Vectors - Finding Unknown Lengths
This lesson covers:
- How to find the magnitude of a vector
- How to find the vector of an unknown length
The magnitude of a vector
The magnitude of a vector tells us the size or length of the vector.
The length of a vector can be found using Pythagoras' theorem.
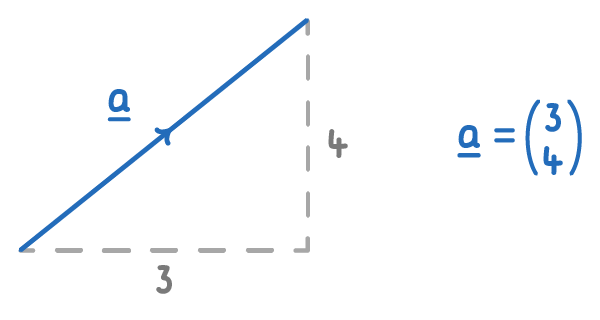
The length of a is also known as the magnitude or modulus. This is represented as ∣a∣.
∣a∣=√32+42=5
OAB is a triangle.
OA
Find AB in terms of a and b.
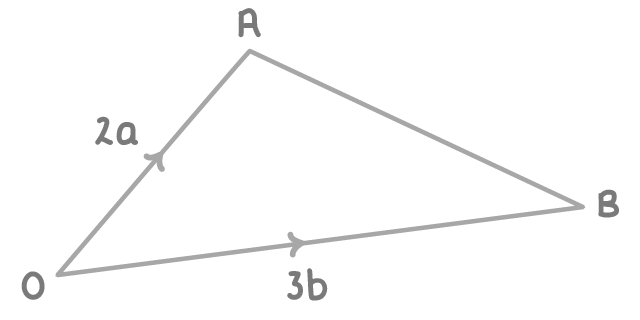
-2a - 3b
2a - 3b
2a + 3b
3b - 2a
|
Calculate the magnitude of the vector:
a = (15)
2.50
6.00
5.10
26.00
|
Calculate the magnitude of the vector:
a = (−312)
5.00
2.23
13.00
3.61
|
Calculate the magnitude of the vector:
a = (64)
3.16
10.00
7.21
52.00
|
Worked example 1: Finding unknown lengths
We can use vectors to help find an unknown length.
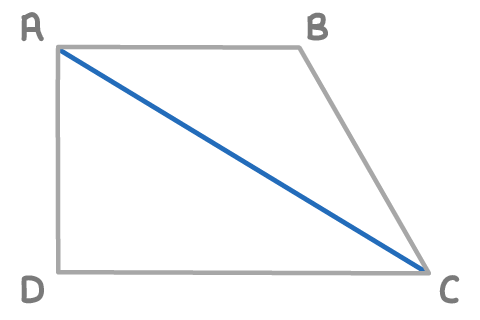
Find the length AC, given the following vectors:
AB
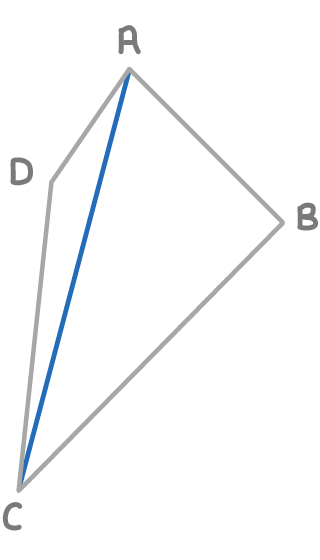
Worked example 2: Finding unknown lengths
Find the length DC, given the following vectors:
AC
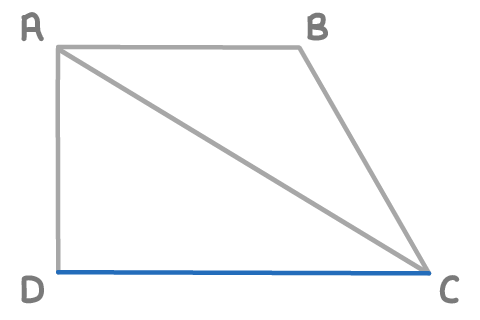
Find the length AC, given the following vectors:
AB
3.58
5.83
4.12
11.05
|
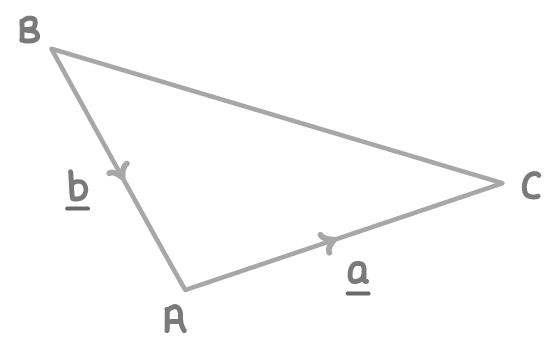
ABC is a triangle.
Given that a = (48) and b = (−616), find the magnitude of the length CB.
14.14
8.5
6.92
-13.7
|