Types of Covalent Structures
This lesson covers:
- The structure and properties of simple molecular substances
- The structure and properties of giant covalent structures
covalent / ionic / simple / complex / small / giant
Atoms can share electrons to form bonds.
Covalent substances that only contain a few atoms are called molecular substances.
On the other hand, covalent substances with millions of atoms are called covalent structures.
|
Which of these is an example of a giant molecular structure?
Water
Silicon dioxide (silica)
Ammonia
Carbon dioxide
|
solid / gaseous / energy / intermolecular / high / low
In simple molecular substances, the individual molecules are held together by forces that exist between the molecules.
These intermolecular forces are weak and so don't require very much to break.
This means that they can be broken at relatively temperatures. As a result most simple molecular substances exist in the state at room temperature.
|
The halogens exist in different states at room temperature.
boiling / solid / liquid / gas / smaller / larger
- Chlorine is a at room temperature.
- Bromine is a at room temperature.
- Iodine is a at room temperature and gives off purple fumes.
The reason they are in different states at room temperature is that they have different melting and points. As you go down group 7, the atoms (and thus molecules) get . This means there will be more intermolecular forces, and so more energy (and a higher temperature) will be required to break them.
|
Select two properties of simple molecular substances:
Low boiling points
High boiling points
Unable to conduct electricity
Conduct electricity
|
Summary of simple molecular substances:
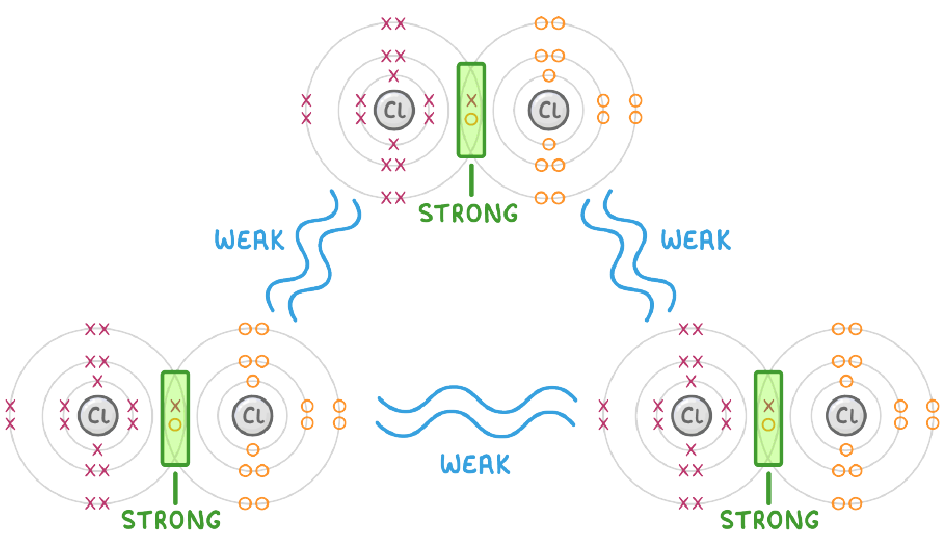
- Strong covalent bonds between the atoms of each molecule.
- Weak intermolecular forces between molecules.
- Low melting and boiling points (so normally gaseous as room temperature).
- Cannot conduct electricity.
small / giant / carbon / hydrogen / shape / lattice
Diamond and graphite are both made from the element , and are examples of covalent structures.
Their atoms are arranged in a regular repeating structure with many multiple covalent bonds between each atom.
|
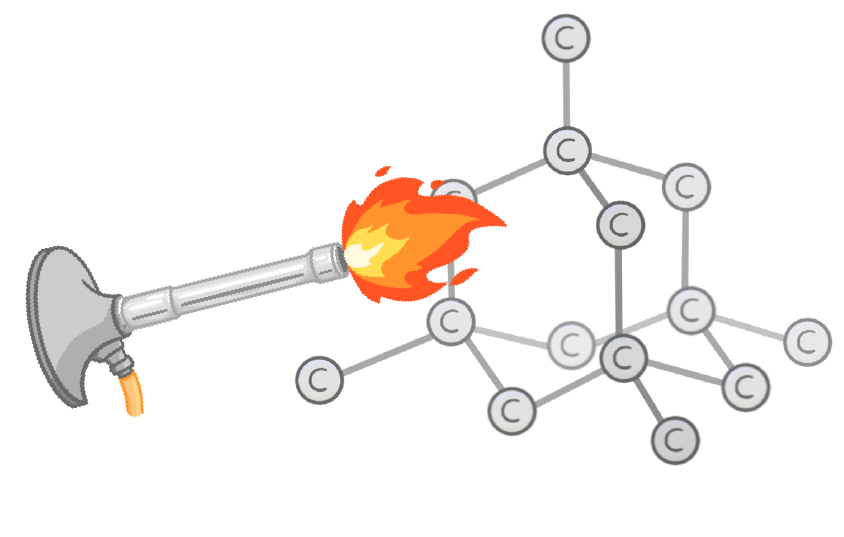
Do giant covalent structures have high or low melting points?
High
Low
|
Summary of giant covalent structures
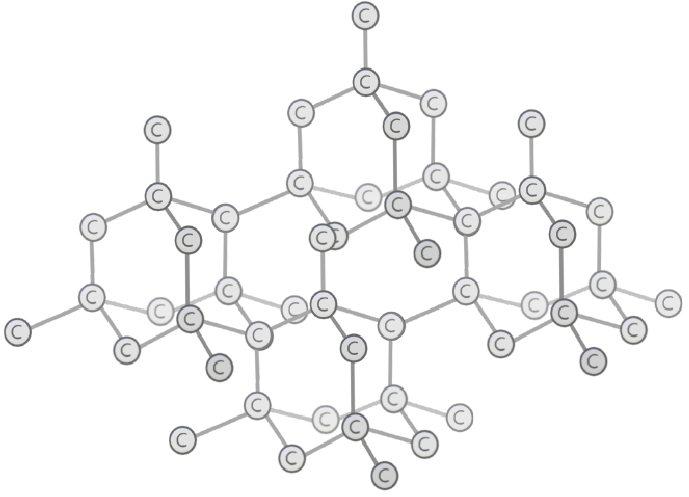
- Every atom is connected by strong covalent bonds
- No weak intermolecular forces as there is only one structure
- High melting and boiling points
- Cannot conduct electricity (except graphite)
Select all the properties of diamond.
(Select all that apply).
Weak
Conducts electricity
Strong
Doesn't conduct electricity
High melting and boiling point
Low melting and boiling point
|