Forces and movement
This lesson covers:
- What forces are and how they interact with objects
- Key effects that forces can have
- Balanced and unbalanced forces
What are forces?
Forces are pushes or pulls between two interacting objects.
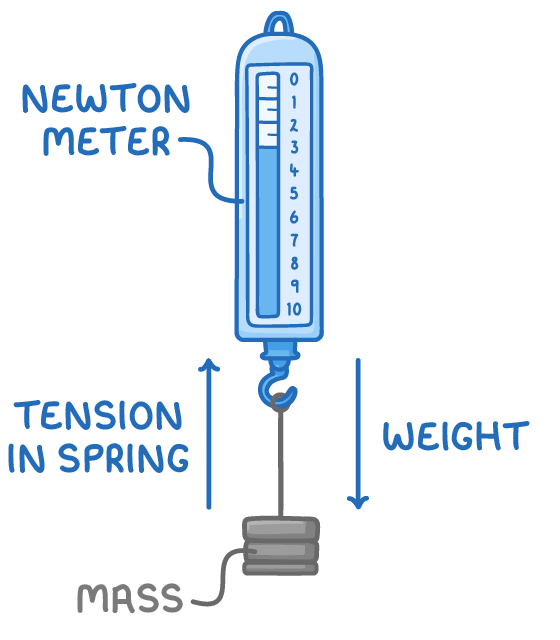
Some key points about forces:
- They cannot be seen directly, only their effects
- Measured in units called newtons (N)
- Usually act in pairs in opposite directions
- Act in a specific direction
- Can be measured using a newton meter
- Forces do not require objects to touch - magnetism, gravity, and static electricity are examples of non-contact forces.
The five effects of forces
Applying a force to an object can cause five different outcomes:
- Speed up or start moving
- Slow down or stop
- Change direction
- Turn or rotate
- Change shape
To make an object move from rest, the applied force must overcome resisting forces like friction.
Balanced forces
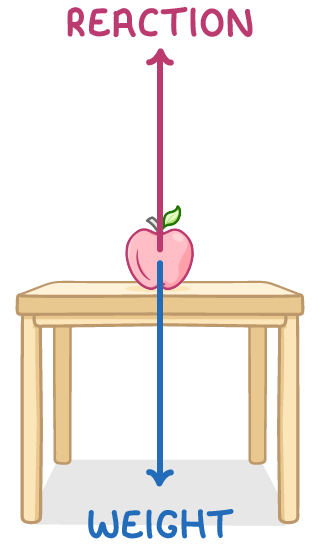
- Balanced forces cause no acceleration.
- For example, a book on a table has balanced downward gravitational force and upward reaction force from the table.
Unbalanced forces
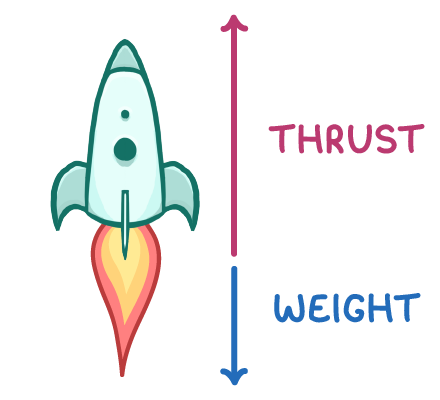
- Unbalanced forces change speed and/or direction of motion.
- For example, a rocket experiences unbalanced forces upwards from thrust and downwards from gravity, causing vertical acceleration.