Energy transfer by heating
This lesson covers:
- How energy can be transferred between objects by heating
- Conduction as a method of energy transfer
- Radiation as a method of energy transfer
- How insulators can slow down the rate of energy transfer
Energy can be transferred between objects by heating
When there is a temperature difference between two objects, energy will be transferred from the hotter object to the cooler object.
This transfer occurs until the objects reach thermal equilibrium - the point at which they are the same temperature.
There are two main ways in which energy can be transferred between objects by heating:
- Conduction
- Radiation
Radiation
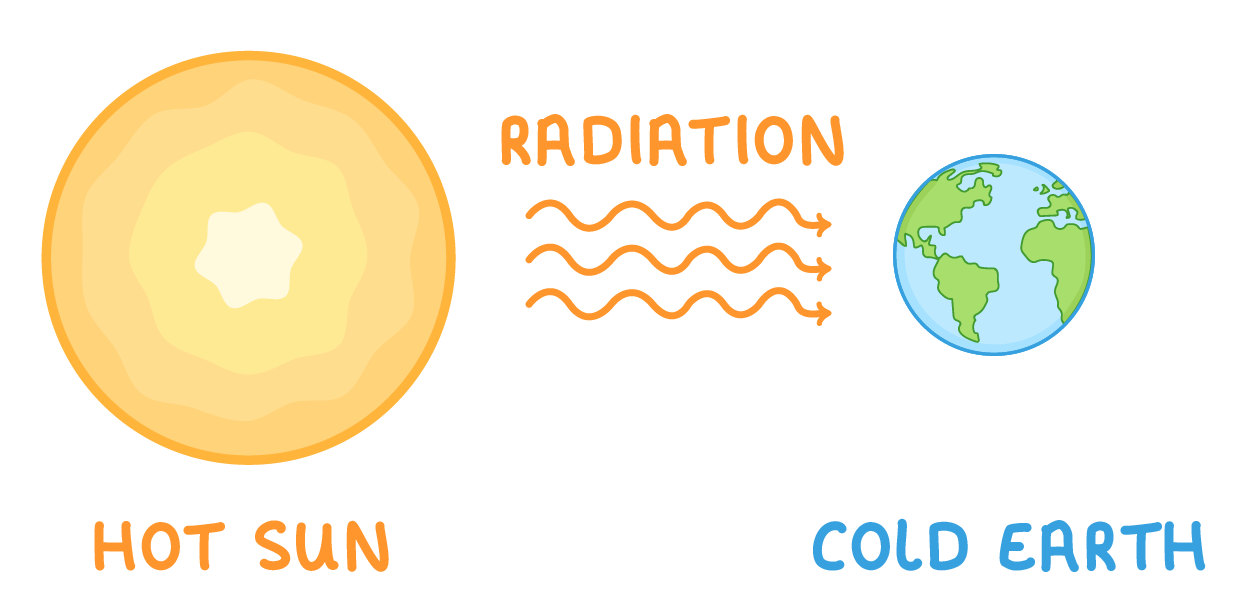
Radiation involves:
- All objects emit invisible waves that transfer energy - hotter objects emit more radiation.
- Radiation does not rely on particle contact - so objects do not need to touch.
- The hot object radiates more energy than it absorbs - so it cools down.
- The cool object absorbs radiation from the hot object - so it heats up.
Insulators and energy transfer
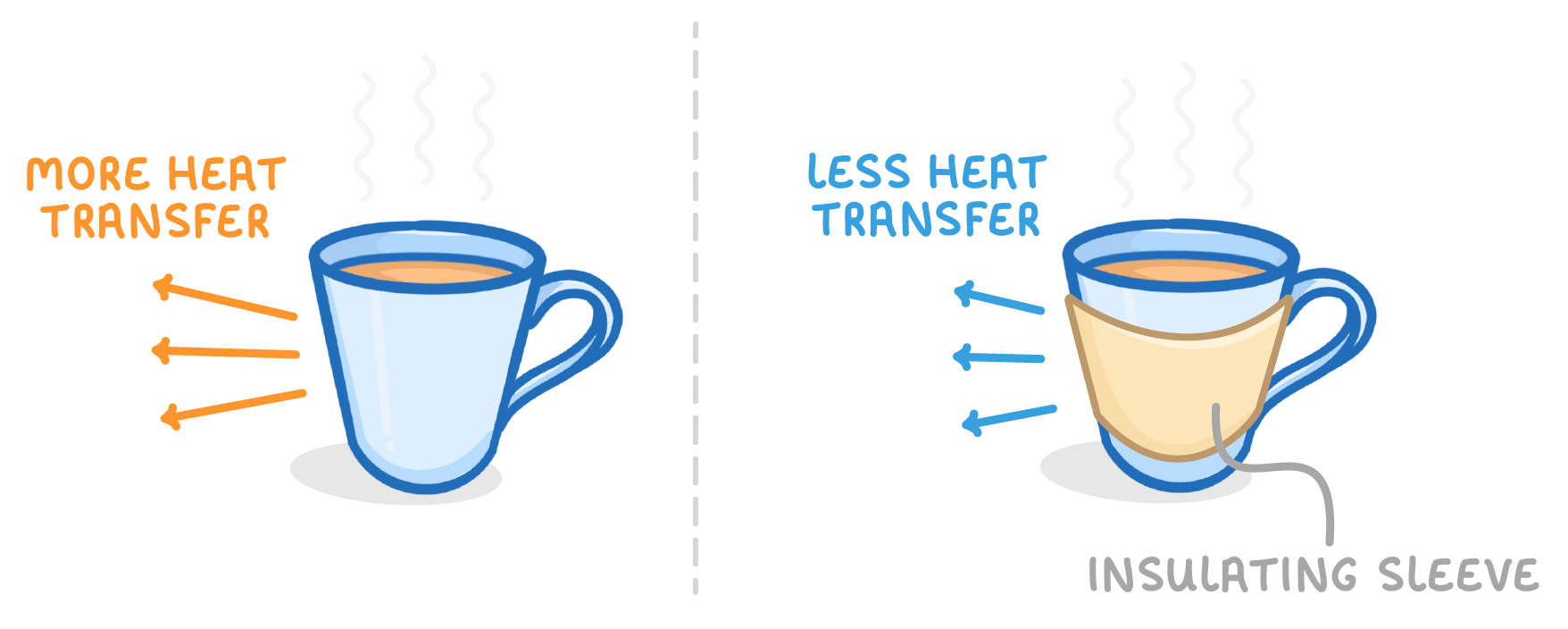
- Some materials like metals easily transfer energy - these are called conductors.
- Other materials like plastics do not transfer energy well - these are called insulators.
- Wrapping an object in an insulator slows down energy transfer.
- So insulators help keep hot things hot and cold things cold.