Velocity-Time Graphs
This lesson covers:
- How to read velocity / time graphs
On a velocity / time graph, the velocity is on the -axis, and the time is on the -axis.
|
A flat line on the velocity / time graph tells us the object is moving at constant .
|
The gradient of a velocity / time graph tells us:
The distance travelled by the object
The acceleration or deceleration of the object
The amount of time elapsed
The velocity of the object
|

The above velocity / time graph shows an object which is:
Decelerating
Stationary
Accelerating
Travelling at a constant velocity
|
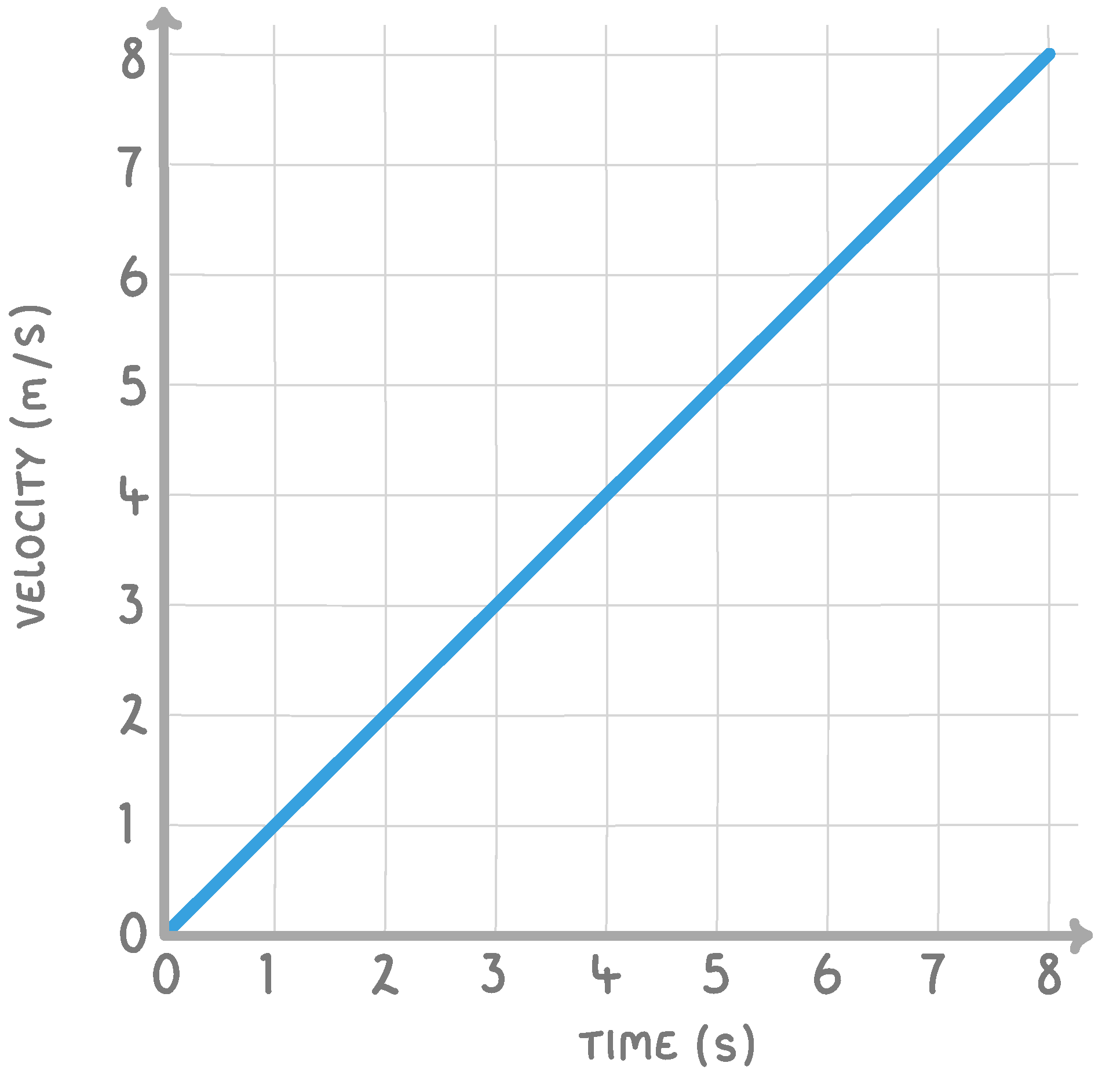
The above velocity / time graph shows an object which is:
Decelerating
Travelling at a constant velocity
Stationary
Accelerating
|
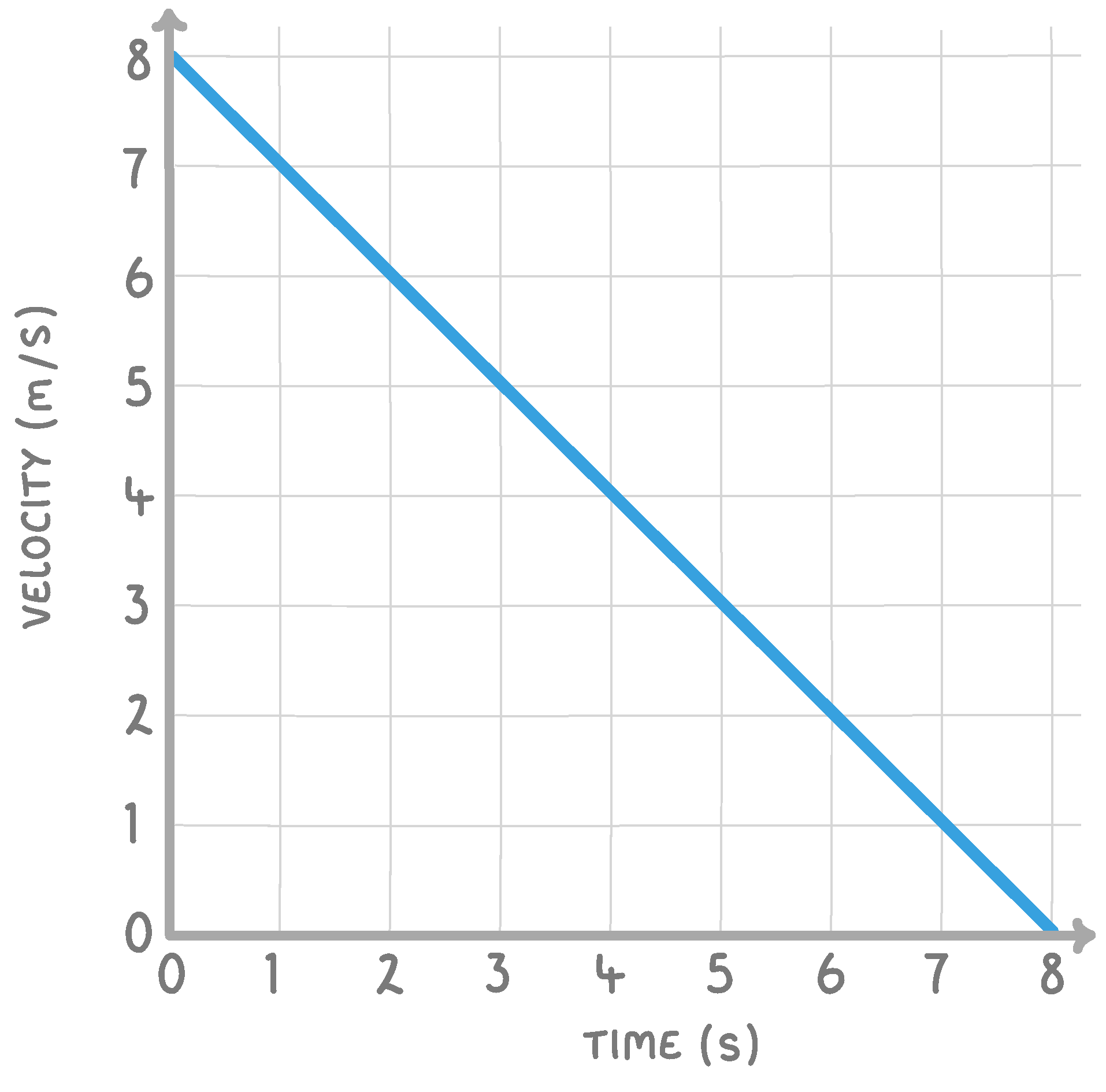
The above velocity / time graph shows an object which is:
Accelerating
Stationary
Travelling at a constant velocity
Decelerating
|
On a velocity / time graph, the distance travelled is shown by:
The gradient of the curve
The height of the curve
The area above the curve
The area under the curve
|
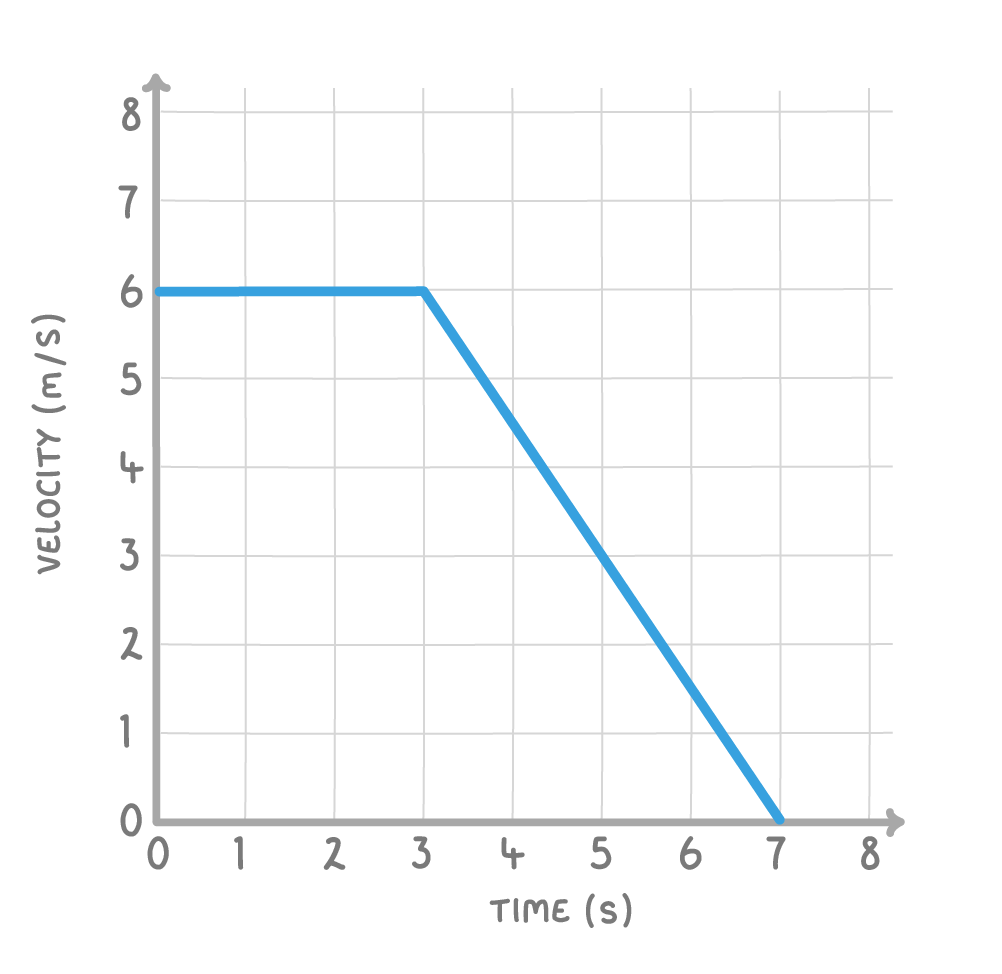
The above velocity / time graph shows a runner travelling at a constant speed, and then slowing to a stop.
Calculate the distance travelled by the runner in the 7 s shown.
m
|