Acids & Bases
This lesson covers:
- What the pH scale is
- How we can measure the pH of a solution
- The definitions of acids, alkalis, and bases
- Examples of neutralisation reactions
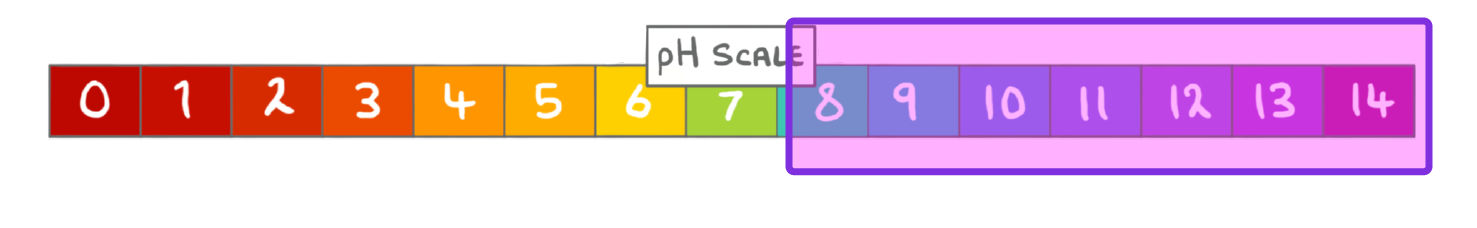
We measure the acidity or alkalinity of a solution using the scale.
|

The pH scale ranges from:
0 to 14
0 to 7
-14 to 7
|
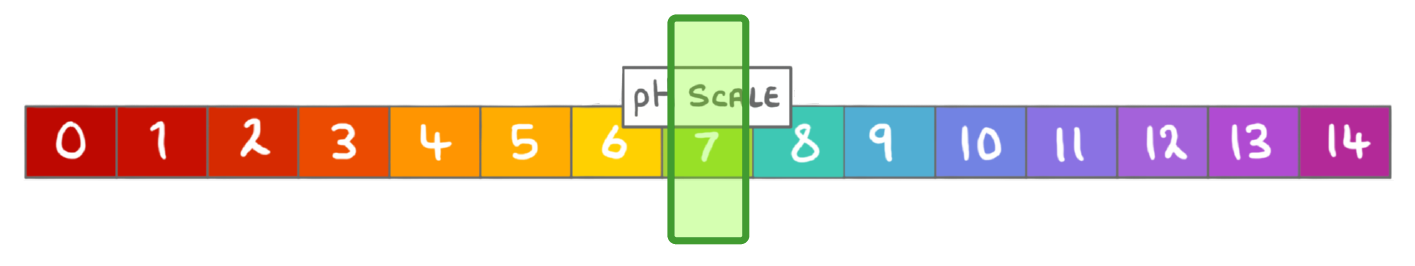
What term can be used to describe solutions with a pH of 7?
Balanced
Acidic
Neutral
Alkaline
|
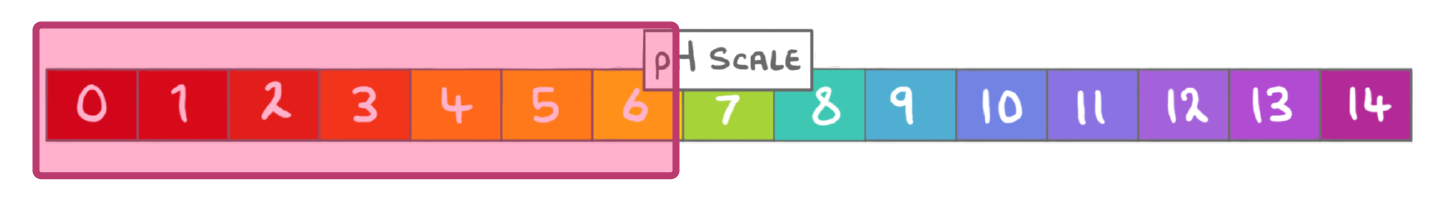
What term can be used to describe solutions with a pH lower than 7?
Alkaline
Neutral
Acidic
|
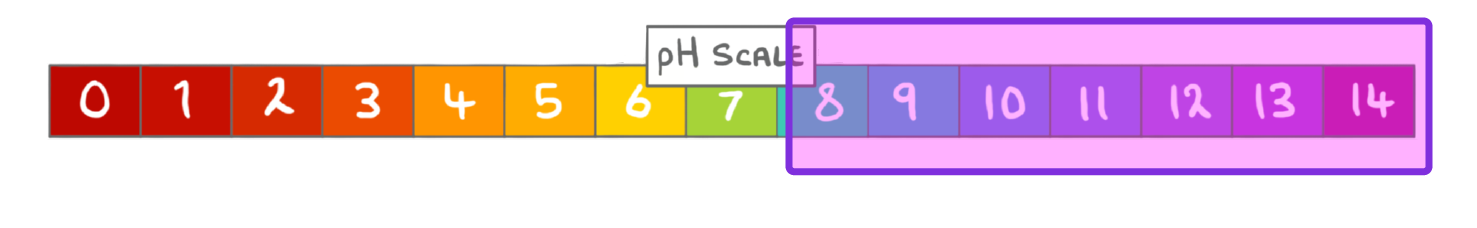
What term can be used to describe solutions with a pH greater than 7?
Neutral
Acidic
Alkaline
|
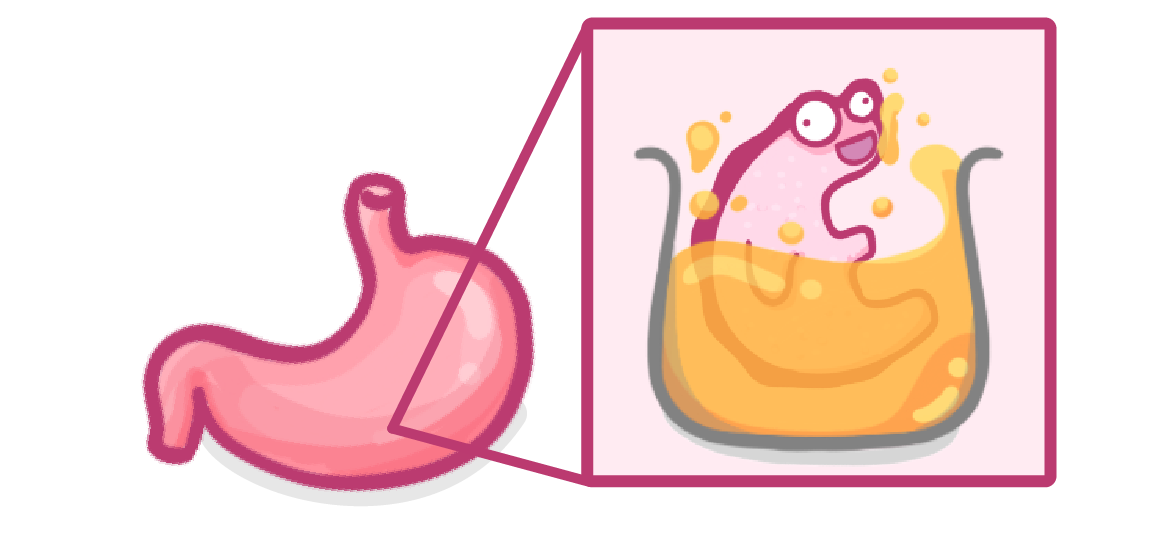
What pH does stomach acid typically have?
About 2
About 7
About 12
|
Select two ways by which the pH of a solution can be measured.
pH probe
Distillation
Chemical indicator
Reaction with water
|
The pH of a solution can be measured using a type of chemical dye that changes colour, depending on the pH of the substance it's mixed with.
This chemical dye is usually referred to as:
pH dye
Acidity checker
Indicator solution
|
indicator is made up of a several different indicator solutions. This means that it undergoes a smooth colour change over a wide range of pH values.
It becomes more in colour in acidic solutions, but more bluey-purple in solutions.
|
What is the pH of pure water?
|
A pH probe electronically measures the pH of a solution.
Select two reasons why using a probe may be more reliable than using an indicator.
Determining the colour of an indicator is subjective
A probe produces a more accurate result
A probe can be used in strongly acidic solutions
|
A substance that forms an aqueous solution with a pH less than 7 is:
An ion
A base
An acid
An alkali
|
Select the ion responsible for making an alkaline pH when dissolved in solution:
Na+
OH-
H+
H2O-
|
Which of the following formulae represents nitric acid?
NaOH
HCl
H2SO4
HNO3
|
Which of the following are acids?
(Select all that apply)
HNO3
CaCO3
HCl
H2SO4
NaOH
|
Which of the following is represented by the formula CaCO3?
Calcium hydroxide
Carbon dioxide
Calcium carbonate
|