Electronic Structure
This lesson covers:
- How electrons are arranged into energy levels, or 'shells'
- How to work out the electron configuration of atoms and ions
Electrons surround the atomic nucleus in regions called s.
The shell closest to the nucleus can hold electrons, whereas the outer ones can hold up to electrons.
|
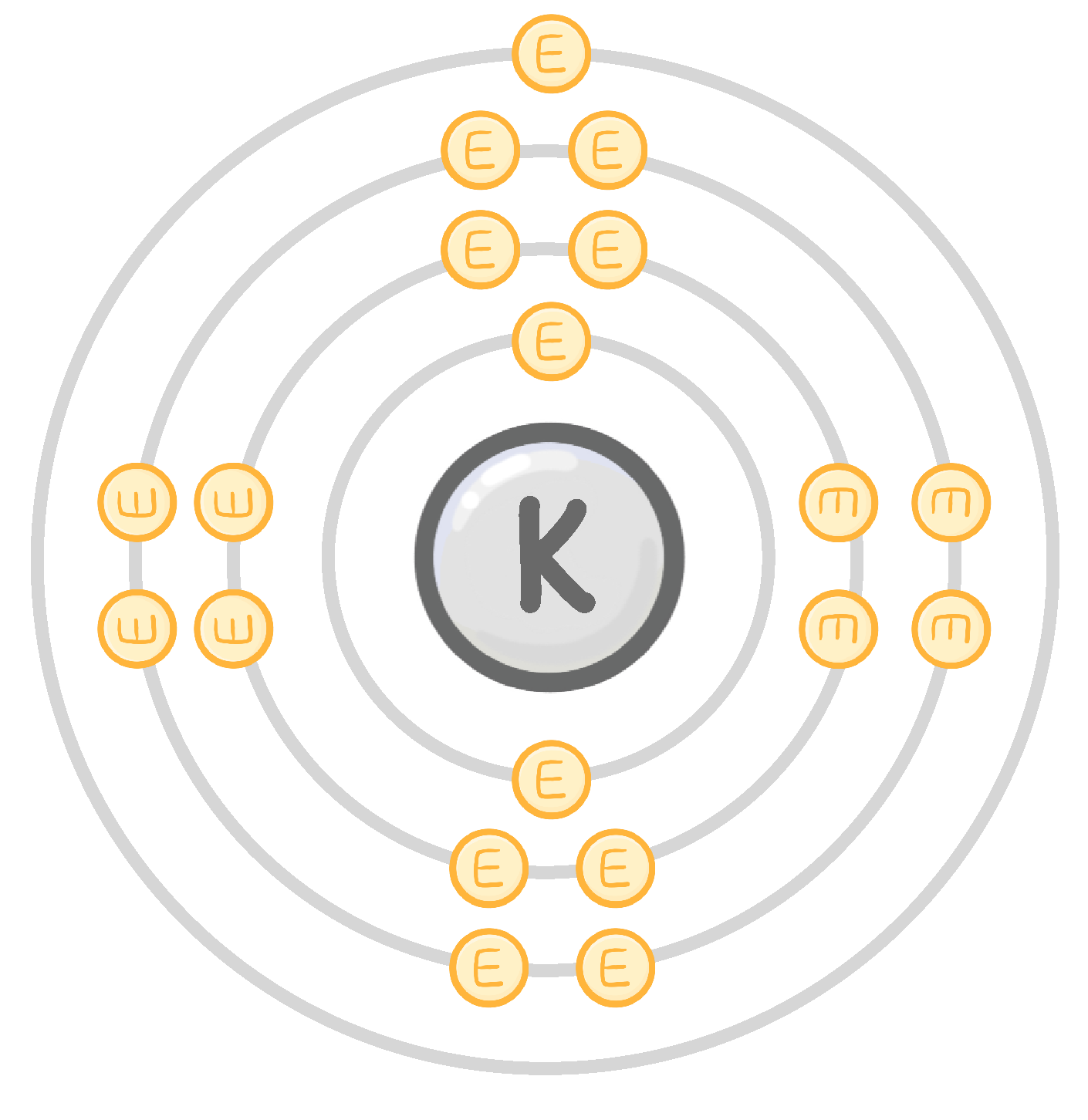
An atom of potassium has 1 electron in its outermost shell.
In a chemical reaction, will potassium gain or lose 1 electron?
Gain
Lose
|

Nitrogen has an atomic number of 7.
Which of the following is the correct electron configuration for an atom of nitrogen?
7
2, 5
3, 4
5, 2
|
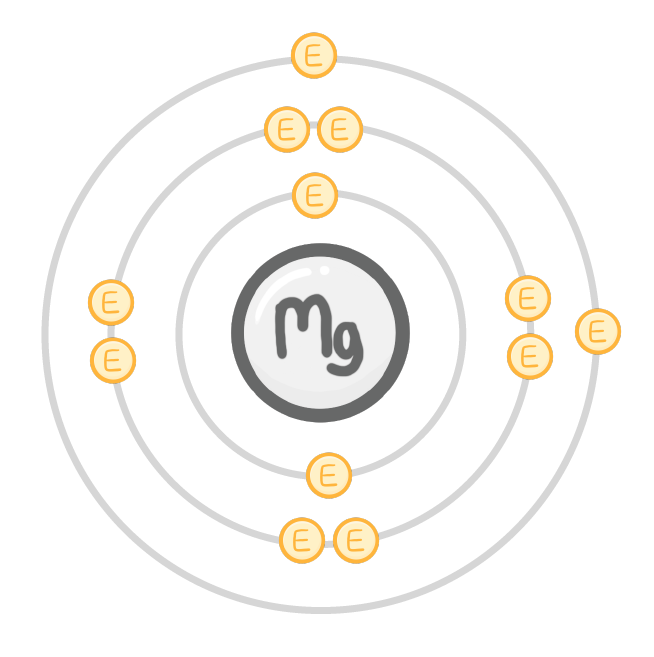
An atom of magnesium has the electron structure 2, 8, 2.
When a magnesium atom takes part in a reaction, the atom loses electrons.
The new electron structure is: , .
|
An atom of oxygen has 6 electrons in the outer shell. In a reaction, it gains 2 electrons.
What is the charge of the oxide ion created?
1+
2+
2-
1-
|