Factors Affecting Rates of Reaction & Collision Theory
This lesson covers:
- What 'collision theory' is
- How temperature, concentration/pressure, surface area, and catalysts, all affect the rate of reaction
- What 'activation energy' is
- How activation energy is represented on a reaction profile
Name four factors that affect the rate of chemical reactions.
|
theory states that for particles to react, they have to collide with sufficient energy.
|
The minimum amount of energy required for a reaction to take place is called the energy.
|
When considering how a condition will affect the rate of reaction, you have to consider how it will affect the of collisions, and/or the of the particles.
|
Explain how the rate of reaction changes with increasing temperature.
|

Which of the following increase the frequency of collisions of the particles in a reaction?
(Select all that apply)
Increasing the temperature
Using powder instead of small chunks
Decreasing the pressure
Increasing the concentration
|
Three grams of magnesium is added to water.
Which form of magnesium would give the highest rate of reaction?
Small chunks
Powder
One large piece
|
A substance that increases the rate of a reaction without being chemically changed, or used up, is called a .
|
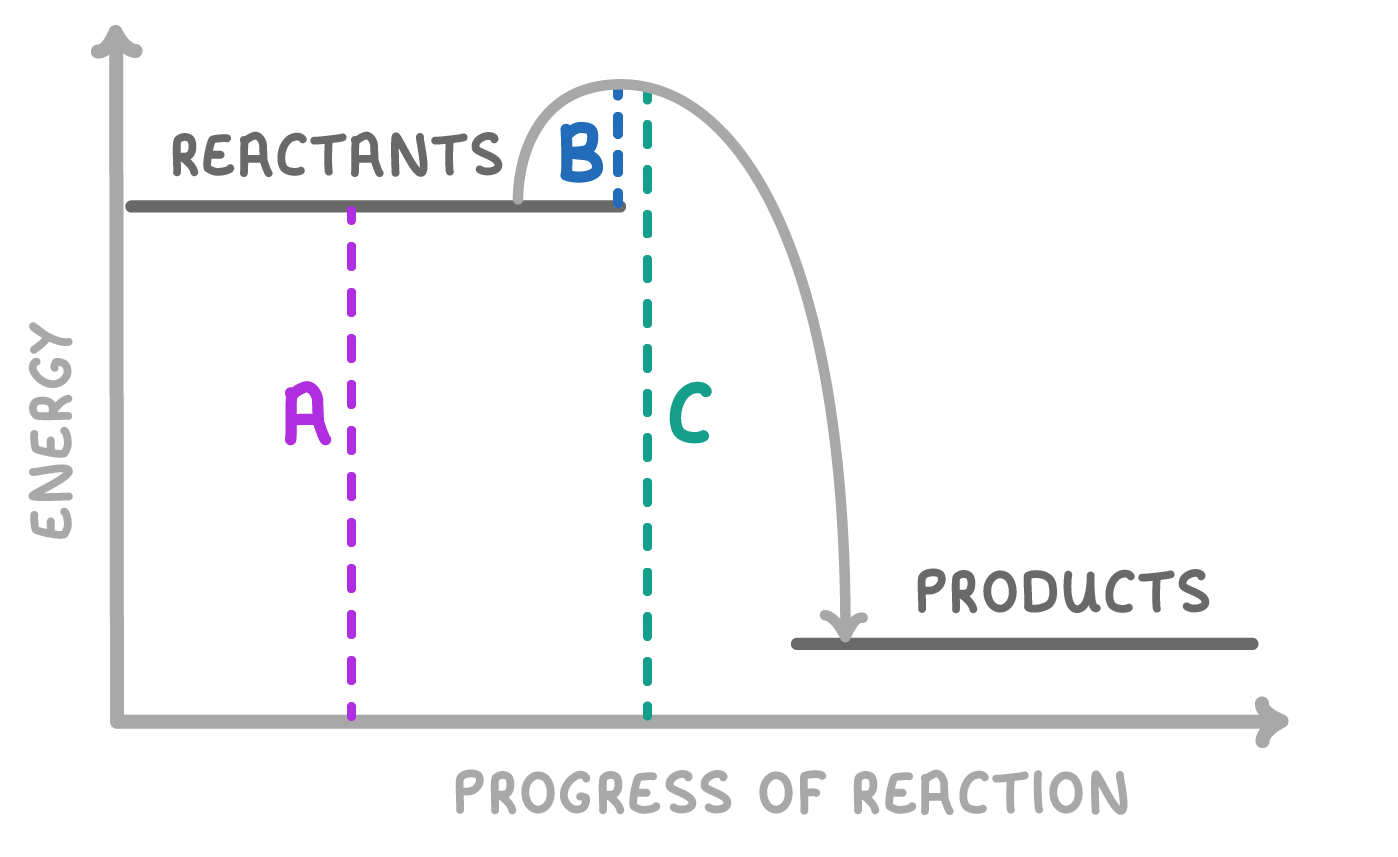
On the image above, which of the lines represents the activation energy of the reaction?
A
B
C
|
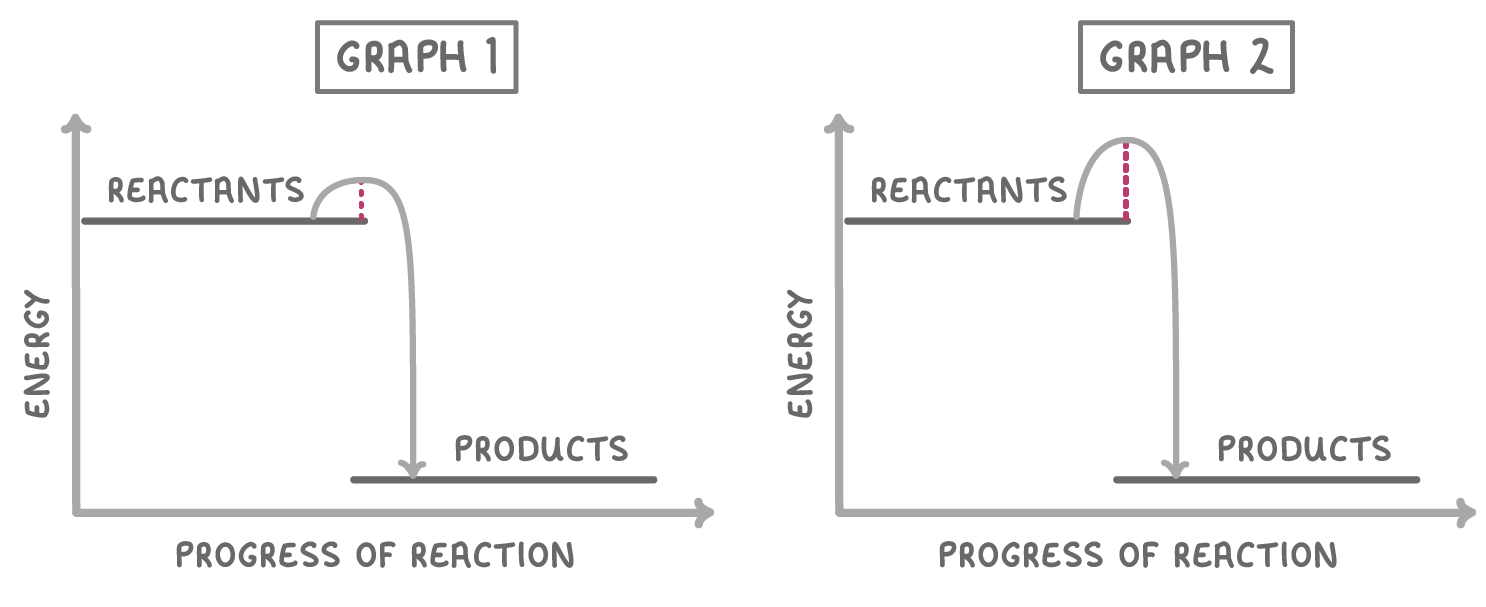
The two graphs above show the same chemical reaction, but in the presence and absence of a catalyst. Which one shows the reaction occurring in the presence of a catalyst?
Graph 1
Graph 2
|
Which three of the following are examples of catalysts?
Enzymes
Oxygen
Cobalt
Nickel
|
Should you include the catalyst in the chemical reaction as one of the reactants?
Yes
No
|
Do transition metals make good catalysts?
Yes
No
|