Energy resources
This lesson covers:
- The Sun as the source of energy resources
- Key energy transfer chains that produce energy resources
- Stores of the Sun’s energy
The Sun provides energy that is transferred and stored
- The Sun radiates an enormous amount of energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation, especially visible light.
- This energy from the Sun is transferred through various processes and stored in different forms.
- Humans can make use of the energy transfers and stores as energy resources.
Energy transfer chains
There are several key energy transfer chains that start with the Sun's energy and end with usable energy resources.
Energy transfer to fossil fuels
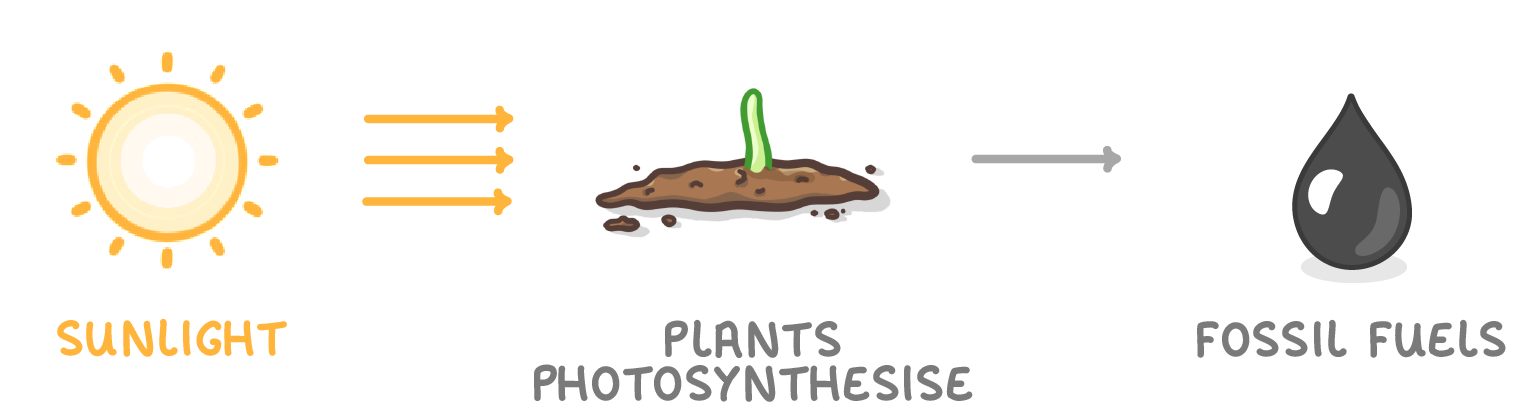
1. Sun → Photosynthesis → Fossil fuels
- Sunlight enables plants to photosynthesise.
- Over millions of years, dead plant matter became coal, oil, and natural gas.
Energy transfer to biomass
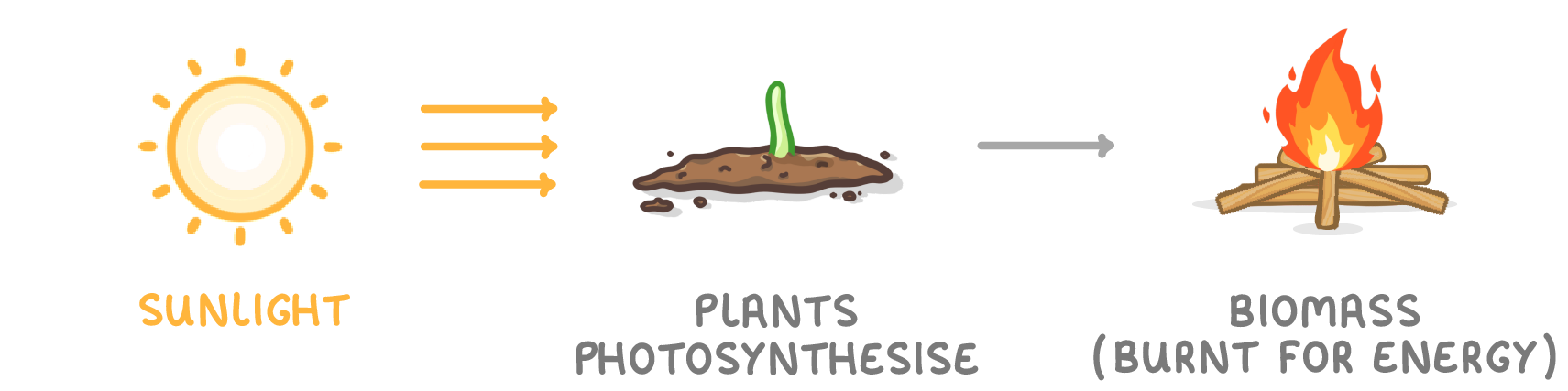
2. Sun → Photosynthesis → Biomass
- Sunlight enables plants to photosynthesise.
- Trees and crops can be burned directly for energy.
Energy transfer to wind
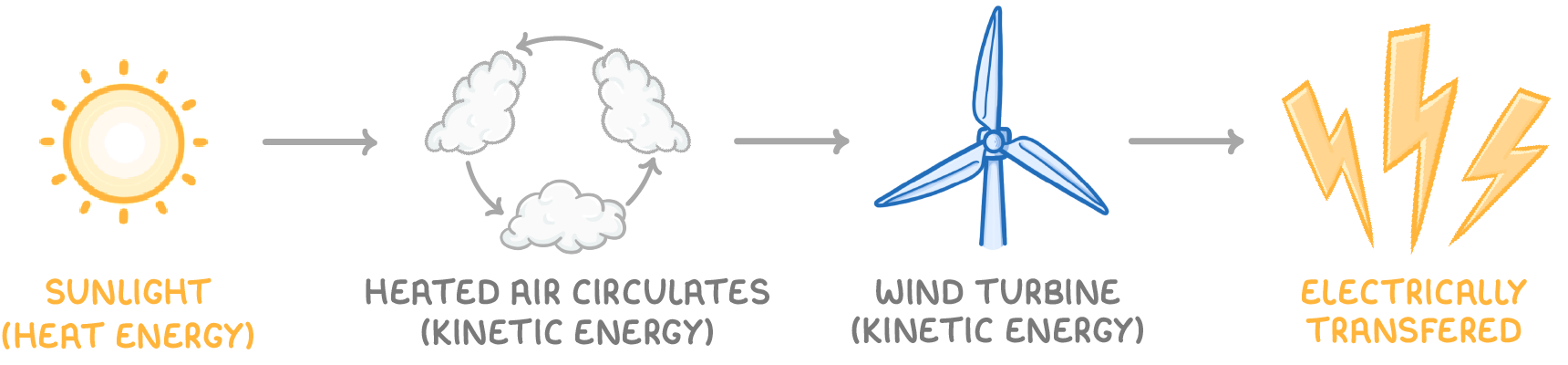
3. Sun → Atmospheric heating → Wind energy
- Sun heats air which circulates to cause winds.
- Wind turbines convert kinetic wind energy into kinetic energy within the turbine.
- The turbine then transfers energy electrically to the National Grid.
Energy transfer to waves
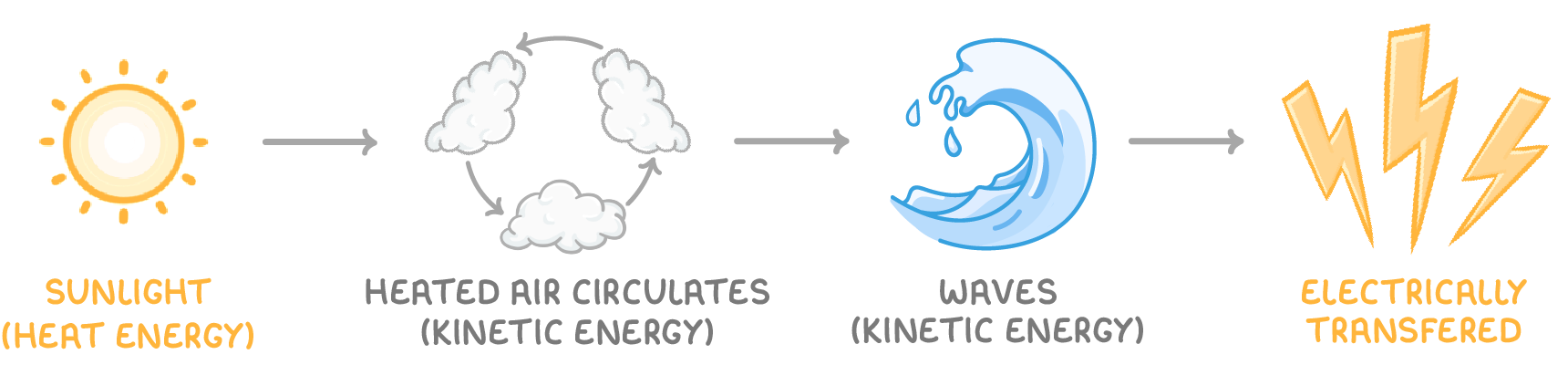
4. Sun → Atmospheric heating → Wave energy
- Sunlight heats the air, causing it to circulate and generate winds.
- Winds cause waves which contain kinetic energy.
Energy transfer to electricity
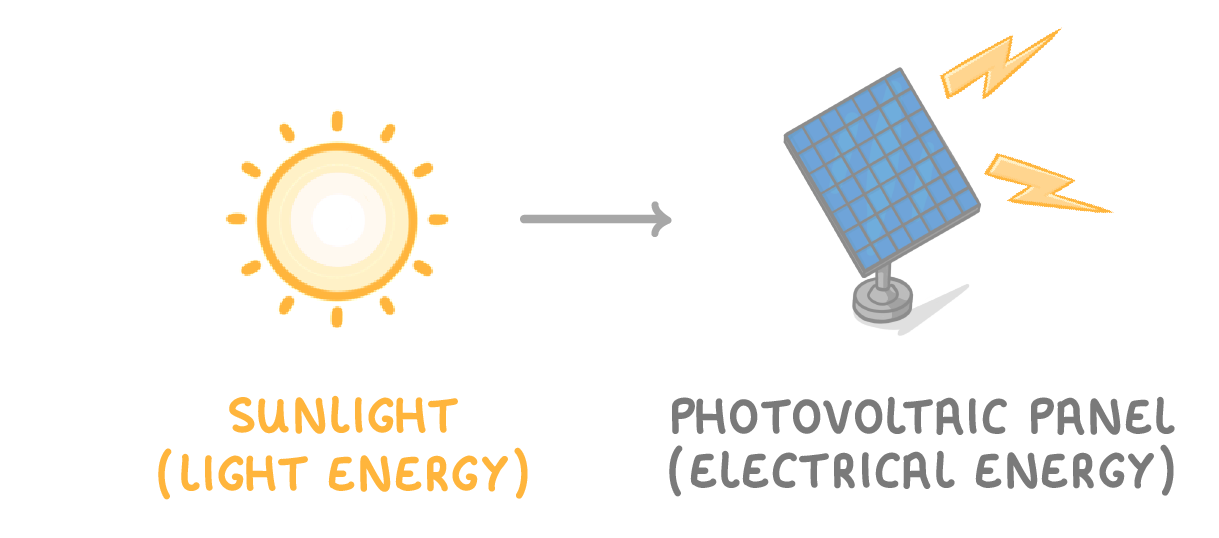
5. Sun → Solar cells
- Sunlight directly strikes solar photovoltaic panels.
- The solar panels convert sunlight into electricity, allowing energy to be transferred electrically.
Energy transfer to food
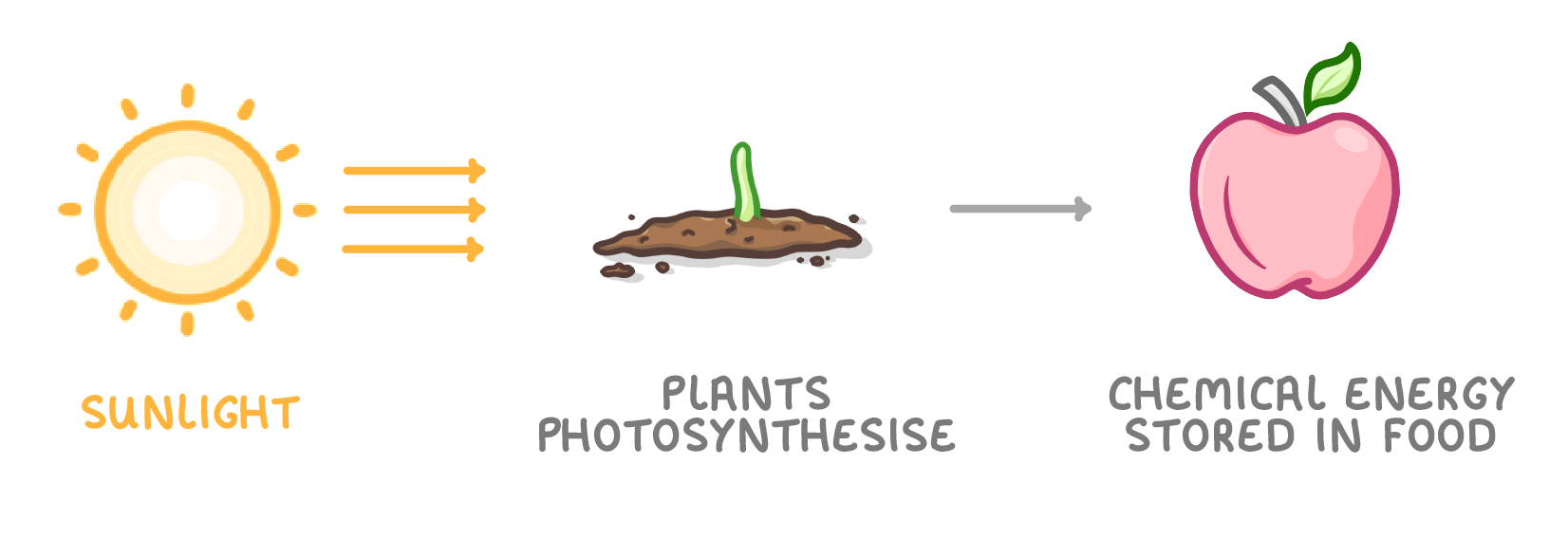
6. Sun → Photosynthesis → Food
- Sunlight enables plants to photosynthesise.
- The chemical energy is stored in food that we eat.
Renewable vs non-renewable resources
Energy resources can be categorised as renewable or non-renewable.
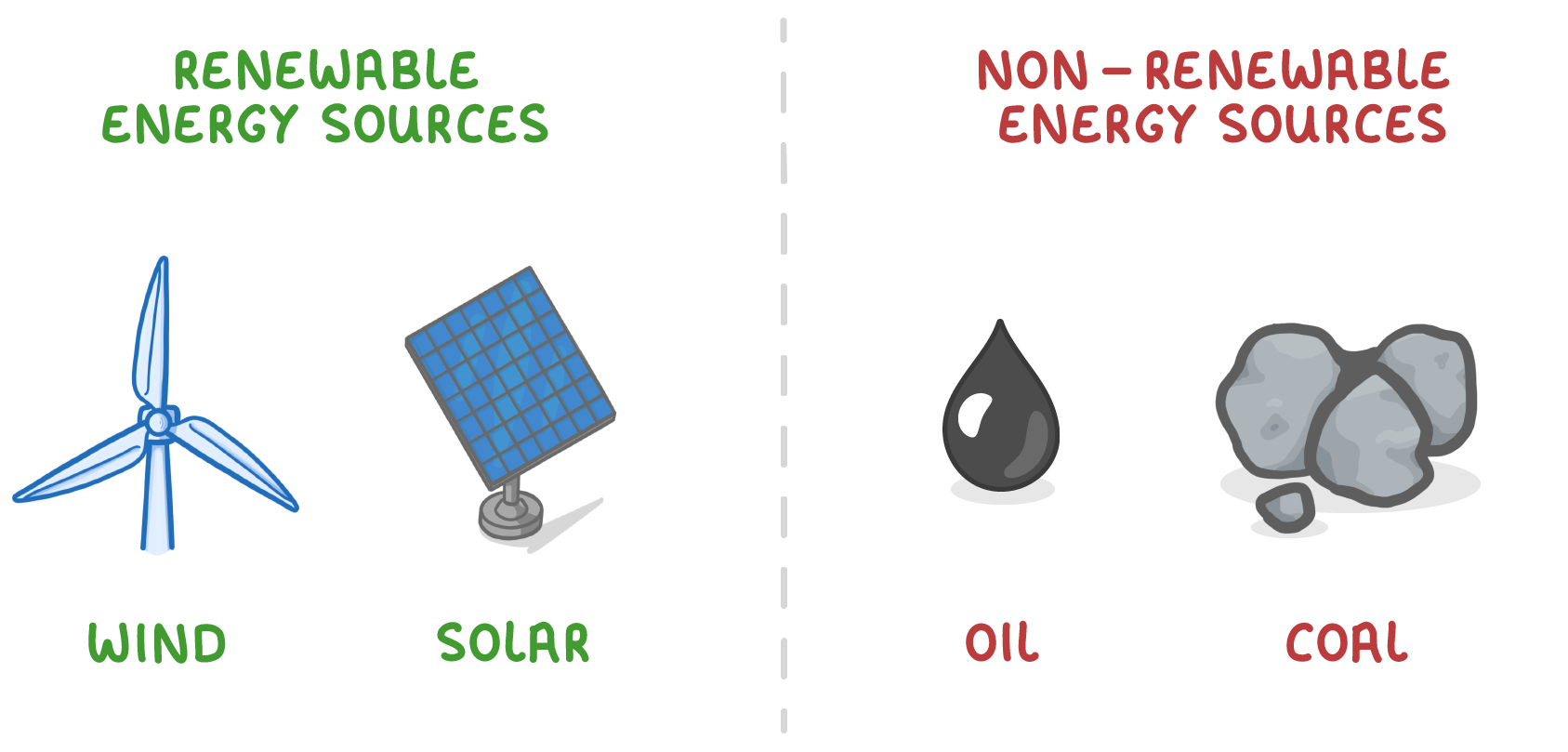
- Renewable energy resources - Will not run out. Examples include: biomass, wind, wave, and solar.
- Non-renewable energy resources - Have finite supplies and will eventually run out. Examples include: fossil fuels like oil, and coal.
Using renewable resources helps sustain energy supplies long-term without depleting reserves.