Peptides & Electrophoresis
This lesson covers:
- How proteins are made of amino acids joined by peptide links
- Separating amino acids by gel electrophoresis
Proteins are polymers of amino acids
Proteins are composed of long chains of amino acids linked together.
- These chains of amino acids are created through condensation reactions between the amine group of one amino acid and the carboxyl group of another, with the release of a molecule of water.
- The bond that forms, known as a peptide bond, connects the amino acids into a polymer chain called a polypeptide.
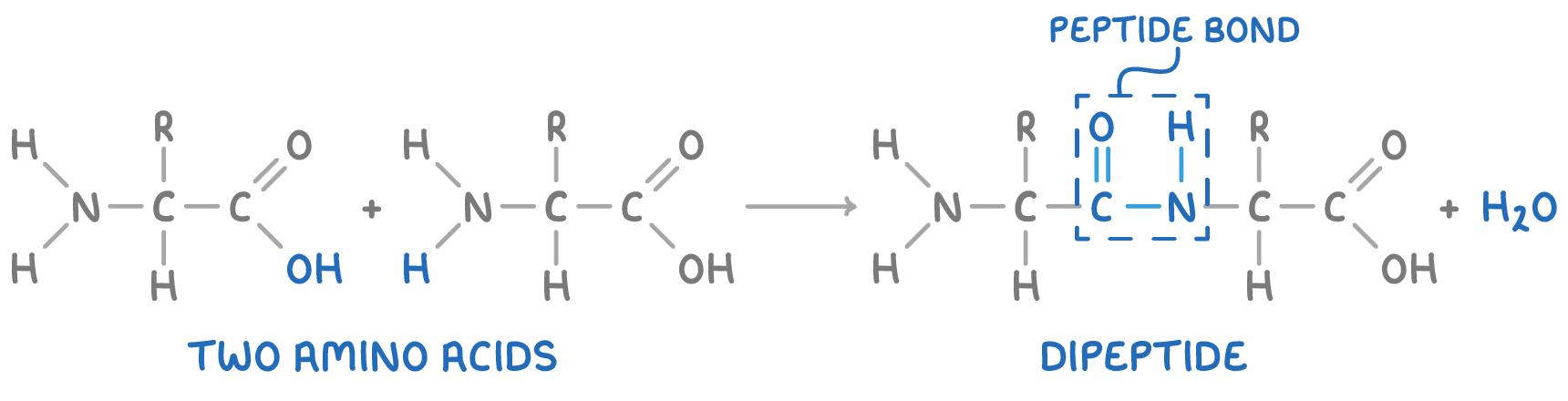
- A dipeptide is formed when two amino acids are joined by a peptide bond, whereas three linked amino acids create a tripeptide.
- When several amino acids join, they form small peptides, and longer chains are termed polypeptides or proteins.
Protein electrophoresis
Protein electrophoresis is a technique used for the separation and identification of proteins.
The process involves the following steps:
- Sample preparation - The protein sample is treated to ensure all proteins carry a consistent negative charge. Fluorescent dyes may be added to aid in visualizing protein migration.
- Gel matrix - The sample is placed into wells at the top of a gel matrix, typically made from polyacrylamide or agarose. The gel is positioned between two electrodes of opposite charge and submerged in a buffer solution. The buffer solution maintains a stable pH environment and conducts electricity, enabling the proteins to migrate through the gel.
- Separation - An electric field is applied to the gel. Proteins migrate towards the positively charged electrode at the bottom, with the gel matrix slowing their movement. Larger proteins move more slowly than smaller ones. Over time, this leads to protein separation based on size.
- Visualisation - After sufficient separation is achieved, the electric field is turned off. The proteins in the gel are stained to visualize the distinct bands.
- Identification - The pattern of these bands is compared to known standards, allowing for the identification of the proteins in the sample.