of the power lines
To accommodate thermal expansion and contraction
|
Which of the following is an example of thermal expansion in everyday life?
A bridge expanding in cold weather
Power lines becoming longer on hot days
A metal rod contracting when heated
|
Which type of substance experiences the least thermal expansion?
Solids
Gases
Liquids
|