Pressure
This lesson covers:
- What pressure is and how it is calculated
- Atmospheric pressure
- Pressure in liquids
What is pressure?
Pressure is defined as the force applied over a certain area.
Calculating pressure

Pressure can be calculated using the formula:
Pressure = AreaForce
The formula triangle shows the relationship between pressure, force and area.
Calculating pressure example
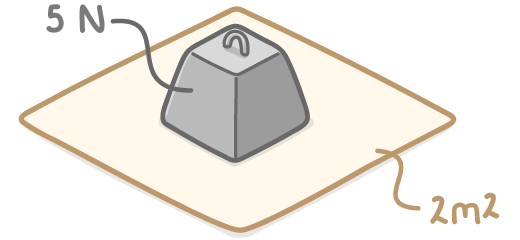
For example:
A force of 5 newtons (N) is applied over an area of 2 square metres (m2).
Calculate the pressure.
Step 1:
Use the formula: Pressure = AreaForce
Step 2:
Substitute the correct values:Pressure = 25
Step 3:
Complete the calculation: Pressure = 25= 2.5
Pressure = 2.5 N/m2
Pressure is measured in pascals
Pressure is measured in units of newtons per square metre, which is given the name pascals (Pa).
- 1 pascal = 1 N/m2
- Applying 1 N of force over 1 m2 results in a pressure of 1 Pa.
Atmospheric pressure
The atmosphere surrounding Earth exerts a downward force due to its weight. This creates atmospheric pressure.
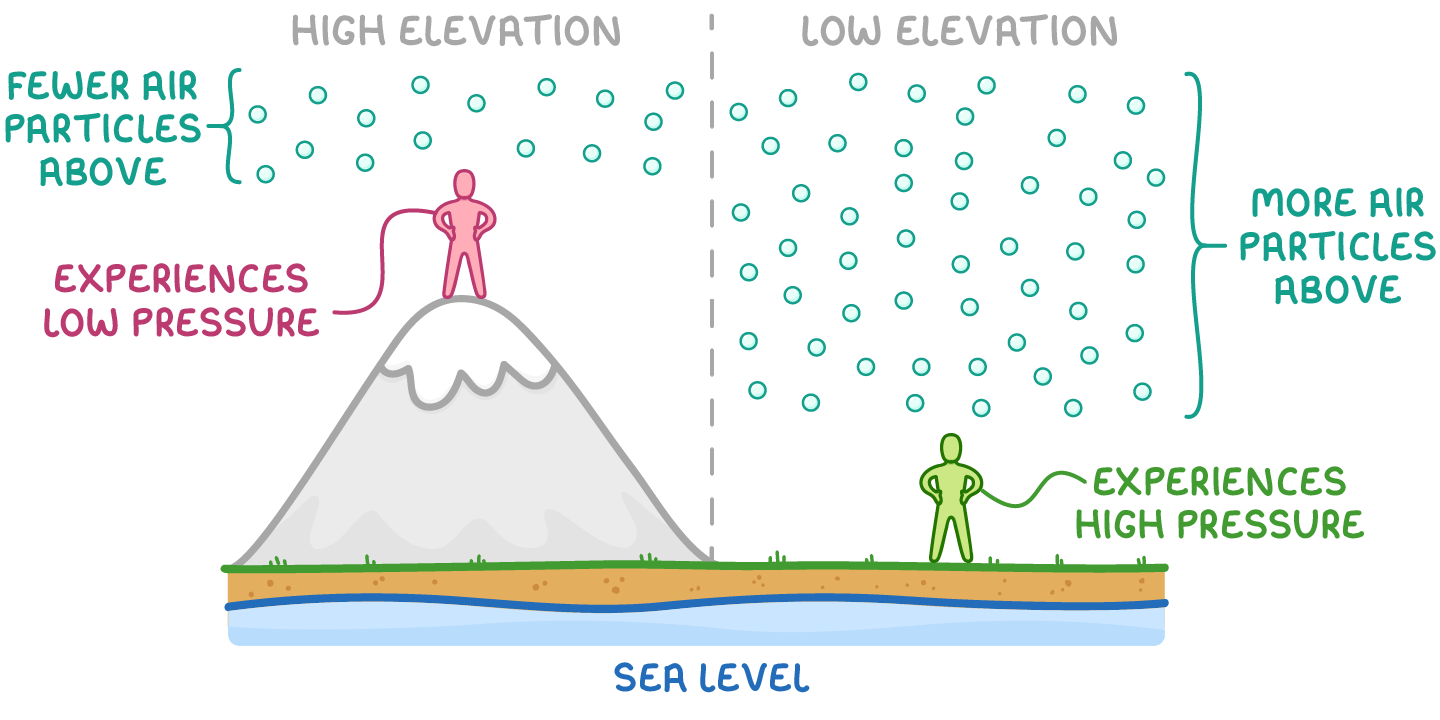
- Pressure increases closer to sea level since there is more atmosphere weighing down from above.
- Pressure decreases with height/elevation since there is less atmosphere above weighing down.
- Pressure exceeds 100,000 Pa at sea level but drops to ~33,000 Pa at the top of Mt. Everest (~8800 m elevation).
Pressure in liquids
In liquids like water:
- Pressure increases with depth, due to the greater weight of liquid pressing down from above.
- Pressure causes upthrust - an upward force which acts on the object due to being in a liquid.
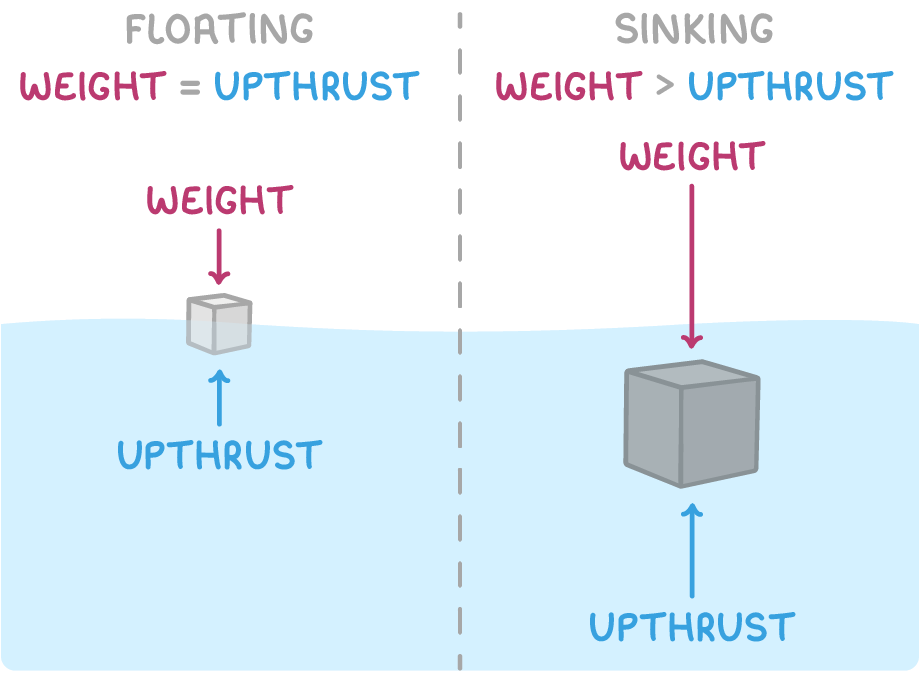
Will it sink or float?
An object will float if the weight is equal to the upthrust.
An object will sink if the weight is greater than the upthrust.