Refractive Index & Snells Law
This lesson covers:
- What 'refractive index' means
- How to find the refractive index of a material
- How to use the Snell's Law equation
Refractive index The refractive index of a material is a measure of the speed of light as it passes through that material, compared to the speed of light as it passes through a vacuum. |
Materials through which light travels more slowly, for example diamond, have a higher refractive index (e.g. diamond has a refractive index of 2.4). |
Materials through which light travels more quickly, for example water, have a lower refractive index (e.g. ice has a refractive index of 1.3. |
The medium with the lowest refractive index is a vacuum, as light travels fastest in a vacuum. A vacuum has a refractive index of 1. |
Will the refractive index of glass be higher or lower than 1?
Higher
Lower
|
Ice has a refractive index of 1.3, while sapphire has a refractive index of 1.8.
Which medium will light travel fastest through, ice or sapphire?
Ice
Sapphire
|
How to find the refractive index of a material
To find the refractive index of a material we can use the equation below, where n is the refractive index, c is the speed of light in a vacuum, and v is the speed of light in that material.
it can also be written as:
The formula for the refractive index is:
|
Refractive index - worked example:
'Light travels at 3 x 108 m/s in a vacuum and 1.24 x 108 m/s in diamond.
Calculate the refractive index of diamond.'
The refractive index of water is 1.33. The speed of light in a vacuum is 3.00 x 108m/s.
What is the speed of light in water?
3.14 x 108 m/s
2.26 x 108 m/s
1.56 x 108 m/s
2.58 x 108 m/s
|
The speed of light in Perspex is 1.99 x 108 m/s, while the speed of light in a vacuum is 3.00 x 108 m/s.
What is the refractive index of Perspex? Give your answer to 2 d.p.
|
Snell's law 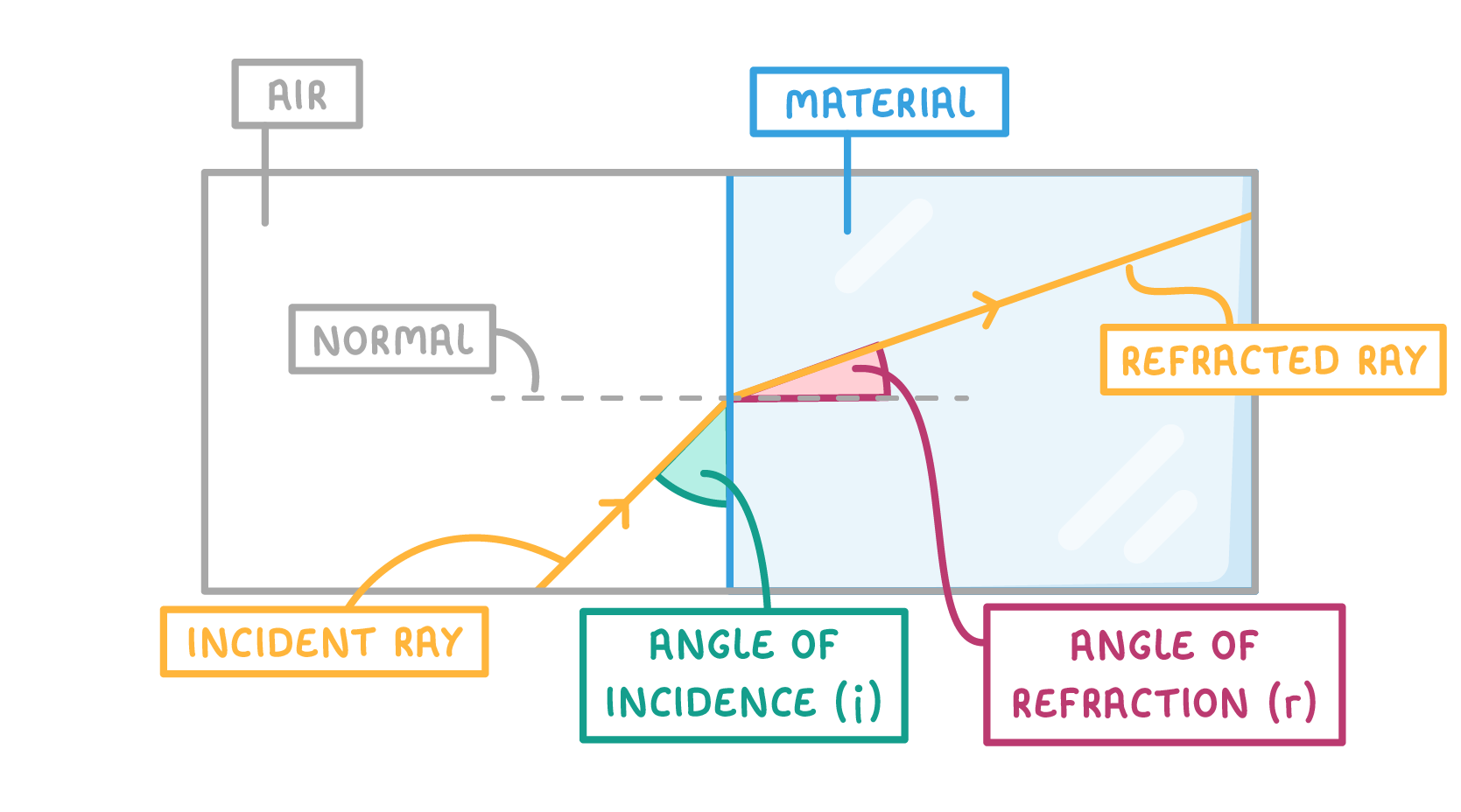 Snell's law is an equation that links the refractive index (n), the angle of incidence (i), and angle of refraction (r). The formula for Snell's law is: n=sin(r)sin(i) |
Snell's law - worked example
A ray of light travels from air into glass.
The angle of incidence is 28°, and the angle of refraction is 18°.
Calculate the refractive index of the glass.
A ray of light enters a beaker of acetone with an angle of incidence of 35°. The ray is refracted with an angle of refraction of 25°.
What is the refractive index of acetone? Give your answer to 2 d.p.
|
A ray of light enters a pane of glass with an angle of incidence of 40°. The refractive index of the glass is 1.5.
What will the angle of refraction be? Give your answer to the nearest degree.
°
|
Snell's Law is:
|