Distance-Time Graphs
This lesson covers:
- How to interpret a distance-time graph
- What the different parts of a distance-time graph tell us about the motion of the object
On a distance / time graph, the distance is on the -axis and the time is on the -axis.
|
The gradient of a distance / time graph tells us:
The speed of the object
The amount of time elapsed
The object's acceleration
The distance travelled by the object
|
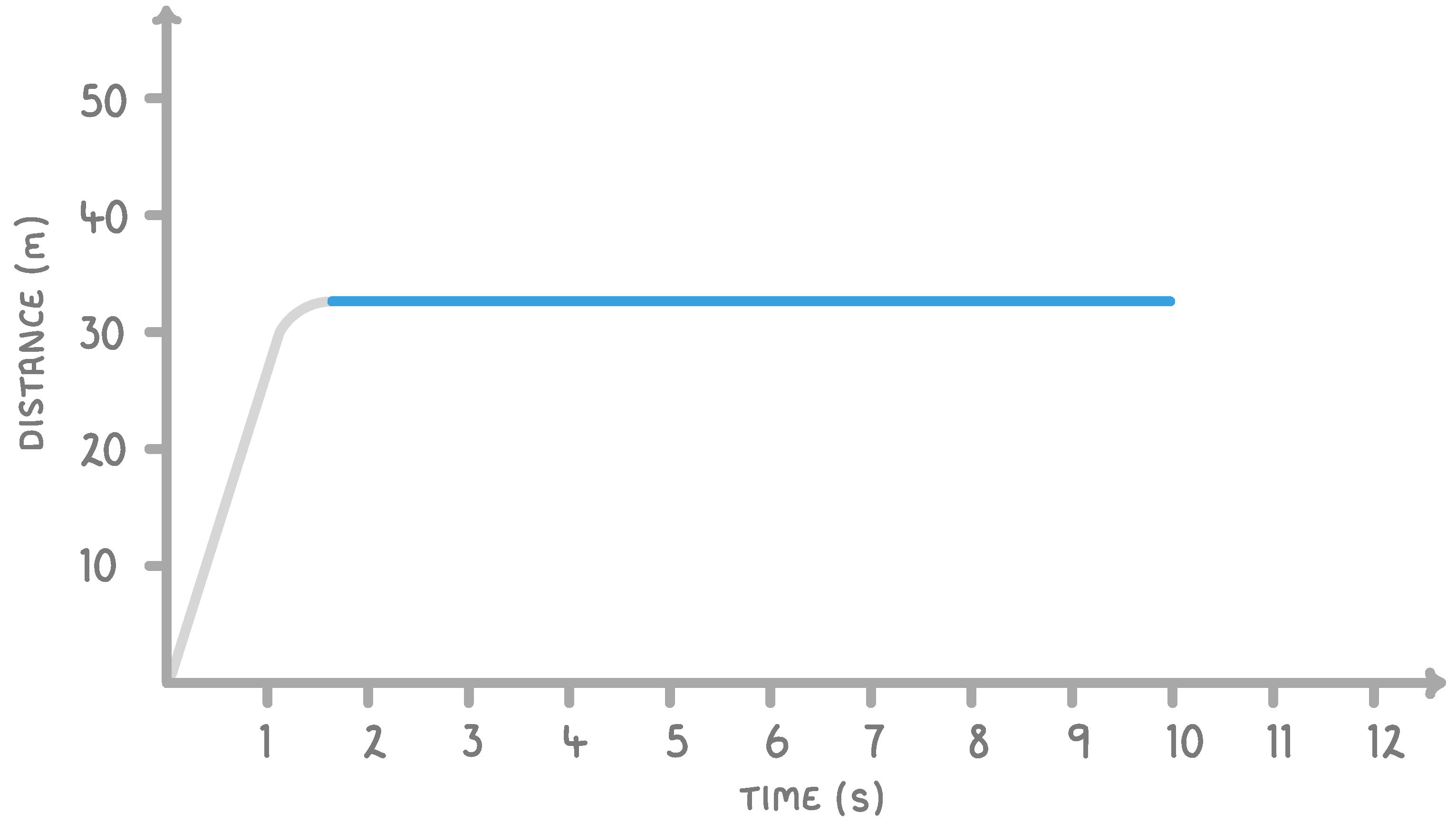
What does a flat line on a distance / time graph tell us about the movement of an object?
The object is stationary
The object is moving
|
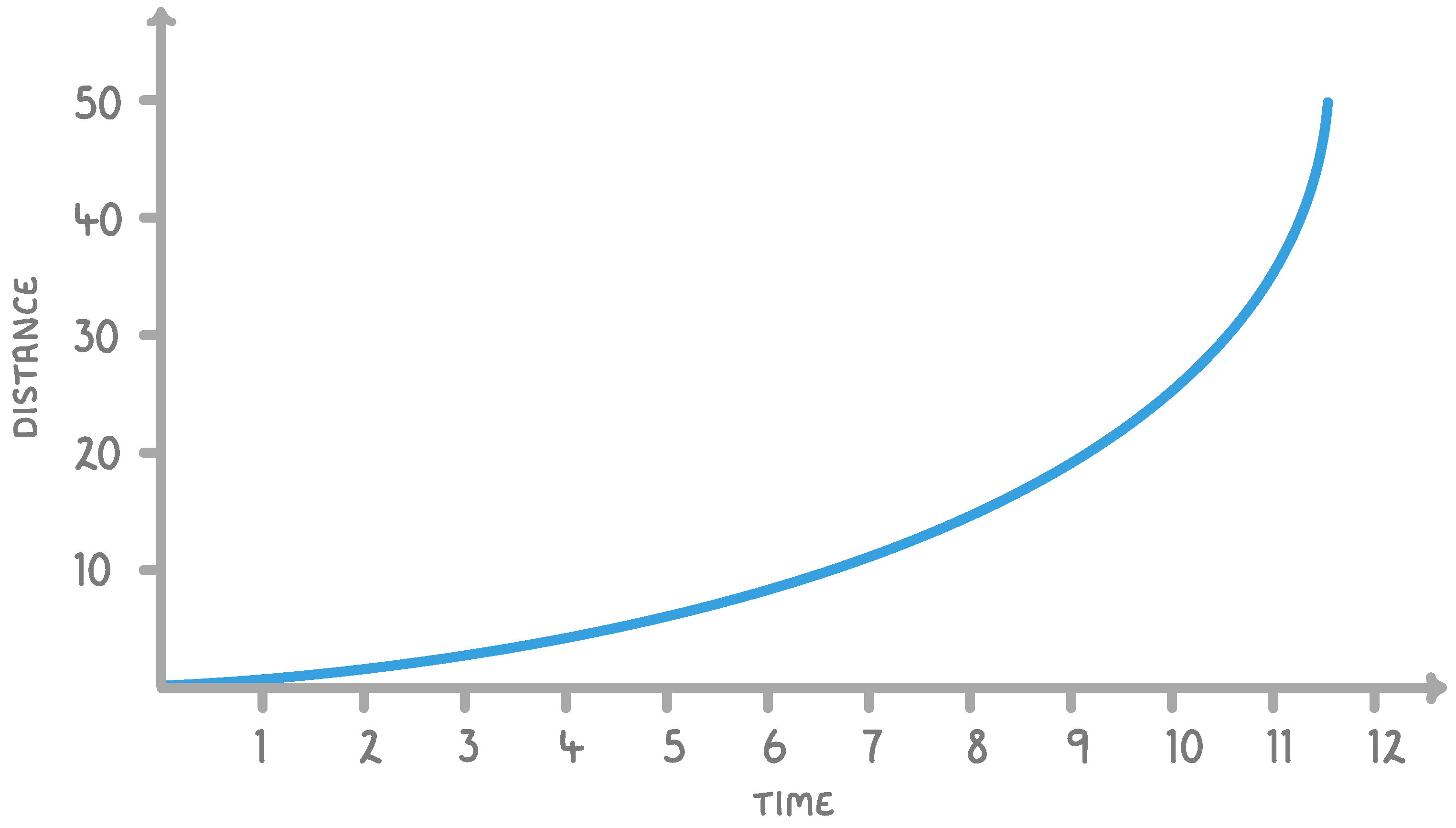
The above distance / time graph shows an object that is __________.
moving at a constant speed
accelerating
stationary
decelerating
|
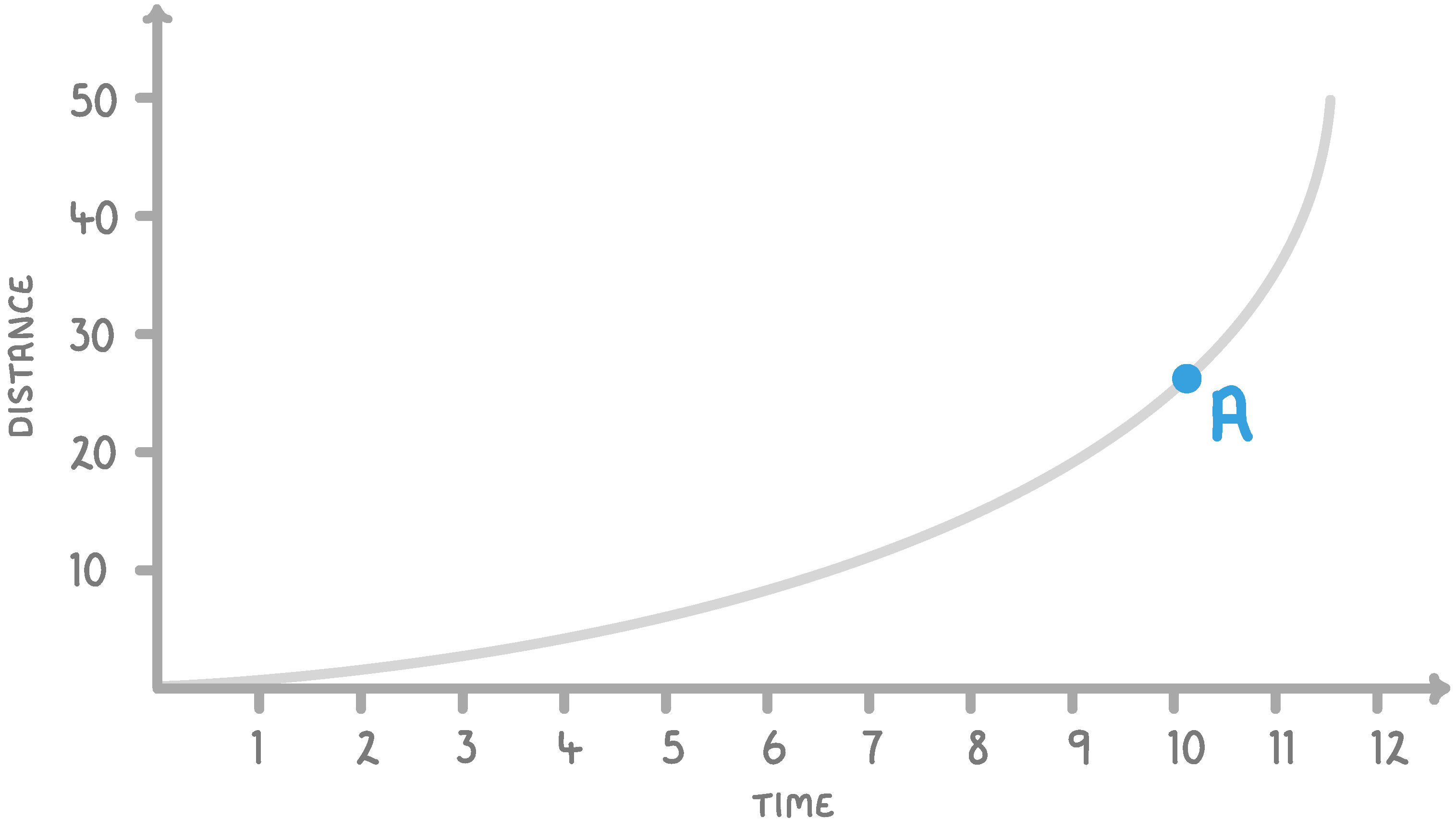
To find the velocity at point A on the graph, we need to:
Draw a tangent at that point, and use it to find the gradient of the line
Find the time at that point and divide by the distance
Find the distance at that point and divide by the time
Find the area under the graph
|
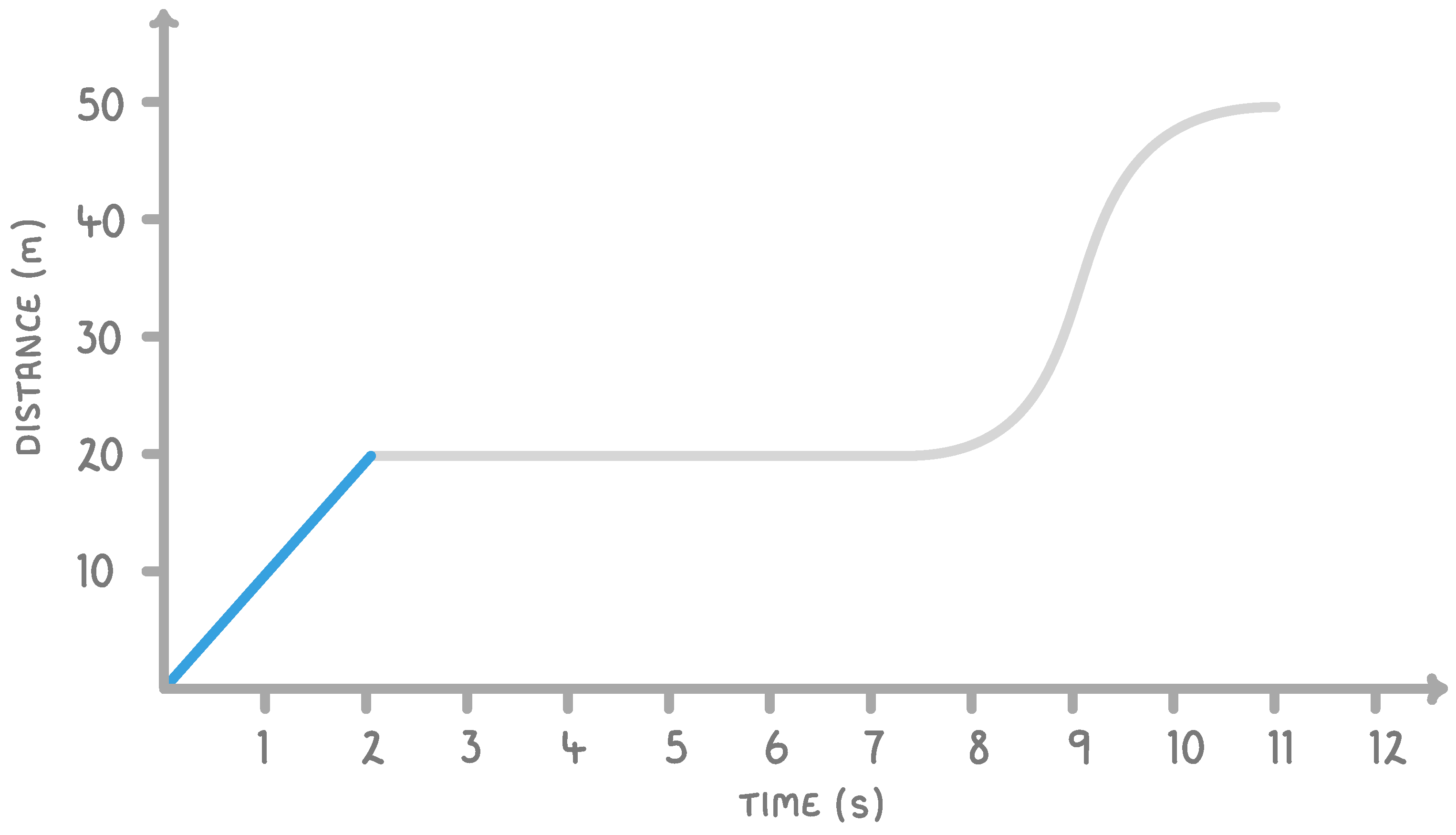
On the graph above, what does the highlighted region tell us about the movement of the object?
The object is stationary
The object is decelerating
The object is moving at a constant speed
The object is accelerating
|
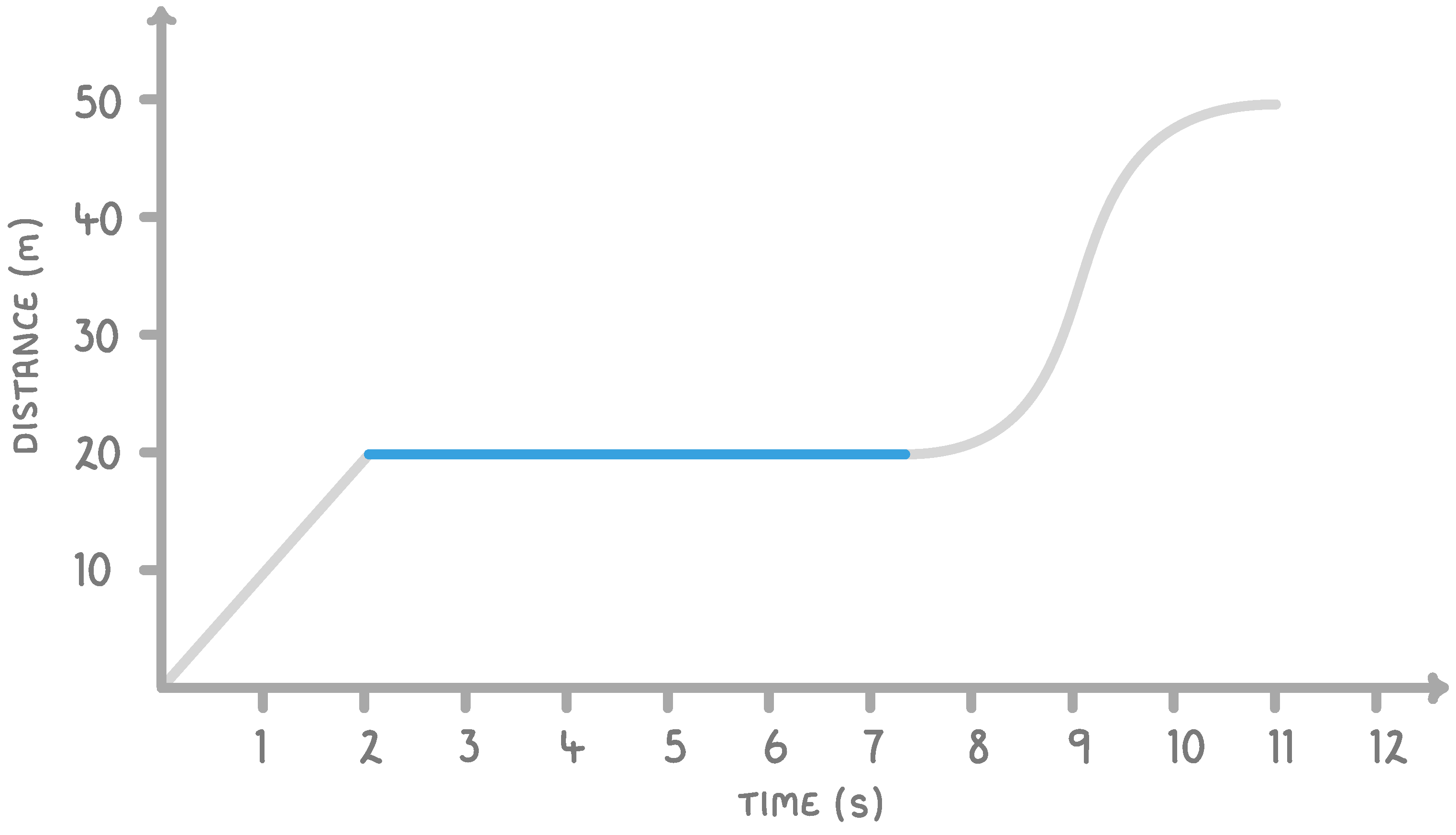
On the graph above, what does the highlighted region tell us about the movement of the object?
The object is stationary
The object is decelerating
The object is accelerating
The object is moving at a constant speed
|
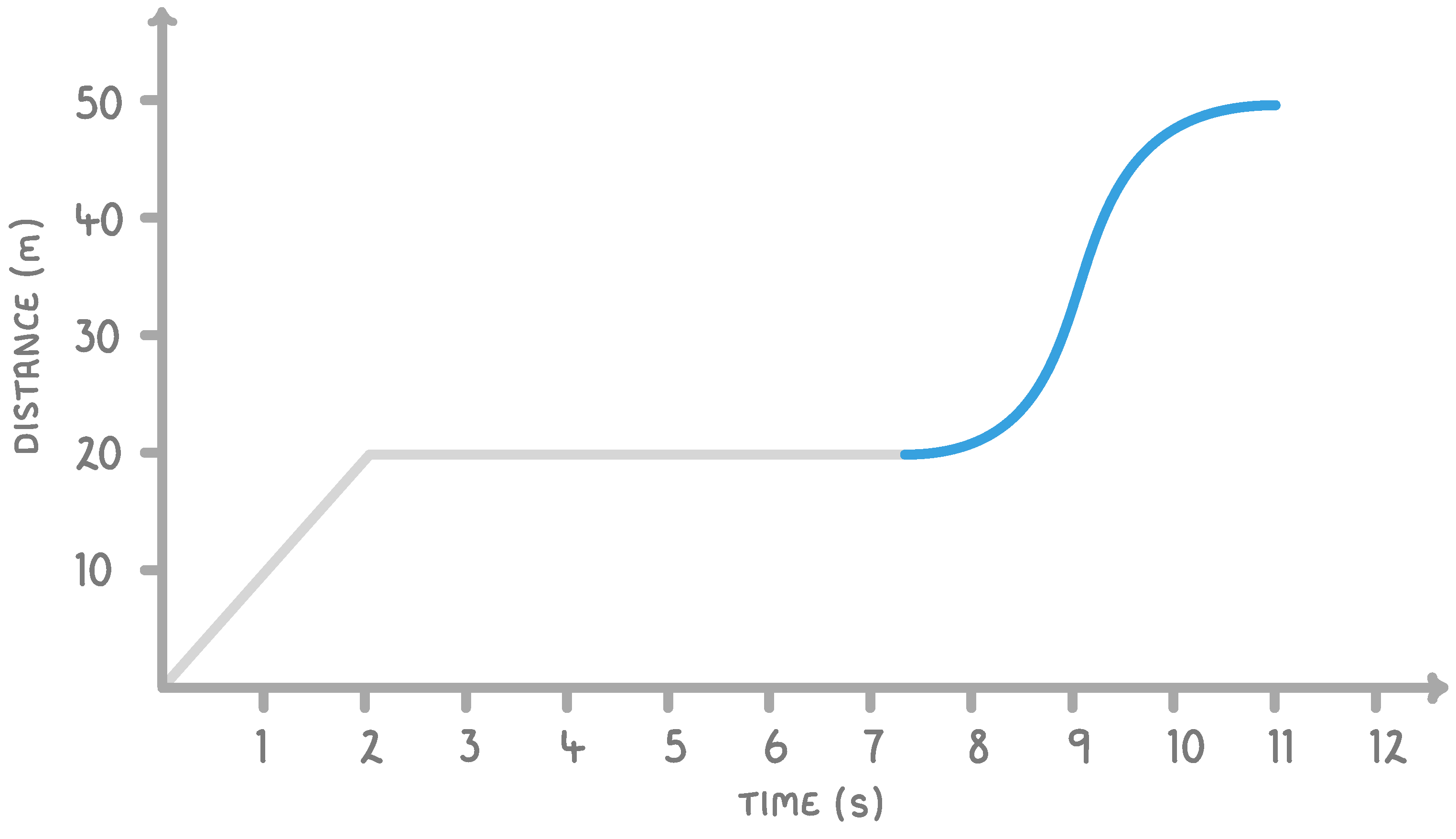
On the graph above, what does the highlighted region tell us about the movement of the object?
The object is accelerating, then decelerating
The object is decelerating, then accelerating
|