Redox Reactions
This lesson covers:
- The definitions of 'oxidation' and 'reduction'
- How redox reactions occur
- How to write ionic equations and half equations
Oxidation and reduction - oxygen or electrons? The terms 'oxidation' and 'reduction' can be a bit confusing, because we can describe them in terms of the gain / loss of oxygen, or the gain / loss of electrons. |
In terms of oxygen: oxidation is the gain of oxygen, and reduction is the loss of oxygen. |
 |
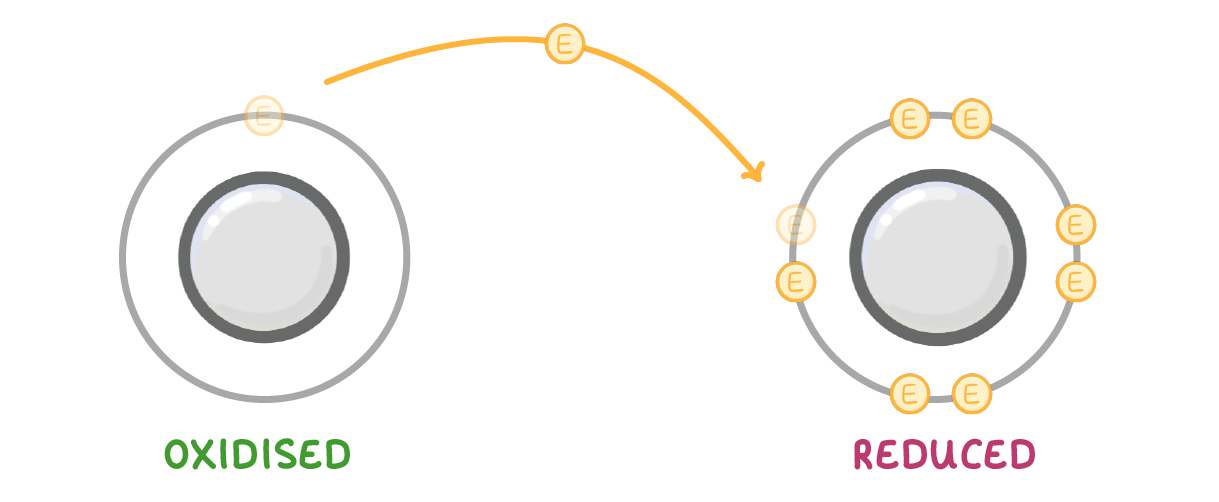
For electrons it's the opposite way around. An easy way to remember it is by remembering the phrase 'OIL RIG'. |
Oxidation Is Loss Reduction Is Gain |
Just remember that OIL RIG only works for electrons, not oxygen. |

With respect to electrons, reduction is:
The loss of electrons
The gain of electrons
|
Which of these reactions is an example of oxidation?
Ca ➔ Ca2+ + 2e-
Ca2+ + 2e- ➔ Ca
Ca2+ ➔ Ca + 2e-
|

When a metal reacts with an acid, a redox reaction takes place.
The metal ions lose electrons, so we say they've been .
The hydrogen ions from the acid gain electrons, so we say they've been .
|
Sodium reacts with iron sulphate.
Select the two half equations involved in this process.
Fe2+ + 2e- ➔ Fe
Na+ + e- ➔ Na
Na ➔ Na+ + e-
Fe ➔ Fe2+ + 2e-
|
Select the ion being oxidised in the following ionic equation:
2Li + Zn2+ ➔ 2Li+ + Zn
Lithium
Zinc
|
Reduction and oxidation rarely happen on their own.
Usually a reaction involves one species being reduced, and another being oxidised.
(a 'species' just means atom / ion / molecule)
What do we call these reactions?
Addition reaction
Oxiduction
Thermal decomposition
Redox
|
Select the spectator ion present in the following equation:
2K + CuCl2 ➔ 2KCl + Cu
Carbon
Potassium
Copper
Chloride
|
CuSO4 + Mg ➔ MgSO4 + Cu
Which of the following statements is true about the reaction of copper(II) sulfate with magnesium?
Magnesium atoms are oxidised
Magnesium atoms are reduced
Copper ions are oxidised
|