Isomerism
This lesson covers:
- Structural isomers and stereoisomers
- The three types of structural isomer: chain, positional, and functional group
Types of isomerism
Isomers are molecules with the same molecular formula but different arrangements of atoms.
They fall into two main categories:
- Structural isomers - These molecules have the same atoms but different connections.
- Stereoisomers - These molecules are connected in the same way but have different spatial arrangements of atoms.
This lesson will focus solely on structural isomerism and its various subcategories.
Structural isomers
Structural isomers are divided into three sub-types:
- Chain isomers - Differ in the carbon skeleton arrangement (e.g., straight chain vs branched chain).
- Positional isomers - The functional group is attached at different carbon atoms.
- Functional group isomers - The atoms form different functional groups.
Worked example 1 - Identifying chain isomers in butane
Determine the possible chain isomers of butane.
Step 1: Identify the molecular formula
Butane has the molecular formula C4H10.
Step 2: Determine possible structures
- Butane - A straight chain of four carbon atoms.
- Methylpropane - A branched chain with three carbon atoms in the main chain and one methyl group branching off.
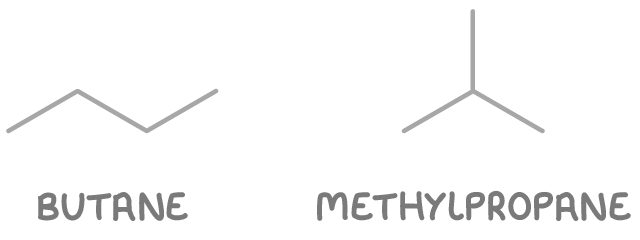
So there are two chain isomers of C4H10: butane and methylpropane.
Worked example 2 - Identifying positional isomers of chloropentane
Determine the positional isomers of chloropentane.
Step 1: Identify the molecular formula
Chloropentane has the molecular formula C5H11Cl.
Step 2: Determine possible structures
- 1-chloropentane - Chlorine on the first carbon.
- 2-chloropentane - Chlorine on the second carbon.
- 3-chloropentane - Chlorine on the third carbon.
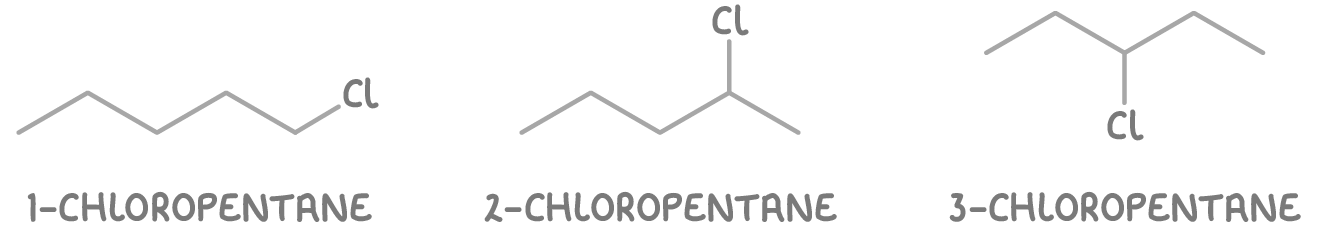
So there are three positional isomers of chloropentane: 1-chloropentane, 2-chloropentane, and 3-chloropentane.
Note: 4-chloropentane and 5-chloropentane mirror 2-chloropentane and 1-chloropentane due to the symmetry of the pentane chain, so they aren't distinct isomers.
Worked example 3 - Identifying functional group isomers of C3H6O
Determine the functional group isomers for C3H6O.
Step 1: Identify functional groups and carbon skeleton
C3H6O can form different functional groups like aldehydes or ketones.
Step 2: Determine possible structures
- Propanal - An aldehyde at the end of a three-carbon chain.
- Propanone - A ketone in the middle of a three-carbon chain.
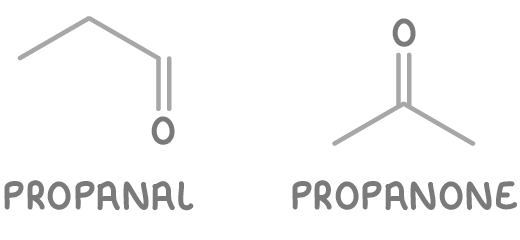
So C3H6O has two functional group isomers: propanal, and propanone.