Ceramics, Composites & Polymers
This lesson covers:
- The idea that different materials have different properties
- Ceramics, composites, polymers and alloys
Different materials have different properties |
Different materials have different properties. This makes different materials useful for different things. |
In this lesson we'll look at ceramics, composites, polymers, and metals. We'll look the structure of each material, and then how the structure determines the material's properties. |
 |
Here's a recap of the common properties a material has:
|
In physics, what is meant by a material's strength?
The resistance of a material to an applied force
The resistance of a material to being scratched or indented
The temperature at which a solid changes into a liquid
The ability of a material to conduct electricity
|
What does it mean for a material to be brittle?
It is difficult to bend
Electricity can conduct through it easily
It will only boil at very high temperatures
It will snap easily
|
Ceramics |
Ceramics are hard to define, but are basically a group of hard, brittle, heat-resistant, and corrosion-resistant materials. They are made by shaping and then firing a nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Two main groups of ceramics are clay ceramics and glass. |
 |
Clay ceramics  Clay ceramics include brick, china and porcelain. They are made by shaping wet clay while it's soft and then heating it to a high temperature in a furnace, which causes it to harden. They have a high compressive strength, which is why bricks can be used for building. |
 |
Glass Most of the glass we use is soda-lime glass. This is made by melting a mixture of sand (silicon oxide), sodium carbonate, and limestone, then allowing the molten liquid to cool and solidify. Borosilicate glass is made by heating sand with boron trioxide. Borosilicate glass has a much higher melting point than soda-lime glass. Glass is transparent, strong and a good thermal insulator, which makes it useful for windows. |
Are ceramics soft or hard?
Soft
Hard
|
Which three materials are used to make soda-lime glass?
Clay
Limestone
Sand
Boron trioxide
Sodium carbonate
|
Composites |
A composite material consists of two or more materials with different properties, that have been combined to produce a material with more desirable properties. |
 |
Most composite materials are made from two components: |
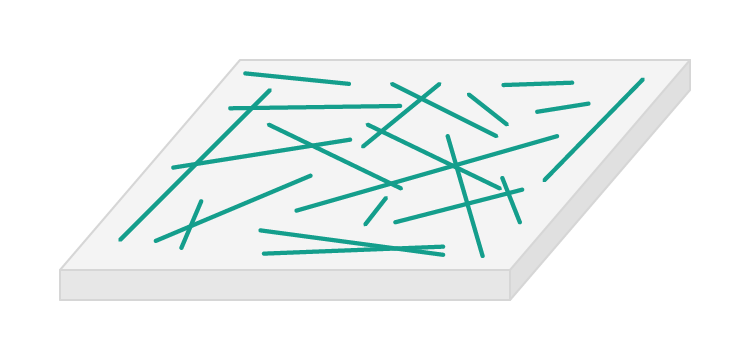 1The reinforcement - often long solid fibres or fragments. |
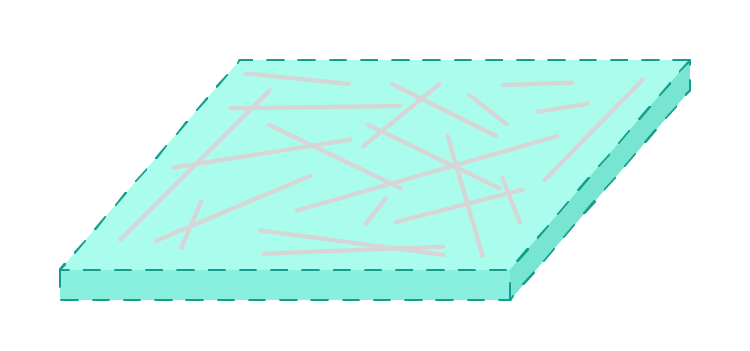 2The matrix - which binds the reinforcement together. Usually something that starts soft and then hardens. |
The two components of a composite material are called the r and the m.
|
Which component of a composite often consists of long solid fibres or fragments?
The matrix
The reinforcement
|
Polymers |
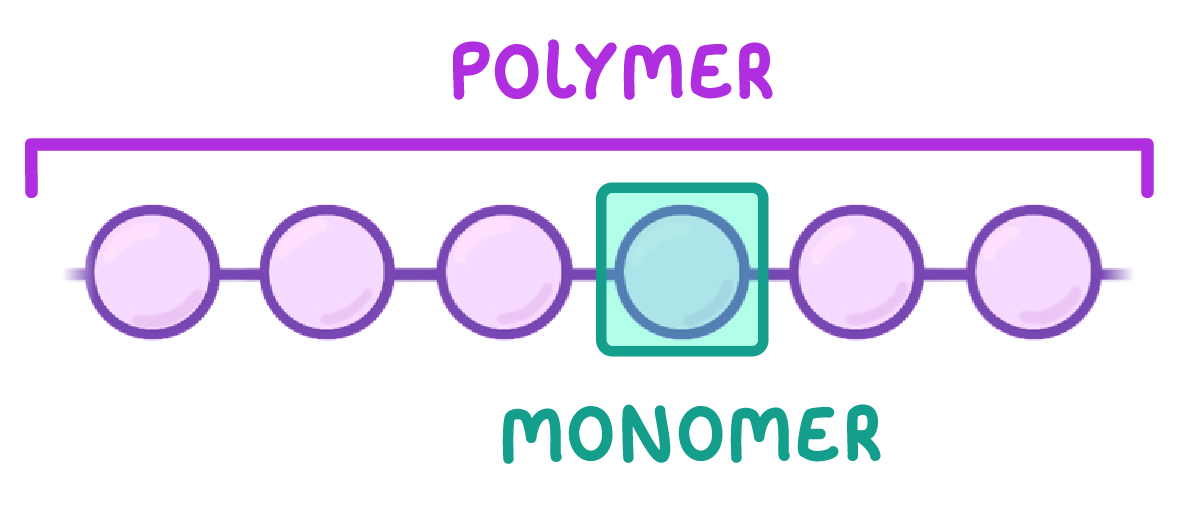 Polymers are large molecules of high relative molecular mass and are made by linking together large numbers of smaller molecules called monomers. |
The properties of a polymer depend on the monomers from which it was made and the conditions of the chemical reaction. |
Generally, polymers are flexible, easily shaped, and good insulators of heat and electricity. |
What do we call the individual units that make up a polymer?
|
What does LDPE stand for?
|
Which type of poly(ethene) is most flexible, but weakest?
LDPE: low-density poly(ethene)
HDPE: high-density poly(ethene)
|
Which type of polymers melt easily when heated?
Thermosoftening polymers
Thermosetting polymers
|
Metals & alloys |
We've covered metals and alloys in previous lessons, but it's worth a quick recap because they also come up in this topic. |
 Metals are generally malleable, ductile, good conductors of heat and electricity, and have high melting and boiling points |
 |
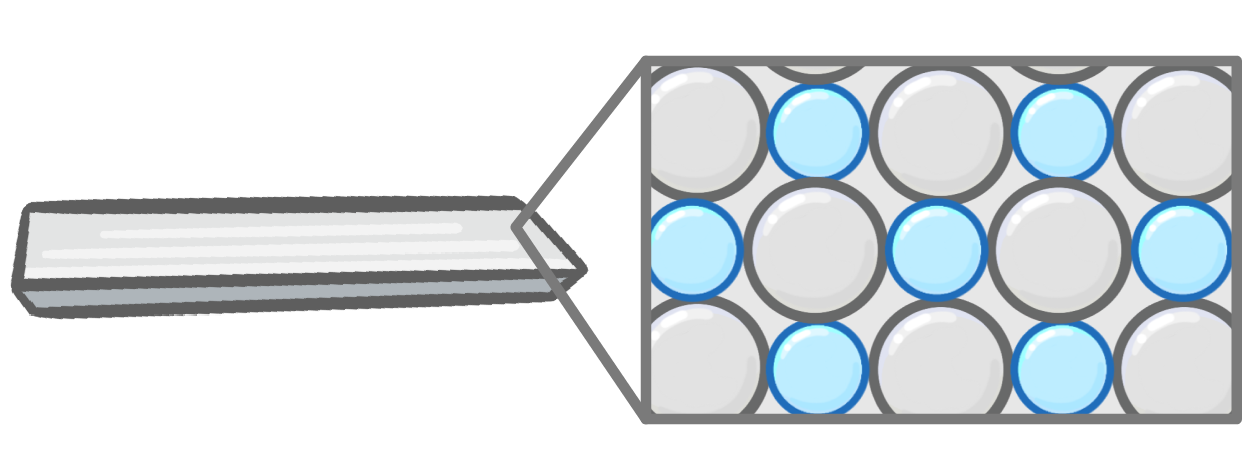 Alloys on the other hand, which are metals with atoms of another element mixed in, are much stronger (no longer malleable). This makes them useful for purposes where they might be put under stress - like in buildings. |
What is the key difference between metals and alloys?
Alloys do not conduct electricity
Alloys are not malleable
Alloys do not have high melting points
|