Group 7 & Group 0 (Halogens & Noble Gases)
This lesson covers:
- The properties of the halogens (group 7 elements)
- Reactions of halogens with metals
- Displacement reactions among the halogens
- Properties of the noble gases (group 0 elements)
For questions involving halogen displacement reactions, you will often be asked about the colour changes that take place. |
The key information to remember is:
|
This means that when you mix chlorine water, bromine water, or iodine water with a halide salt you may get a colour change. |
This table summarises the colour changes. We've shown the examples using potassium halides (KCl, KBr, KI), but the same logic would apply to other halide salts. 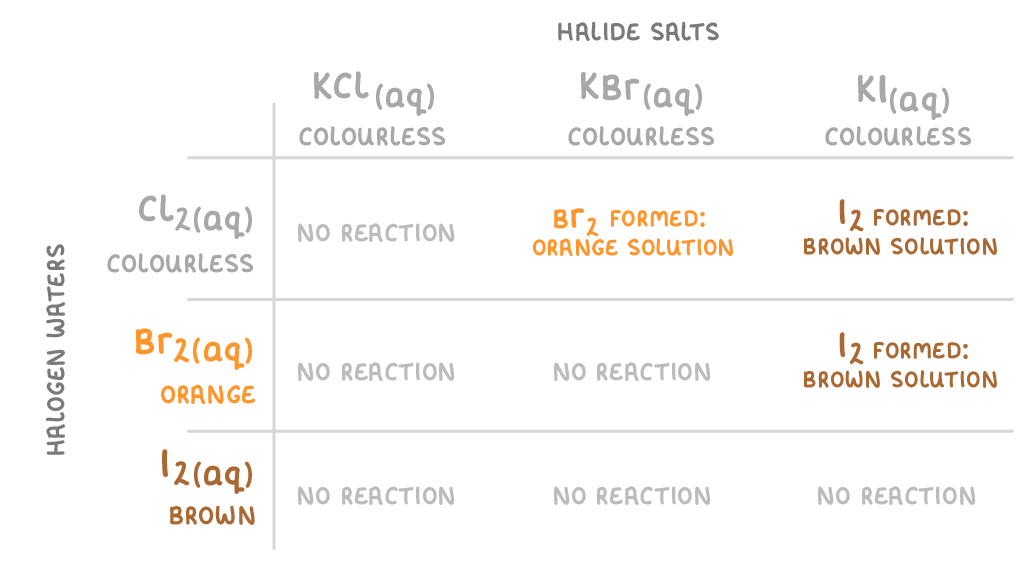 |
Colours and physical states of the halogens at room temperature
solid / gas / liquid / green / yellow / grey
- Fluorine is a poisonous coloured gas and is the most reactive halogen
- Chlorine is a coloured gas.
- Bromine is a red-brown volatile which is also poisonous.
- Iodine is a coloured solid with purple vapours.
|
Which two of these properties are seen in group 7 elements?
Their ions usually have a 1- charge
They can form covalent bonds with other non-metals
They exist as single atoms
Reactivity increases down the group
|
Do the melting and boiling points of the halogens increase or decrease as you go down the group?
Increase
Decrease
|
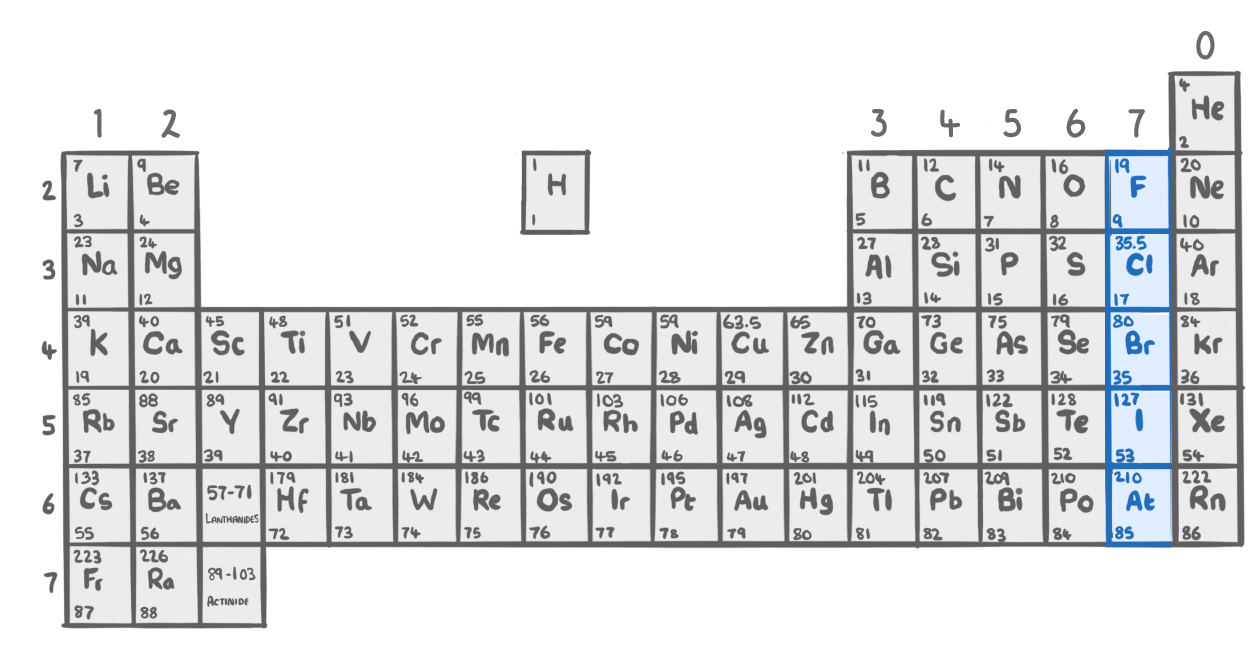
Based on the reactivity of the halogens, which of these displacement reactions is possible?
2HBr + F2 ➔ 2HF + Br2
2HF + Cl2 ➔ 2HCl + F2
2HCl + I2 ➔ 2HI + Cl2
|
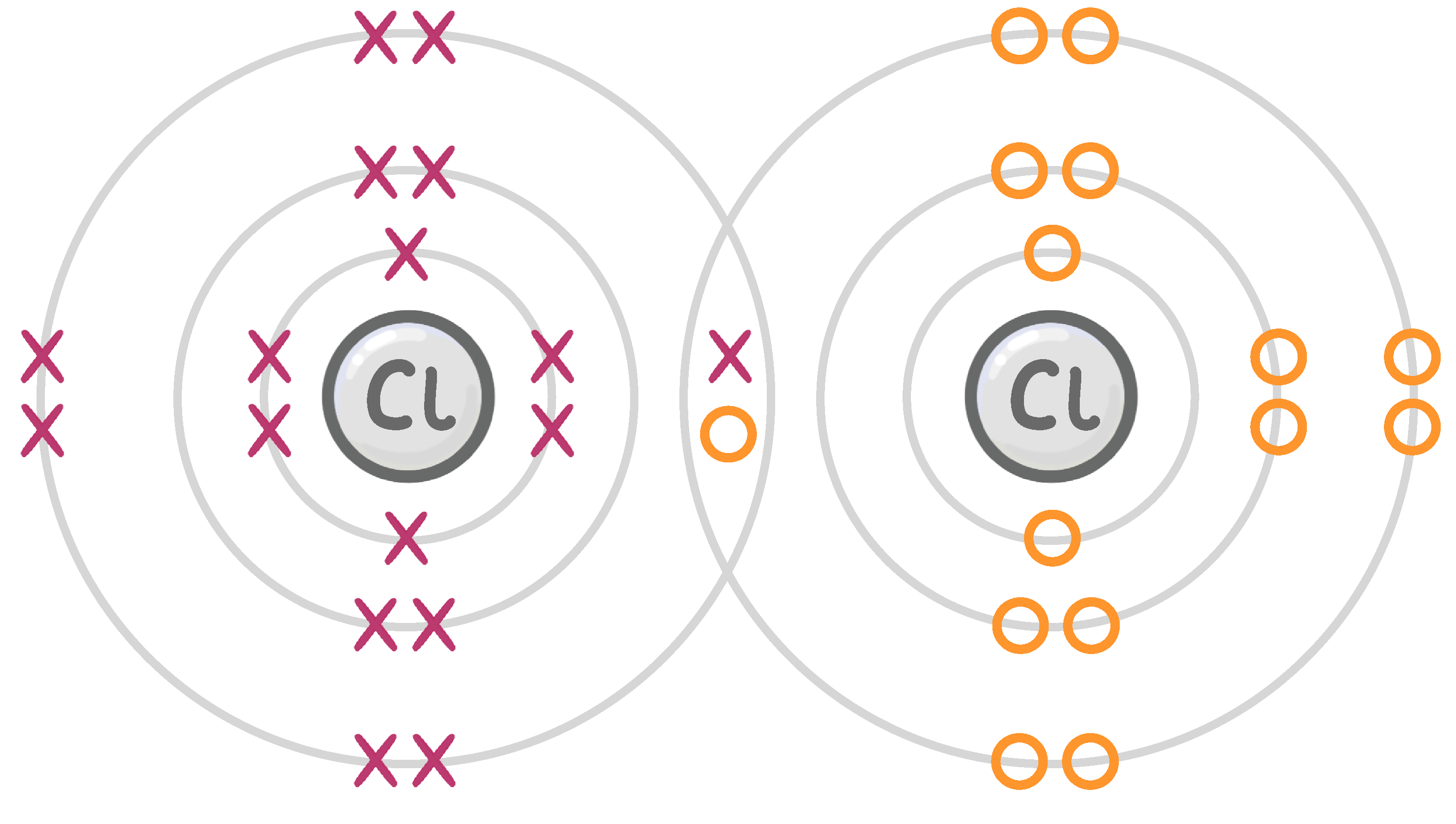
double / diatomic / covalent / ionic
The halogens exist as molecules, meaning each molecule consists of two atoms.
The two atoms are joined by a bond, which allows each atom to share an electron, giving each atom a full outer shell.
|
Are noble gases flammable?
No
Yes
|
Why are the noble gases inert?
('inert' means chemically unreactive)
The atoms are non flammable
They form colourless gases
The atoms have a full outer shell of electrons
|