Condensation Polymers
This lesson covers:
- What 'condensation polymers' are
- How dicarboxylic acids and diols can form polyesters
- Why condensation polymers are biodegradable
ester / acid / alkali / monomers / diol
Condensation polymers can be made by joining together dicarboxylic monomers and monomers. These monomers are joined together by links.
|

What does the coloured box represent?
The shape of the molecule
The colour of the molecule
The rest of the molecule in simplified form
|
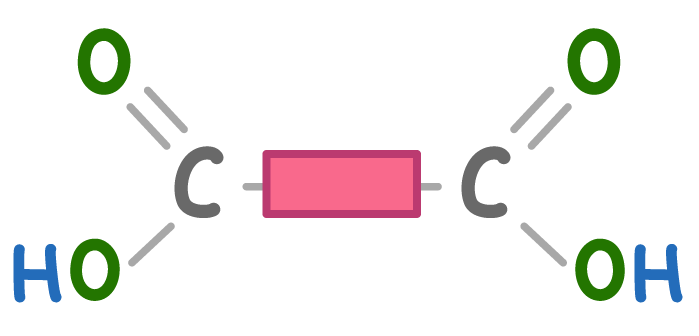
What is the molecule above?
A dicarboxylic monomer
A diol monomer
|
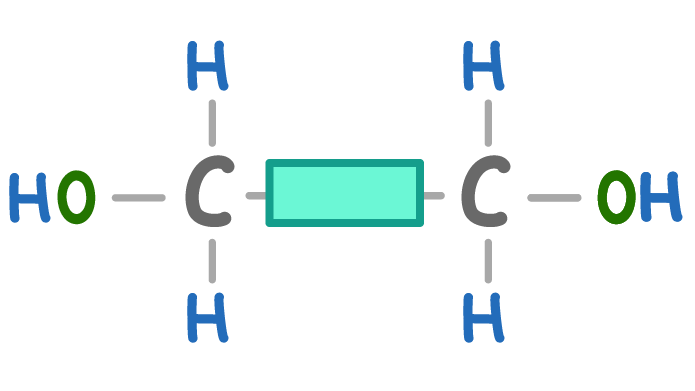
What is the molecule above?
A diol monomer
A dicarboxylic monomer
|
What is a dimer?
Three monomers combined
A type of currency
Two monomers combined
|
When is a polymer referred to as a 'condensation' polymer?
When the reactants condense from a gas state into a liquid state
When water is a produced as a by-product of the reaction
|
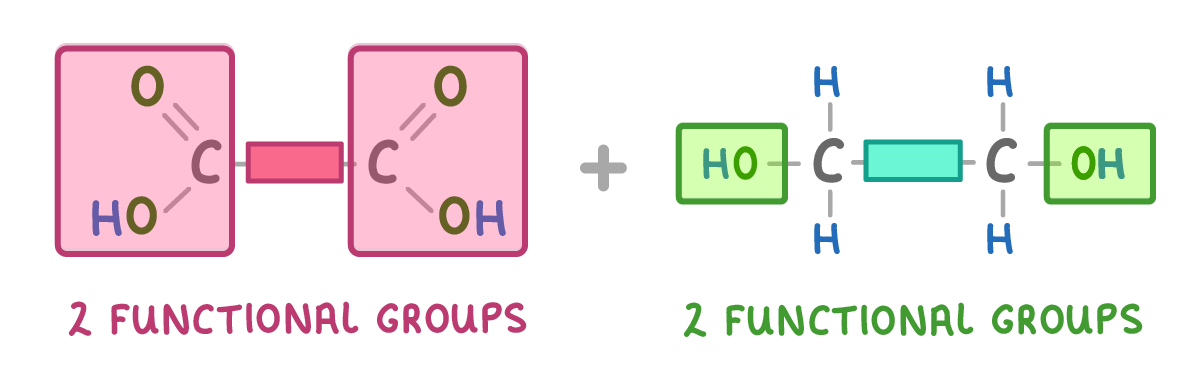
To make a polyester condensation polymerisation, the monomers need to have enough carboxylic acid and alcohol functional groups to form a long continuous chain. This means that each monomer needs to have at least two functional groups.
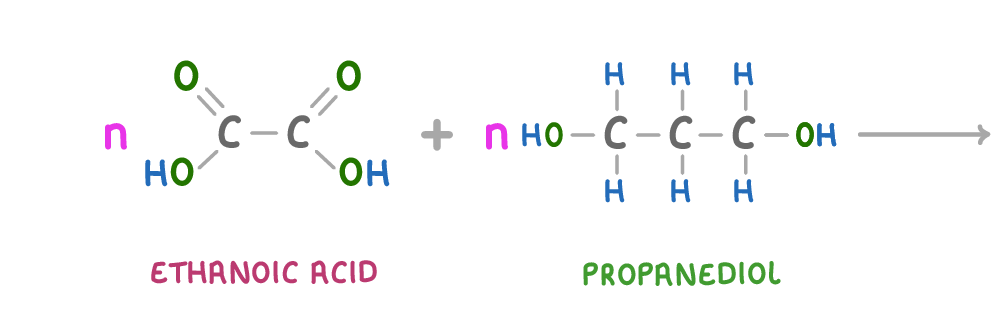
Using pen and paper, complete the above chemical equation and diagram to form a repeating unit of a polyester and water.
(Click 'Continue' when you're ready to check your answer)
|
Which type of polymers are biodegradable?
Condensation polymers
Addition polymers
|
Why are condensation polymers biodegradable?
Ester links disintegrate in water
Carboxylic bonds are weak
Ester links can be broken down by microorganisms
|