Separating Metals from Metal Oxides
This lesson covers:
- How to separate pure metals from metal oxides
- The definitions of oxidation and reduction
- How carbon can be used to obtain some metals from ores
The terms 'oxidation' and 'reduction 'can be described either in terms of gain/loss of oxygen, or in terms of gain/loss of electrons. In this topic though, we're only describing them in terms of oxygen.
The definition of oxidation is:
The loss of oxygen
The gain of oxygen
|
Is the following reaction an example of oxidation or reduction?
2Mg + O2 ➔ 2MgO
Oxidation
Reduction
|
lithium / carbon / oxidised / reduced / more / less
Pure metals can be extracted from metal oxides using the element .
The carbon causes the metal to lose its oxygen, so the metal becomes .
This produces CO2, and can only work for metals reactive than carbon.
|
Which of the following metals could be reduced from their oxides, by reacting them with carbon?
(Select all that apply)
Calcium
Zinc
Iron
Copper
Potassium
Sodium
|
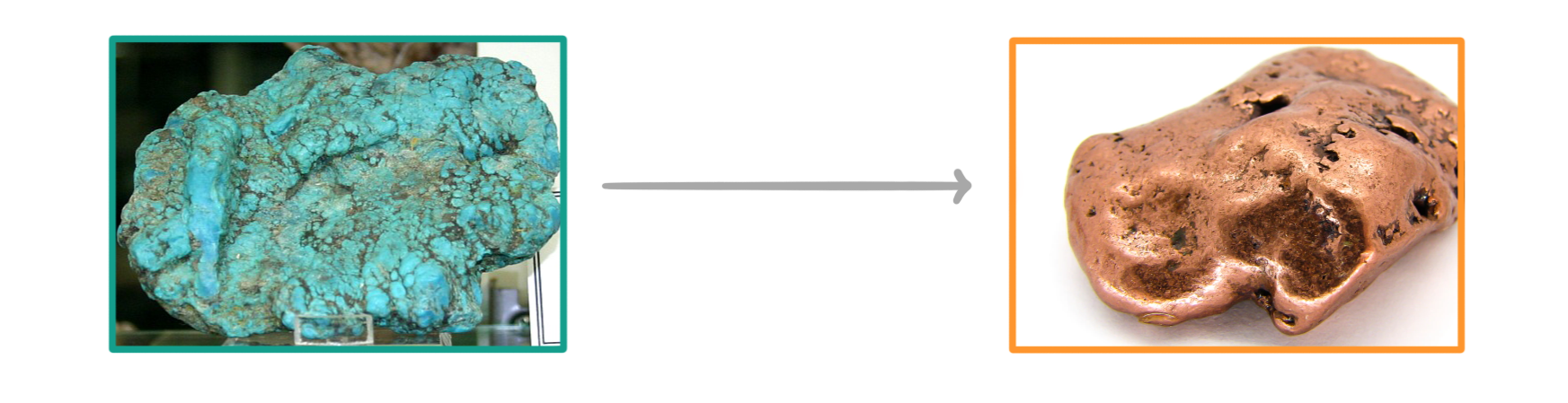
Balance the following equation showing the reduction of copper oxide:
CuO + C ➔ Cu + CO2
|
Why do we find pure gold in the ground, but not pure iron?
|
Reduction can be defined as the loss of .
|