Center Of Gravity
This lesson covers:
- What the 'centre of gravity' is
- How to find the centre of gravity for an irregularly shaped object
- How the position of the centre of gravity impacts the stability of an object
Centre of gravity

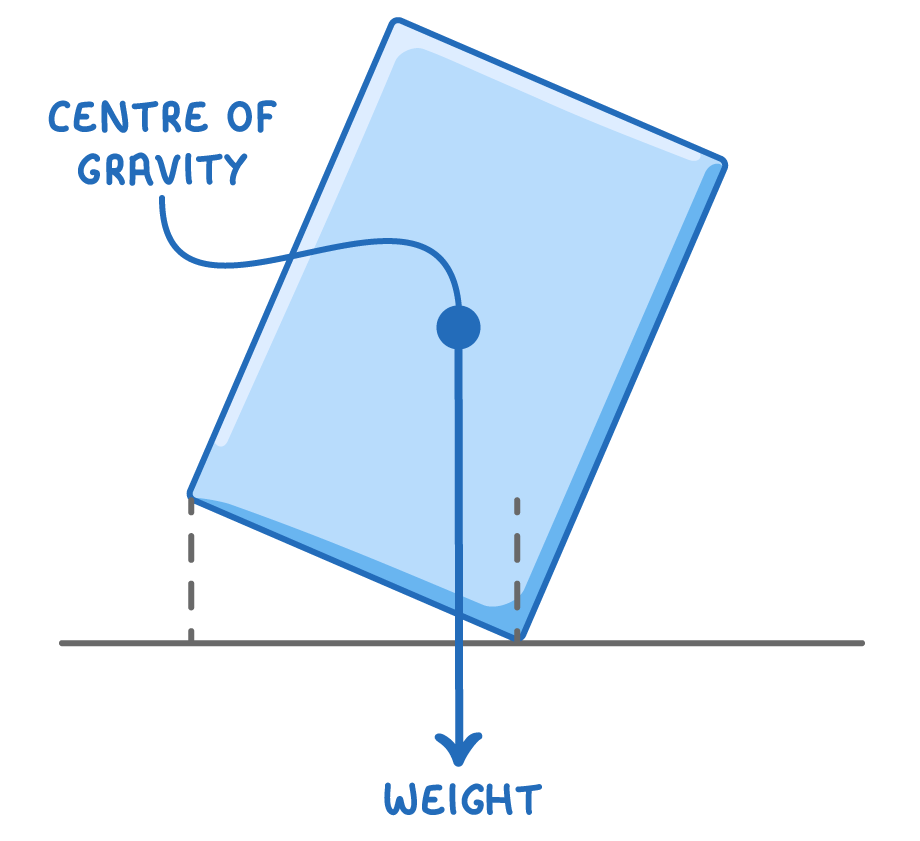
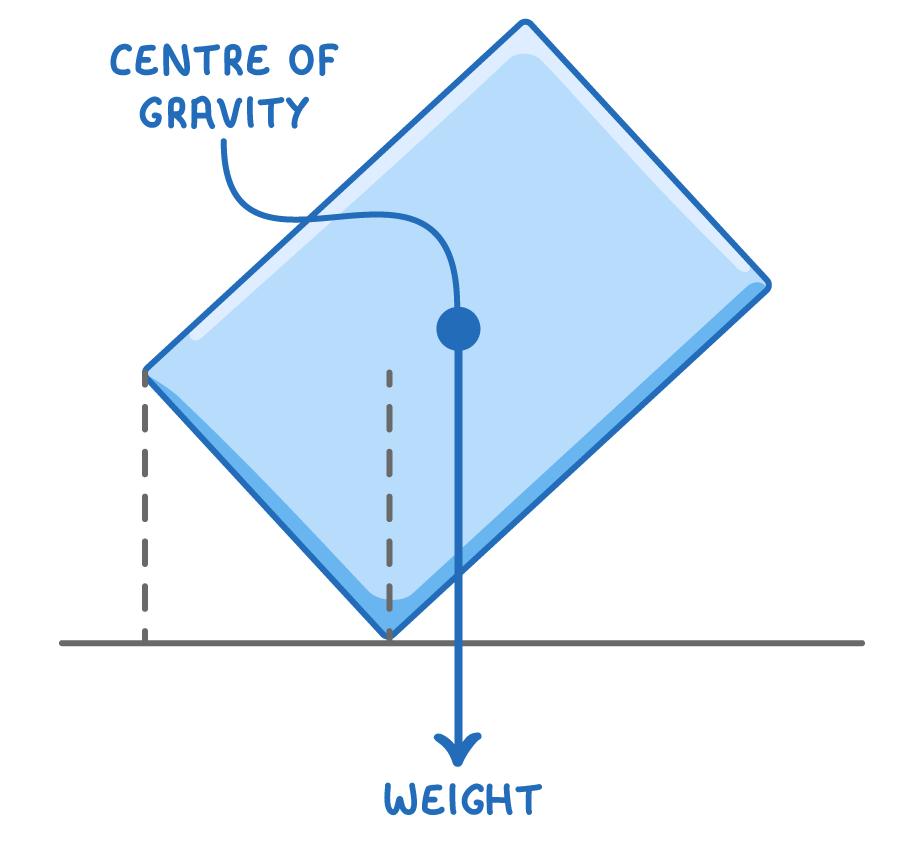
The centre of gravity of an object is is the location where an object's weight appears to act.
For uniform, regular shapes, like a square, this will be in the centre.
For irregular shaped objects or those with uneven densities, it will be off centre.
Experiment: Finding the centre of gravity
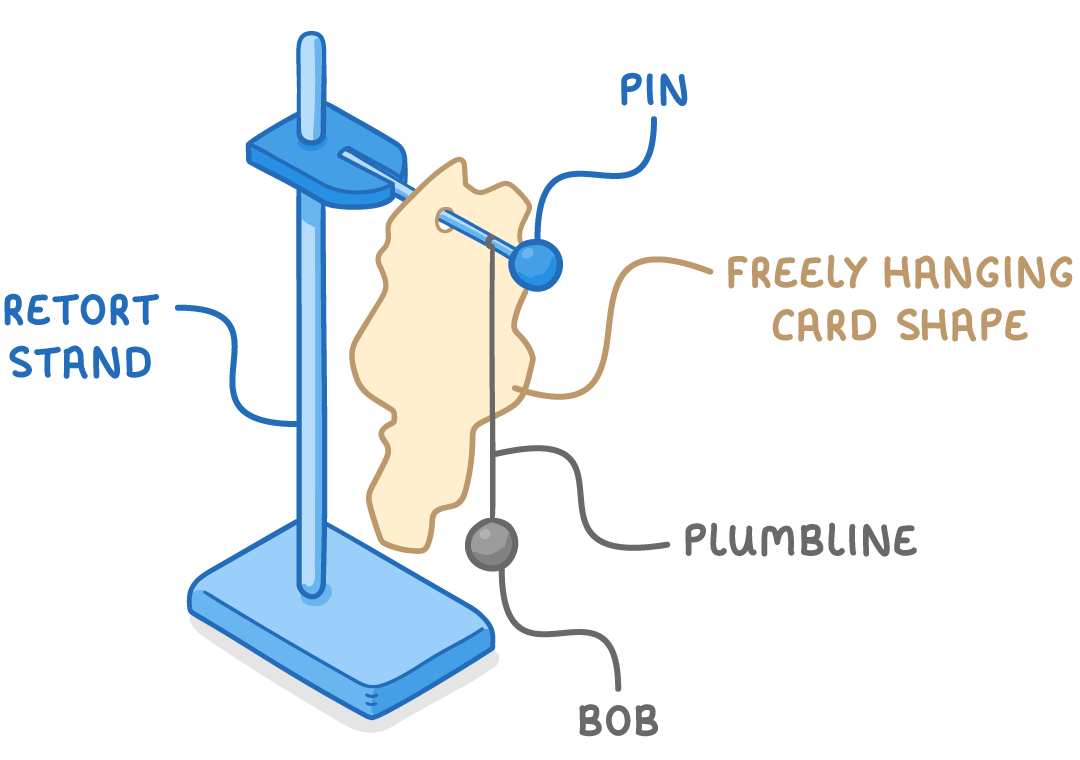
Method:
- Suspend the irregularly shaped object from a clamp stand.
- Attach a plumb line to the clamp stand.
- Mark the plumb line on the object using a pencil.
- Remove the object and suspend from a different point. Repeat steps 2 and 3.
- Repeat step 4 until a minimum of three lines have been drawn.
- The centre of gravity is located where all lines cross.
How centre of gravity affects stability
An object's stability depends on its centre of gravity. By considering where the centre of gravity is located and how the weight acts on the object, we can determine if the object will be stable or unstable when tilted (i.e. whether or not it will fall over).
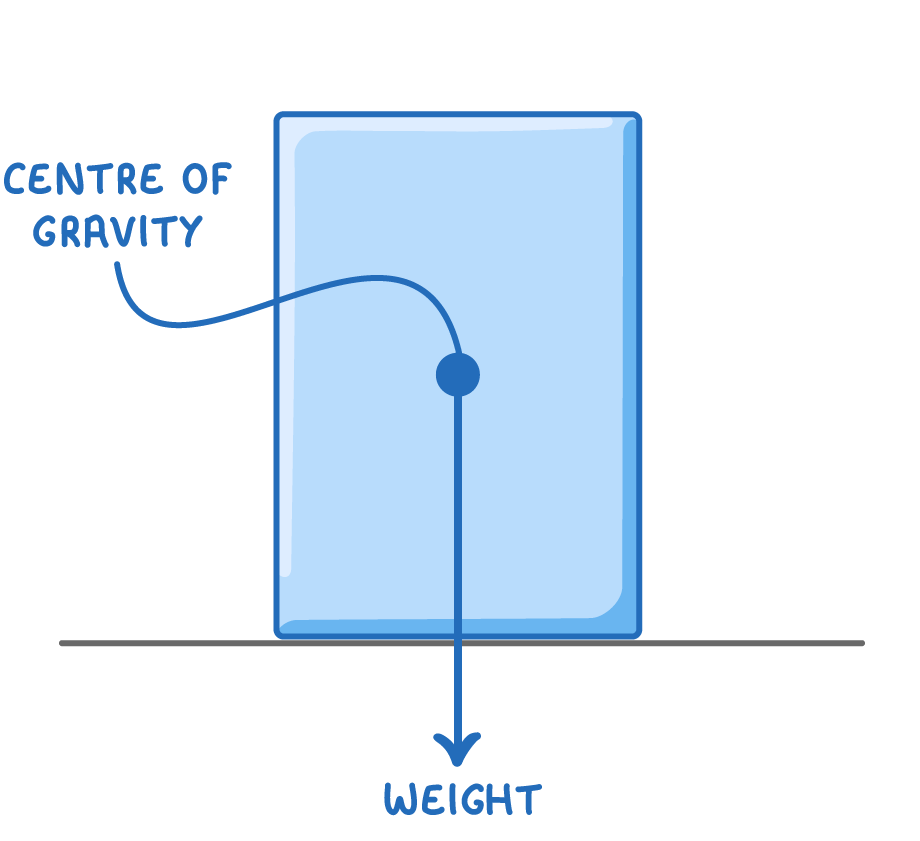
An objects weight always acts vertically downwards from its centre of gravity.
If the weight acts within the base of an object, it is stable.
Objects which have a wide base and a low centre of gravity are the most stable.
For which type of objects will the center of gravity be off center?
Objects that are stable
Objects with a wide base and low centre of gravity
Uniform, regular shapes
Objects with uneven densities
|
What happens to the weight of an object when it is tilted?
The weight becomes lighter
The weight moves towards the pivot point
The weight increases
The weight remains in the same position
|
What happens to an object when its weight no longer acts within the base?
The object becomes lighter
The object topples over
The object becomes more dense
The object becomes more stable
|
What is meant by the centre of gravity?
A measure of how stable an object is
The point where the weight can be assumed to act from
The point where all the mass is
The centre of the object
|
Which objects are most stable?
Objects with an even density
Objects with a wide base and a low centre of gravity
Objects with a high centre of gravity
Objects with a narrow base and a high centre of gravity
|