Electrolysis 2 - Aluminium Oxide
This lesson covers:
- How electrolysis can be used to separate reactive metals from their ores
- The case of extracting aluminium from aluminium oxide
Which two of the following chemical processes are used to extract metals from their ores?
Thermal decomposition
Reduction with carbon
Electrolysis
|
How is a metal extracted from a metal compound using electrolysis?
A metal compound is heated with carbon to produce the metal and carbon dioxide
A compound is split into its elements using electricity
A metal is pounded at high pressures to physically separate the metal
|
Why is electrolysis not used to extract all metals?
Electrolysis is expensive because it requires a large amount of electricity
Electrolysis isn't very effective at extracting metals
Electrolysis is cheaper than carbon reduction
|
When should a metal be extracted by carbon reduction?
When the metal is less reactive than carbon
When the metal is more reactive than carbon
|

Which method of metal extraction would be used to extract iron?
Electrolysis
Reduction with carbon
|
Why is electrolysis used to extract aluminium from its ores?
It is more reactive than carbon
It is less reactive than carbon
|
What is the name of the substance that is mixed with aluminium oxide to lower its melting point?
|
Balance the equation below for the separation of aluminium from oxygen.
Al2O3 ➔ Al + O2
|
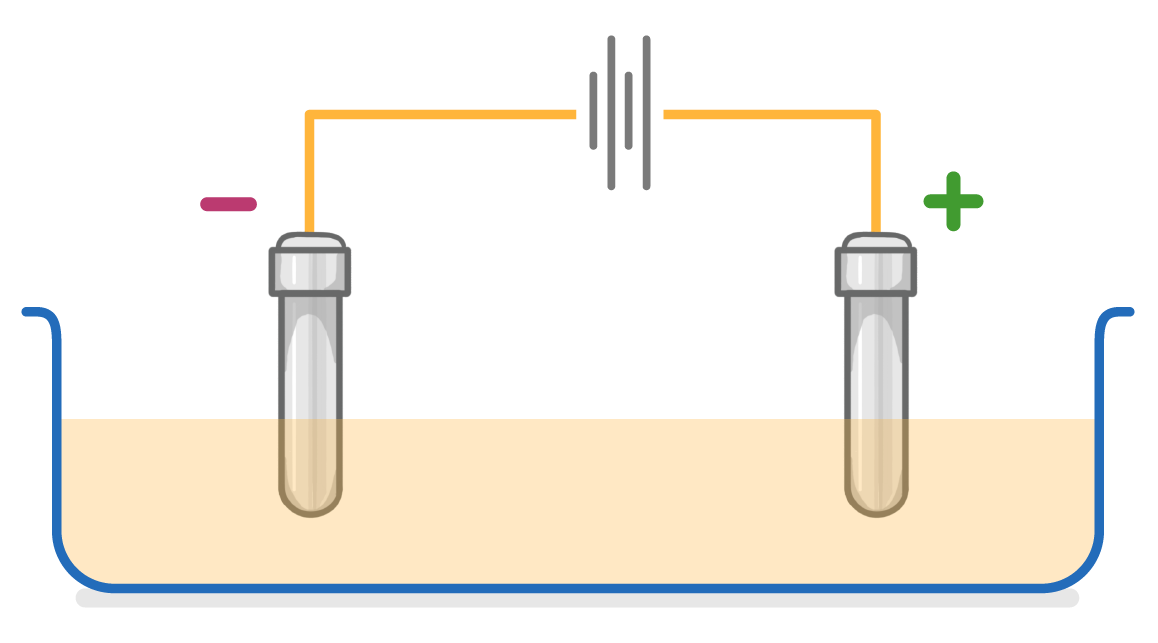
In electrolysis, which electrode are the Al3+ ions attracted to?
Anode
Cathode
|
During the electrolysis of molten aluminium oxide, are the O2- ions oxidised or reduced?
Oxidised
Reduced
|