Forces and elasticity
This lesson covers:
- How forces can deform objects
- What work and energy transfer involve
- Hooke's Law and springs
- Equilibrium of forces
Work and energy transfer during deformation
Deforming an object requires energy to be transferred into it and work to be done on it.
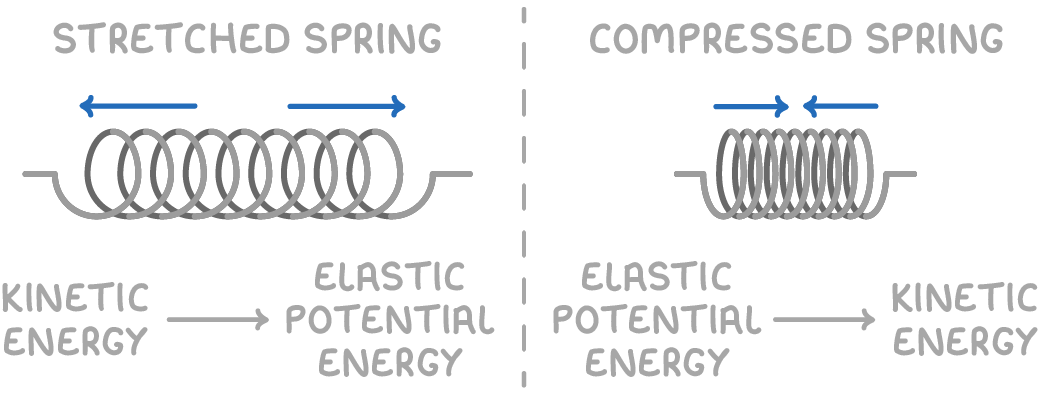
- For example, stretching a spring transfers energy from you to the spring's elastic potential energy stores.
- When the spring rebounds, energy transfers back into kinetic energy.
Hooke's Law - force and extension
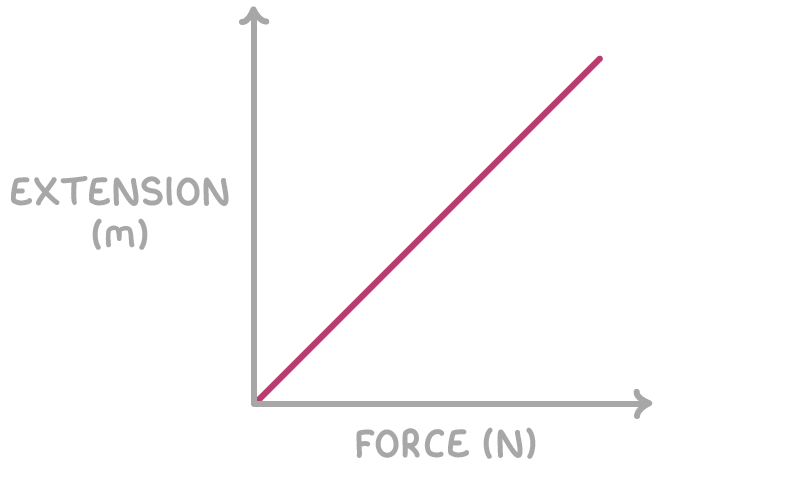
Hooke's Law applies to springs. It states:
The extension of a spring is directly proportional to the force applied to it.
The relationship can be described by:
Force (N) = spring constant ×extension (m)
F = k ×e
This linear relationship only applies up to a certain maximum force.
Equilibrium occurs when forces are balanced
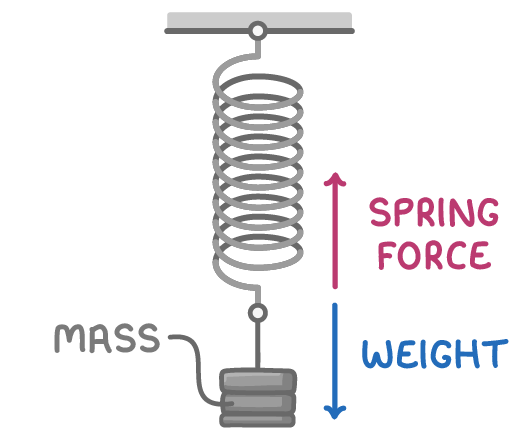
- Equilibrium means balanced, opposing forces.
- When a mass hangs from a spring, the downward weight force equals the upward spring force.
- The forces are balanced, so the spring remains stationary.