Soluble & Insoluble Salts
This lesson covers:
- How to tell whether a salt will be soluble or insoluble
Rules to know |
A salt is a compound that contains a positive ion (cation) and a negative ion (anion). |
For example sodium chloride (NaCl) is a salt because it contains a positive sodium ion (Na+) and the negative chloride ion (Cl-). |
 |
 Some salts, such as NaCl, are soluble in water (meaning they dissolve in water), but others, such as AgCl, are insoluble in water (they do not dissolve in water). |
 |
There's no easy way to know which salts are soluble and which are insoluble. Instead, you need to memorise the following rules: 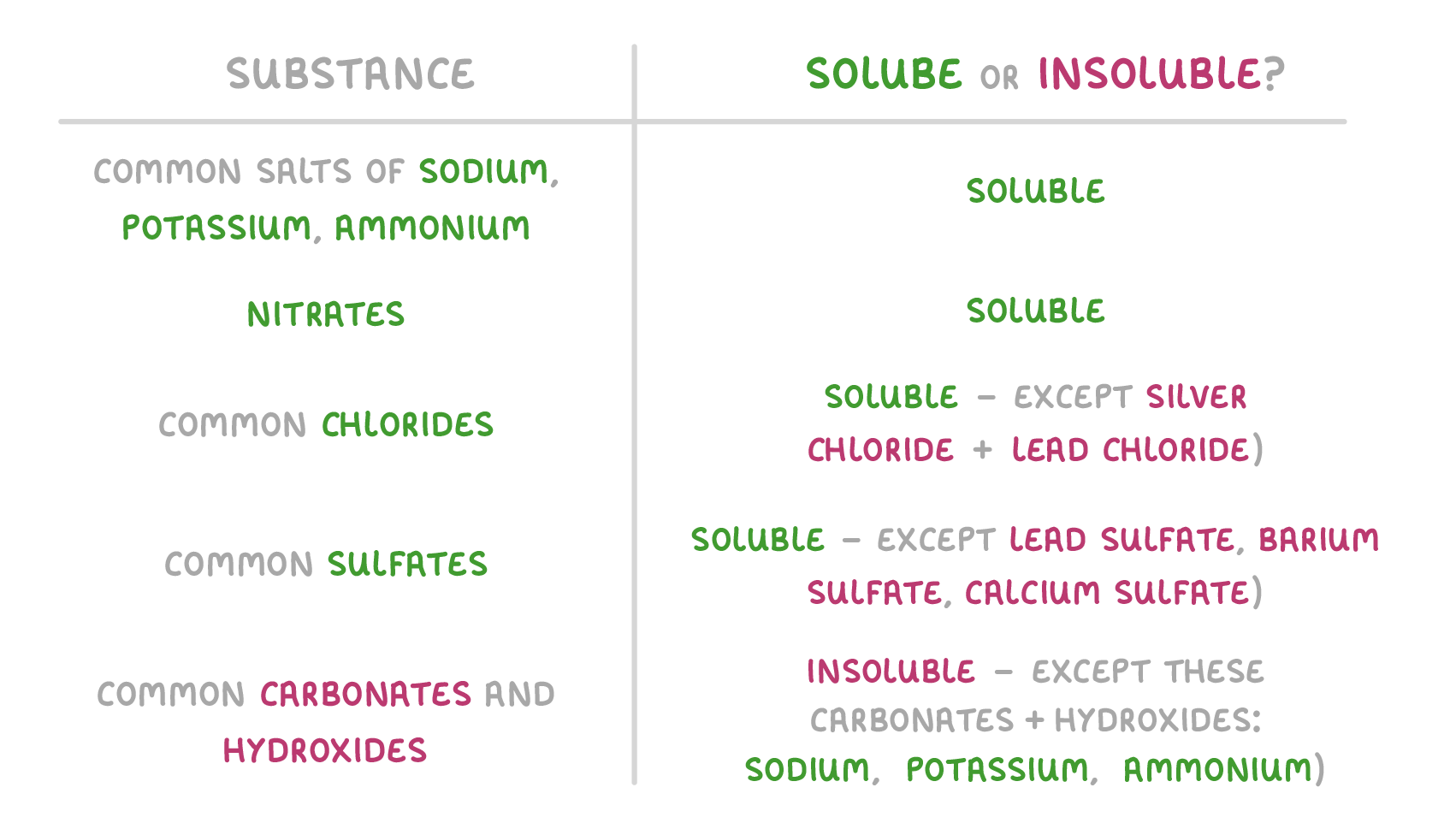 |
Is sodium chloride soluble or insoluble?
Soluble
Insoluble
|
Is lead sulfate soluble or insoluble?
Soluble
Insoluble
|
Are salts of nitrates usually soluble or insoluble?
Soluble
Insoluble
|
Which of the following salts is insoluble in water?
Sodium hydroxide
Ammonium nitrate
Silver chloride
|
Is sodium carbonate soluble or insoluble?
Soluble
Insoluble
|
Is potassium nitrate soluble or insoluble?
Soluble
Insoluble
|