Relative motion
This lesson covers:
- What relative motion is
- How to calculate relative motion for two objects moving towards each other
- How to calculate relative motion for two objects moving in the same direction
What is relative motion?
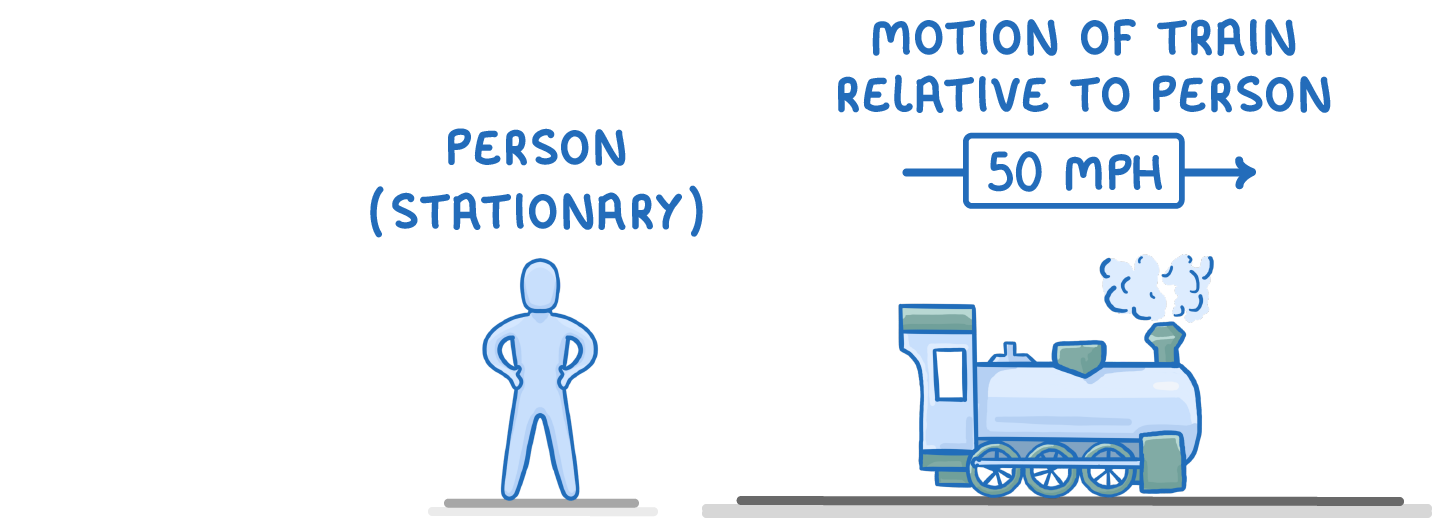
Relative motion refers to the motion of an object from the perspective or frame of reference of another moving object.
For example, if you are traveling on a train moving at 50 mph, your motion relative to a stationary person on the platform is 50 mph.
Calculating relative motion of approaching objects
If two objects are moving in opposite directions along the same line, you can calculate their relative motion by adding their speeds.

For example, if Train A is travelling at 40 mph and Train B is travelling towards it at 25 mph:
- From Train A's perspective, Train B is approaching at 40 + 25 = 65 mph.
- So the speed of Train B relative to Train A is 65 mph.
The objects are getting closer faster than if one was stationary because both are in motion towards each other.
Calculating relative motion of objects moving in the same direction
If two objects are moving in the same direction along the same line, you can calculate their relative motion by subtracting the speed of one from the other.

For example, if Train B is moving at 20 km/h and Train A approaches it from behind at 30 mph:
- From Train A’s perspective, it is gaining on Train B at a relative speed of 30 - 20 = 10 mph.
- So the speed of Train B relative to Train A is 10 mph.
The trains are getting closer together slower than if one was stationary, because both are in motion in the same direction.